Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (64 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
11.27Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
• ↓ O
2
→ HbS polymerizes → RBC sickles, ↓ RBC deformability →
hemolysis
&
microvascular occlusion
•
Anemia
: chronic hemolysis ± acute aplastic (parvo. B19) or splenic sequestration crises •
Vaso-occlusion and infarction
: painful crises, acute chest syndrome, CVA, splenic sequestration, hand-foot syndrome, renal papillary necrosis, aseptic necrosis, priapism •
Infection
: splenic infarction → overwhelming infection by
encapsulated organisms
; infarcted bone →
osteomyelitis
(
Salmonella
,
Staph. aureus
) • Diagnosis: sickle-shaped RBCs and Howell-Jolly bodies on smear; Hb electrophoresis • Treatment:
hydroxyurea
causes ↑ HbF → ↓ painful crises, acute chest episodes and may ↓ mortality (
NEJM
2008;358:1362); allogeneic HSCT may have a role in young Pts w/ severe disease (
Blood
2000;95:1918) and adults (
NEJM
2009;361:2309) • Supportive care: folic acid qd; pneumococcal, meningococcal,
H. flu
& HBV vaccination; pain crises treated with
hydration
,
oxygen
and
analgesia
; simple or exchange transfusion for TIA or stroke, severe acute chest syndrome, or preop (goal Hb 10 g/dL)
Hereditary spherocytosis (HS)
(
Br J Hematol
2004;126:455)
• Defect in a cytoskeletal protein of RBC membrane → membrane loss mutations in ankyrin, a-and β-spectrin, band 3 and pallidin have been identified • Most common in N. European populations (1/5000 births);FHx (75% of Pts) • Anemia, jaundice (mostly neonates), splenomegaly, pigmented gallstones • Diagnosis: spherocytes on smear,
osmotic fragility test (~80% Se), ↓ eosin-5-maleimide (EMA) binding (92% Se; 99% Sp) • Treatment: folate, transfusions, splenectomy for moderate and severe HS (balance w/ ↑ risk of future thrombosis and infection (
J Thromb Haemost
2008;6:1289)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
(see above)
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)
• Acquired, antibody-mediated RBC destruction •
Warm AIHA
:
IgG
Abs opsonize RBCs
at body temp
→ removal by spleen Etiologies: idiopathic, lymphoproliferative (CLL, NHL), autoimmune (SLE), drugs •
Cold AIHA
:
IgM
Ab binds to RBCs
at temp
<
37
°
C
→
complement fixation
→ intravascular hemolysis and acrocyanosis on exposure to cold
Etiologies: idiopathic, lymphoprolif. disorders (eg, Waldenström’s; monoclonal),
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infxn and infectious mononucleosis (polyclonal)
• Diagnosis: spherocytes on smear,Coombs’
; ✓ cold agglutinin titer, splenomegaly • Treatment: treat underlying disease
warm AIHA
: corticosteroids ± splenectomy, IVIg, cytotoxic agents, rituximab
cold AIHA
: avoid cold; steroids ineffective; rituximab (
Blood
2004;103:2925)
Drug-induced hemolytic anemia
• Acquired, antibody-mediated, RBC destruction precipitated by a medication:
abx: cephalosporins, sulfa drugs, rifampin, ribavirin
CV: methyldopa, procainamide, quinidine, thiazides
TCAs, phenothiazines, NSAIDs, sulfonylureas, MTX, 5-FU, rasburicase (G6PD defic.)
• Diagnosis: Coombs’ usually negative, ↑ LDH
• Treatment: discontinue offending agent
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
• Intra-arteriolar fibrin damages RBCs → acquired intravascular hemolysis • Etiologies:
hemolytic-uremic syndrome
(
HUS
),
thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
(
TTP
),
disseminated intravascular coagulation
(
DIC
), malignancy, malignant HTN, eclampsia/HELLP, mech. cardiac valves, infected vascular prostheses • Diagnosis:
schistocytes
± thrombocytopenia ± abnormalities a/w specific disorders (eg, ↑ PT in DIC, ↑ Cr in HUS, ↑ LFTs in HELLP) • Treatment: treat underlying abnormality;
urgent plasma exchange for TTP
Hypersplenism
• Stasis/trapping in spleen → mf attack & remodeling of RBC → spherocytosis → hemolysis
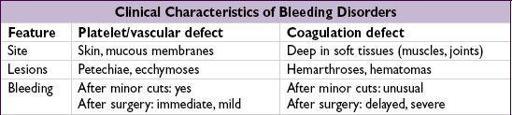
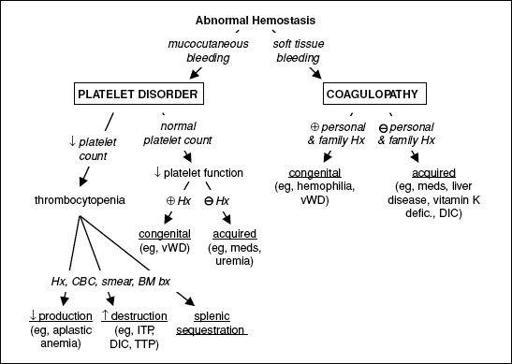
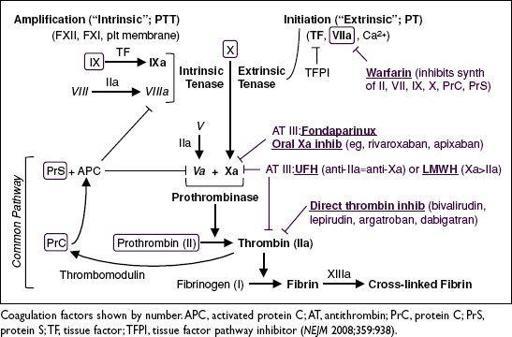
DISORDERS OF HEMOSTASIS
Figure 5-3 Approach to abnormal hemostasis
Figure 5-4
Coagulation Cascade
Purpura
(
nonblanching
purple/red lesions due to extravasation of RBCs into dermis)
•
Nonpalpable
(macular; ≤3 mm in diameter = petechiae; >3 mm = ecchymoses)
platelet disorder
: thrombocytopenia, defect in platelet fxn
thromboemboli
: DIC, TTP, cholesterol or fat emboli
trauma or vascular fragility: amyloidosis, Ehlers-Danlos, scurvy
•
Palpable
(papular);
vasculitis
: leukocytoclastic, HSP, PAN, RMSF;
infectious emboli
: meningococcemia, bacterial endocarditis
•
Purpura fulminans
(aka retiform purpura):
purpura + hypotension + DIC
; typically due to infxn/sepsis, protein C or S deficiency or APS (see section on DIC)
PLATELET DISORDERS
THROMBOCYTOPENIA (PLT COUNT <150,000/µL)
Other books
Blue Smoke by Nora Roberts
Iberia by James Michener
1970 - There's a Hippie on the Highway by James Hadley Chase
The Prophet of Yonwood by Jeanne Duprau
Neighborhood Watch by Bollinger, Evan
Unwind by Neal Shusterman
Rise of the Firebird by Amy K Kuivalainen
A Scholar of Magics by Caroline Stevermer
Rebekah: Women of Genesis by Orson Scott Card
What Are Friends For? by Lynn LaFleur