Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (80 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto

removed and others can be independently installed to produce a customized IIS 7.5.
Ultimately, the system is made more secure and easier to manage as you only install
and manage the features you need.
.
Improved management tools—
Microsoft has completely rewritten the Internet
Information Services (IIS) Manager toolset, including the user interface. The new
user interface can manage both IIS and ASP.NET settings from one utility, increasing
ptg
administrators’ productivity through centralized management. IIS 7.5 also introduces
a new command-line tool called appcmd.exe to help automate common IIS 7.5
management tasks and configuration changes, which does away with all the admin-
istration scripts as you knew them in IIS 6.0. Finally, IIS 7.5 is tightly integrated with
Windows PowerShell, meaning greater productivity can be achieved by scripting
management and administration tasks.
.
Diagnostics and troubleshooting—
IIS 7.5 introduces enhancements to IIS logs,
automatic failures, and error codes to reduce overall IIS downtime. By providing
detailed error messages and trace events, troubleshooting has become a whole lot
easier in IIS 7.5. For example, the IIS logs are much more detailed and include more
status codes to help troubleshoot, diagnose, and repair an error much more effi-
ciently and effectively. In addition, the Runtime Status and Control API (RSCA)
further improves IIS 7.5 troubleshooting abilities as it provides detailed runtime
diagnostics about the server. It can also be used to examine and manage other
things, including, but not limited to, sites and .NET application domains.
.
A contemporary FTP server that supports SSL—
A much-desired and requested
feature was to have a secure FTP solution for streamlined content publishing based
on today’s industry standards. The FTP server component has been completely
rewritten and now not only supports Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) for enhanced secu-
rity, but also includes virtual hostname support and user isolation. This FTP server
will support UTF8, IPv6, COM, and .NET extensibility, and .NET membership inte-
gration with SQL Server and other repositories. The FTP component is an out-of-
band offering; however, it is fully integrated into IIS 7.5. Unlike IIS 7.0, which
needed to be downloaded and installed as an out-of-band offering from Microsoft,
IIS 7.5 is fully integrated and included with Windows Server 2008 R2.
Understanding Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5
379
.
Delegated and remote administration—
A new role-based administration concept
has been introduced into IIS 7.5 to maximize administration efficiently and securely.
Administrators can log on to the same IIS management console and manage only
their particular site. In addition, administrators, along with a few other designated
people, can remotely manage IIS over the web using HTTP/SSL.
.
12
Improved server farm support—
Now, it is possible to share both the .config and
applicationHost.config files on a central Universal Naming Convention (UNC) share.
This improves server farm support when running more than one node in a Network
Load Balancing (NLB) cluster as all nodes can access the same .config file, which
means management of server farms is much easier. In addition, the configuration
settings are stored within the .config files; therefore, they can be easily copied from
one server to another without the need for replication programs, which tend to be
error prone.
.
Enhanced developer experience—
The all-new server application programming
interface (API) allows tight ASP.NET integration utilizing the latest .NET Framework.
Hands down, developers are provided with the best experience and extensibility ever
with this version of IIS. Classic ASP and other commercial frameworks are still
supported.
.
Best Practices Analyzer (BPA)—
By leveraging BPA via Windows Server 2008 R2’s
ptg
Server Manager and/or Windows PowerShell, it is now possible to scan the IIS 7.5
Web Server role to ensure that there aren’t any best-practice compliance or configu-
ration violations.
.
.NET on Server Core—
The .NET Framework is an installation option now available
on Server Core. This means that the full use of PowerShell cmdlets can be leveraged
because ASP.NET applications on IIS installations can be enabled by administrators
on Server Core. In addition, this also allows for greater support for remote manage-
ment tasks. The versions of the .NET Framework include 2.0, 3.0, 3.51, and 4.0.
.
Windows PowerShell Provider—
Common IIS administrative tasks can be auto-
mated via the Windows PowerShell Provider for IIS. A collection of task-oriented
cmdlets provides an easier way to manage websites, applications, and servers.
Understanding the New IIS Manager Tools
The centerpiece of IIS 7.5 is the new Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager user
interface. The user interface is used to manage IIS and ASP.NET, health and diagnostics,
and security. It is, however, the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager snap-in tool
that reigns supreme as it contains the majority of the features and tools that are necessary
for configuring and managing various functions of IIS 7.5.
IIS is configured through the IIS Manager snap-in, which can be accessed by selecting
Start, Administration Tools, and Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager. Because
understanding the console is a must to comprehend how to administer IIS and where to
conduct the task, the next sections examine the layout of the new user interface.
380
CHAPTER 12
Internet Information Services
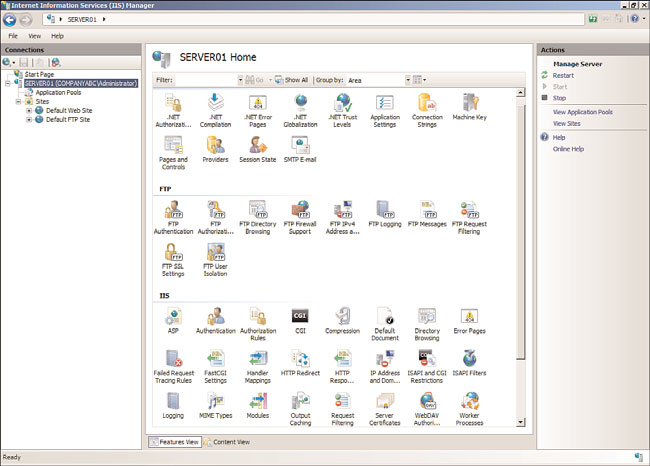
Exploring the IIS Manager Administration Panes
Each area within the IIS Manager console is referenced by a descriptive word, as shown in
Figure 12.1. For example, the descriptive words associated with the areas or panes such as
the Connections pane make it easier to identify the location of the IIS features. The follow-
ing is a list of the panes included in the IIS Manager console and their respective functions:
.
