Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (102 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
6.03Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
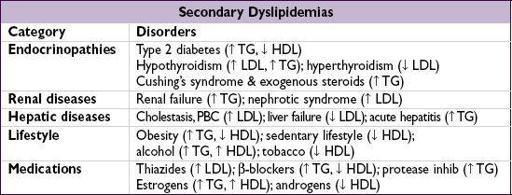
Primary dyslipidemias
• Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH, 1:500): defective LDL receptor; ↑↑ chol, nl TG; ↑ CAD
• Familial defective apoB100 (FDB, 1:1000): similar to FH
• Familial combined hyperlipidemia (FCH, 1:200): polygenic; ↑ chol, ↑ TG, ↓ HDL; ↑ CAD
• Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia (FDBL, 1:10,000): apoE ε2/ε2 + DM, obesity, renal disease, etc.;↑ chol and TG; tuberoeruptive and palmar striated xanthomas; ↑ CAD
• Familial hypertriglyceridemia (FHTG, 1:500): ↑ TG, ± ↑ chol, ↓ HDL, pancreatitis
Physical exam findings
• Tendon xanthomas: seen on Achilles, elbows and hands; imply LDL >300 mg/dL
• Eruptive xanthomas: pimple-like lesions on extensor surfaces; imply TG >1000 mg/dL
• Xanthelasma: yellowish streaks on eyelids seen in various dyslipidemias • Corneal arcus: common in older adults, imply hyperlipidemia in young Pts
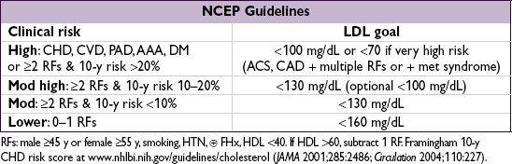
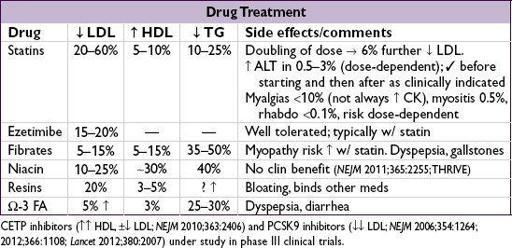
Treatment
• Every 1 mmol (39 mg/dL) ↓ LDL → 22% ↓ major vascular events (CV death, MI, stroke, revasc) in individuals w/ & w/o CAD (
Lancet
2010;376:1670); in healthy individuals w/ LDL <130 mg/dL & hs-CRP >2, rosuvastatin → 47% ↓ CVD/MI/stroke (
NEJM
2008;359:2195) • Fewer clinical data, but TG <400 and HDL >40 are additional reasonable targets
ARTHRITIS—OVERVIEW
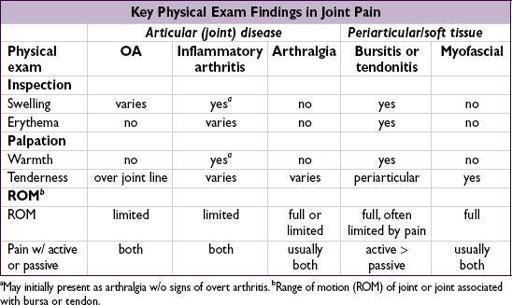
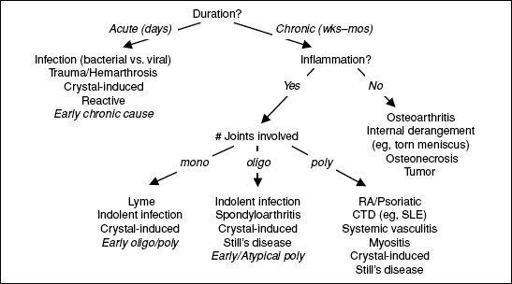
Approach to patient with joint pain
•
Articular
vs.
periarticular
(bursitis, tendinitis) pain: typically active ROM more painful in periarticular process than passive ROM
•
Inflammatory
vs.
noninflammatory
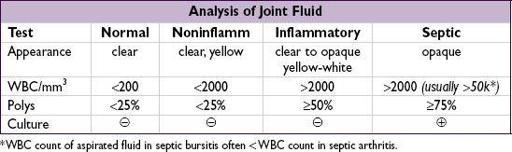
pain: features of inflammatory pain include swelling, warmth or redness in specific joint, persistence over days to weeks, prolonged morning stiffness (>30 min), improvement of pain/stiffness w/ motion/exercise • Physical exam (see table): localize complaint and identify objective signs of inflammation • The physical exam is only 50–70% sensitive for detecting inflammatory arthritis
a
May initially present as arthralgia w/o signs of overt arthritis.
b
Range of motion (ROM) of joint or joint associated with bursa or tendon.
Approach to arthritis
Figure 8-1 Approach to arthritis
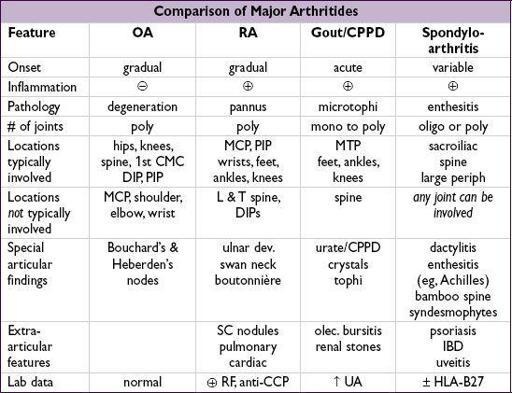
Radiologic features
•
OA
plain films:
osteophyes
, asym joint space narrowing (JSN), subchondral sclerosis/cysts MRI may show early disease not seen on plain films; U/SMRI for structural damage •
RA
plain films: early=periarticular
osteopenia
; late=
erosions
, symmetric JSN MRI & U/S able to detect early and subclinical disease; MRIU/S for erosions •
Gout
plain films: early=nonspec swelling; late=
tophus
, joint erosions w/ overhanging edges U/S > MRI for detection of microtophi (double contour sign); MRIU/S for erosions •
Spondyloarthritis
(sacroiliac joint)
plain films: pseudo-widening of joint space (early), sclerosis, erosions,
ankylosis
MRI most sensitive for early Δ in SIJ; U/SMRI for early detection of peripheral enthesitis
Other books
In Love and Rescue: When love is the perfect rescue... by K. Alex Walker
The Substitute Countess by Lyn Stone
Outer Dark by Cormac McCarthy
The Clone who Didn't Know (The Genehunter) by Kewin, Simon
Illusions: A prequel novella to Mirage by Alice Tribue
Rewind to You by Laura Johnston
Dare You To by Katie McGarry
The Gallows Bird by Camilla Läckberg
The Present by Johanna Lindsey
1965: The Most Revolutionary Year in Music by Andrew Grant Jackson