Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (65 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
13.78Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
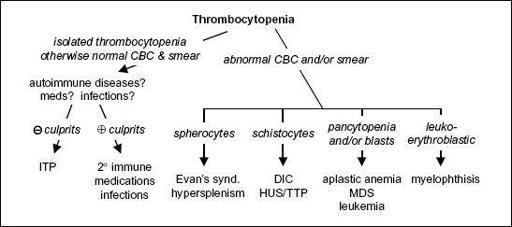
Etiologies
• ↓
production
hypocellular bone marrow
: aplastic anemia (qv), rarely MDS, drugs (eg, thiazides, antibiotics), alcohol, cirrhosis
hypercellular bone marrow
: MDS, leukemia, severe megaloblastic anemia
marrow replacement
: myelofibrosis, hematologic and solid malignancies, granulomas
• ↑
destruction
immune-mediated
(distinguish primary from secondary;
Blood
2009;113:2386) Primary (idiopathic): immune thrombocytopenic purpura (
ITP
, see below)
Secondary: infxn (
HIV
,
HCV
, HSV), collagen vascular diseases (
SLE
), APS, lymphoproliferative (
CLL
, lymphoma), drugs (
many
, including
heparin
, abciximab, quinidine, sulfonamides, vancomycin), alloimmune (posttransfusion)
non–immune-mediated
:
MAHA
(DIC, HUS, TTP), ticlopidine/clopidogrel, vasculitis, preeclampsia/HELLP, cardiopulm bypass, CVVH, IABP, cavernous hemangioma
•
Abnormal distribution or pooling
: splenic sequestration, dilutional, hypothermia •
Unknown
: ehrlichiosis/anaplasmosis, babesiosis, RMSF
Diagnostic evaluation
• H&P: meds, infxns, underlying conditions, splenomegaly, lymph nodes,
bleeding hx
•
CBC with differential
: isolated thrombocytopenia
vs
. multilineage involvement •
Peripheral smear
↑ destruction → look for large plts,
schistocytes
(see “Peripheral Smear” inserts)
↓ production → rarely limited to platelets → look for
blasts
, hypersegmented PMNs, leukoerythroblastic Ds; can see inclusion bodies (anaplasma), parasites (babesia)
r/o
pseudothrombocytopenia
due to platelet clumping (✓ platelet count in non–EDTA-containing tube, eg, citrate-containing yellow top tube)
Figure 5-5
Approach to thrombocytopenia
• Additional laboratory evaluations as indicated (eg, viral titers, flow cytometry, ANA, APLA)
if anemia: ✓ reticulocyte count, LDH, haptoglobin, bilirubin to detect hemolysis
if hemolytic anemia: ✓ PT, PTT, fibrinogen, D-dimer, Coombs, ANA
BM bx for unexplained thrombocytopenia, esp. if associated with splenomegaly
Primary immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
(
Blood
2010;115:168)
• Primary ITP: isolated thrombocytopenia due to immune plt
destruction
& ↓
production
(auto-Ab to megakaryocytes); (2° ITP a/w disease/drug exposure; Rx underlying disorder) • Primary ITP is
diagnosis of exclusion
; no robust clinical or lab parameters, but typically:
CBC: isolated ↓ plt (<100,000/µL); 10% have ITP + AIHA = Evans syndrome
Peripheral smear: large platelets
BM bx: ↑ megakaryocytes; perform in adults >60 y to r/o myelodysplasia
R/o other etiologies
: viral serologies (
HIV
,
HCV
, HBV, EBV),
H. pylori
Ab, ANA, pregnancy test, APLA, TSH, parvovirus, & CMV PCR.
Anti-plt Ab tests not useful
.
• Clinical manifestations: insidious onset of mucocutaneous bleeding;:
= 3:1
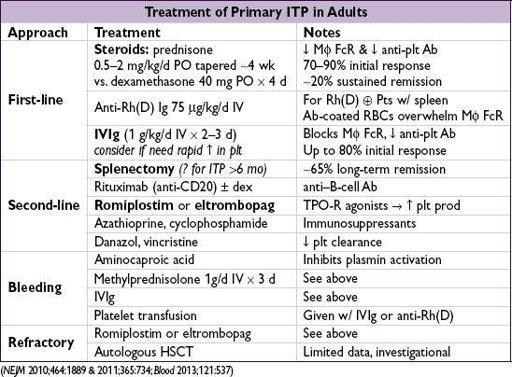
• Treatment: goals based on individual Pt rarely indicated if plt >50,000/µL unless bleeding, trauma/surgery, anticoag, comorbidities
steroids
,
IVIg
, & splenectomy mainstay of initial Rx; romiplostim/eltrombopag if refractory
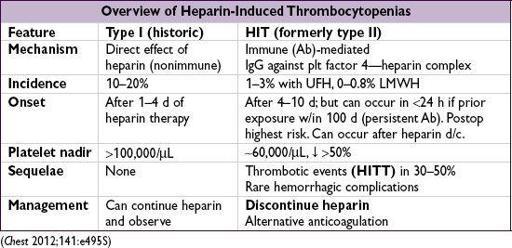
• Pathophysiology (type II): Ab binds heparin-PF4 → immune complex binds to plt →
plt activation
, further PF4 release → plt aggregates removed from circulation →
thrombocytopenia
; procoagulants released by plts and tissue factor released by endothelial cells damaged by HIT Abs →
prothrombotic state
• Diagnosis
(need clinical
+
pathologic)
Clinical
: plt <100k
or
↓ 50% from baseline; or
venous
(DVT/PE) or
arterial
(limb ischemia, CVA, MI) thrombosis (4:1 ratio); skin necrosis; ? ↑ heparin resistance
Pathologic
:HIT Ab using PF4-heparin ELISA (≥90% Se, IgG-specific ELISA Sp 94%), may confirm w/ functional plt aggregation (serotonin-release) assay (>90% Sp)
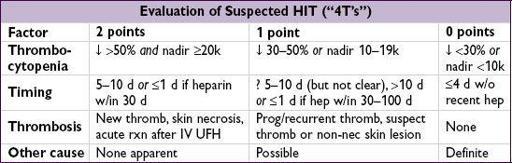
Pretest prob w/ “4T’s” criteria (
Blood
2012;120:4160): ≤3 points → 99% NPV, investigate other causes; 4–5 points 22% PPV & 6–8 points 64% PPV, ✓ lab test and replace UFH
• Treatment of HIT (type II) (
Chest
2012;141:e495S;
Blood
2012;119:2209;
NEJM
2013;368:737)
Discontinue heparin
(including flushes, LMWH prophylaxis, heparin-impregnated lines)
Avoid plt transfusions if not actively bleeding (anecdotally linked w/ thrombotic events)
Nonheparin anticoag
(argatroban, bivalirudin;
NEJM
2013;368:737)
regardless of thrombosis
; start warfarin when plt >150k, overlap ≥5 d (✓ chromogenic Xa to titrate)
thrombosis (HITT): anticoagulate for ≥ 3–6 mo
Other books
Crossings by Betty Lambert
Scream of Eagles by William W. Johnstone
The Old Deep and Dark by Ellen Hart
Bad Sons (Booker & Cash Book 1) by Oliver Tidy
The Baby Boomer Generation by Paul Feeney
How To Avoid Death On A Daily Basis: Book One by V. Moody
All of Me by Kim Noble
4 Witching On A Star by Amanda M. Lee
The Eighth Guardian by Meredith McCardle