The Connections pane—
The Connections pane is located on the left side of the
console and displays the IIS console tree, which is also known as the node tree. Web
administrators can conduct the following tasks from within this pane:
. View the Start Page
. Connect to a server, site, or application
. Manage server settings
. Configure IIS, application pools, FTP, and websites
.
Central Details pane—
Also known as the “workspace,” this large pane is located in
the center of the IIS 7.5 management console. This pane displays the configuration
options for each IIS feature installed. Each feature is represented by a new icon and
replaces the legacy property sheets and tabs that most administrators in the industry
were not too fond of in the past. The feature icons can be grouped by category or
ptg
area; otherwise, grouping can be turned off.
.
Actions pane—
The Actions pane is located on the right side of the console and dis-
plays common actions, including wizards associated with each task. This pane also
FIGURE 12.1
Examining Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
Understanding Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5
381
typically contains multiple tabs for the different options available based on the
node chosen.
Examining the IIS Manager Administration Nodes in the Connections
Pane
12
Many web services components need to be configured to optimize IIS for security, func-
tionality, and redundancy. The IIS snap-in is the interface used to administer IIS services.
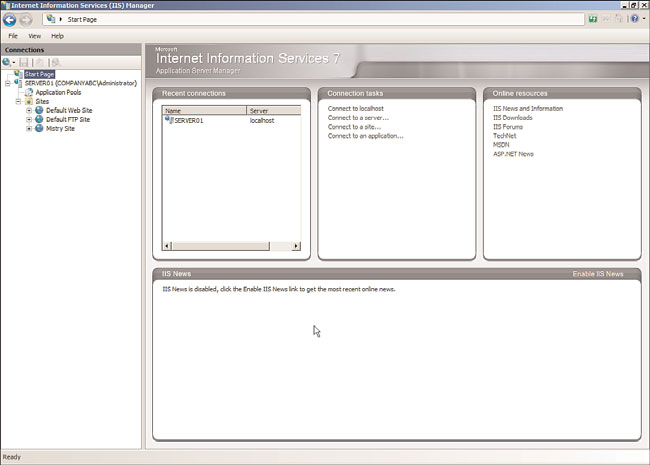
In the left pane of the snap-in, as shown in Figure 12.2, you will see folders or nodes
similar to the following:
.
Start Page—
The Start Page is the first item within the Connections pane and is ulti-
mately a digital dashboard for IIS. It provides users with a wealth of information by
displaying IIS newsfeeds and links to online resources. In addition, the Start Page
includes recent connection information and connection tasks.
.
IIS Server—
The main place to administer and manage server properties and features
is the server node. After being selected, the IIS feature icons are displayed in the
central pane. An administrator must double-click a feature to configure property
settings specific to that feature. Examples of feature icons include Feature
Delegation, Logging, and Machine Key.
ptg
.
Application Pools—
Application pools are actually sections of physical memory
dedicated to the applications running within a pool. Application pools segment
applications from the rest of the memory resources used by other IIS services. This
promotes higher reliability and security, but it also requires more memory to be
FIGURE 12.2
Examining the IIS 7.5 Connections pane.
382
CHAPTER 12
Internet Information Services
configured on the web server. The application pool elements can be sorted based on
Name, Status, .NET Framework Version, Managed Pipeline Mode, Identify, and
Applications.
.
Web Sites—
This folder contains all the websites being hosted on the web server.
The Default Web Site is created during the installation of IIS 7.5.
.
FTP Sites—
This folder contains all the FTP sites being hosted on the web server.
Note that FTP services are not installed by default.
NOTE
An Internet Information Services (7.5) Manager can be started by typing ”start inet-
mgr” at the command prompt.
Planning and Designing Internet Information
Two of the most important tasks to accomplish before implementing IIS 7.5 are thorough
planning and designing. Planning and designing are the beginning phases to properly
ptg
implementing IIS, and they can consist of the following:
. Defining goals and objectives of the IIS 7.5 project
. Identifying and reviewing IIS application types and requirements
. Designing the IIS infrastructure to support the goals and objectives
. Deciding on which IIS 7.5 features will be utilized during the installation process to
meet the goals of the organization
. Defining fault-tolerance requirements
. Designing the back-end infrastructure, such as the database or application tier
. Defining security requirements to meet the goals and objectives and balancing the
security methodologies between risks and end-user experience
. Examining and designing disaster recovery plans, and monitoring requirements and
maintenance practices
. Documenting the current or new IIS infrastructure and the IIS design decisions
Determining Server Requirements
Hardware and software requirements are typically based on the information gathered and
the requirements set forth in the design and planning stages of a project. The necessary
hardware and software requirements should always match the goals and objectives of the
project. This information is very detailed and describes all the resources necessary for
hardware and software.
Installing and Upgrading IIS 7.5
383
IIS 7.5 does not have specific minimum server requirements tailored toward running IIS
