Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (83 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto

.
.NET Profile feature page—
A list of profile properties is used to track custom data
about an application with this feature page.
Installing and Configuring Websites
393
.
.NET Roles feature page—
This page is used to create predefined roles for managing
groups of users’ authorization access. This concept is also known as role-based secu-
rity. To leverage this feature, a default provider must be configured. The two options
available are AspNetWindowsTokenRoleProvider and AspNetSqlRoleProvider.
.
.NET Trust Levels feature page—
This page is used to specify the trust level for
12
managed objects, such as modules, handlers, and applications in the Web.config file.
.
.NET Users feature page—
This feature page identifies and manages the identities
of users for an application. The feature controls the identity management behavior
for users defined for an application. When a user is created, the page displays name,
email addresses, data created, and last logon.
.
.NET Application Settings feature page—
To manage the variables associated with
key/value pairs stored in the website’s .config file, this feature page is recommended.
The application setting variables and value elements are created by selecting Add
Task from the Actions pane. These settings can be accessed from anywhere within
the application.
.
Connections Strings feature page—
This page is dedicated to creating and manag-
ing connections strings for managed web applications. By selecting Add Task in the
Actions pane, you can create connections strings to SQL Server for database access.
ptg
Typically, the credentials used to access the database are Windows Integrated;
however, it is possible to specify a SQL Server account as well.
.
Machine Key feature page—
Because IIS 7.5 is tightly integrated with .NET web
services and there is a major push for security, this page is used to manage encryp-
tion. You can enter encryption and decryption methods, including key generations
to secure forms-based authentication, cookie, and page-level view state data.
.
Pages and Controls feature page—
This page manages how the setting of ASP.NET
pages and controls are compiled on the web server. New controls can be registered
by selecting the task from the Actions pane. Additional elements can be configured,
such as the behavior, user interface, view state, compilation, general, and services.
.
Providers feature page—
When you want to manage and administer a list of
providers the web server can take advantage of, use this features page. Default exam-
ples include AspNetSqlRoleProvider and AspNetWindowsTokenRoleProvider.
Additionally, providers can be added by users by selecting Add from the Actions
pane.
.
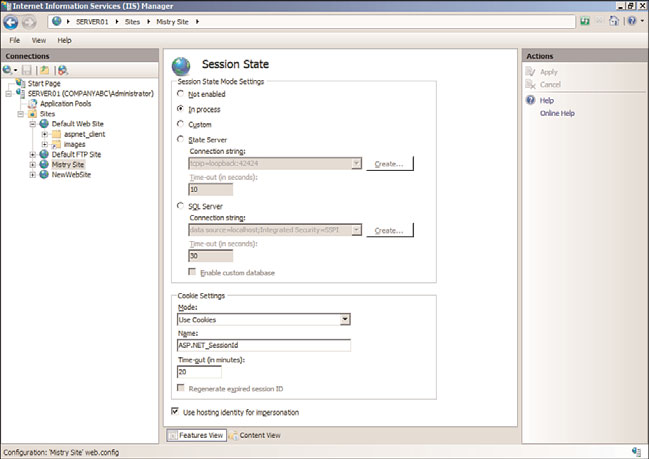
Session State feature page—
This page, as displayed in Figure 12.7, is leveraged
when it is necessary to control the behavior of information across browser sessions.
It is possible to enable or disable a session state or store a session state in the web
browser or in a SQL Server database. Additional elements include defining how
cookies are processed when managing session states. Options include Auto Detect,
Use Cookies, Use Device Profile, or Use URI.
394
CHAPTER 12
Internet Information Services
FIGURE 12.7
Viewing the Session State feature page.
ptg
.
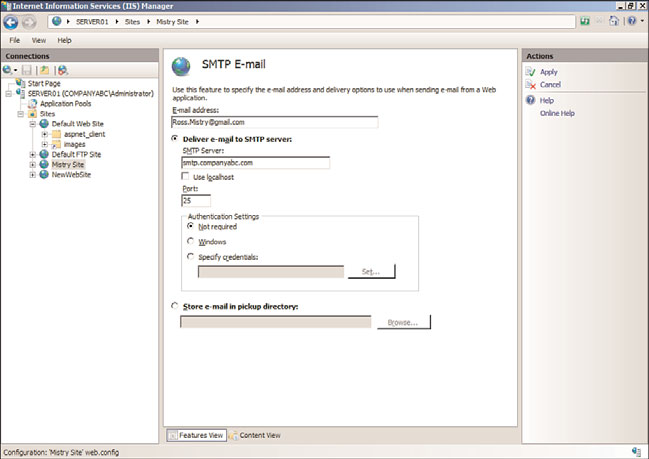
SMTP E-Mail feature page—
The final ASP.NET feature is SMTP E-Mail that uses the
System.Net.Mail API. The feature page, as illustrated in Figure 12.8, includes proper-
ties that need to be specified, such as email address, SMTP server name, and port to
control message sending functionality from the web server.
IIS 7.5 Features Associated with IIS
The following bullets highlight the feature icons and respective configuration pages associ-
ated with IIS configurations:
.
ASP feature page—
The first IIS feature page in the list is ASP. This page is meant for
managing classic ASP settings, such as the following elements: Behavior,
Compilation, Services, Caching Properties, Com Plus Properties, and Sessions
Properties.
.
Authentication feature page—
The Authentication page is synonymous to the
legacy Security tab in IIS. This page is used to configure security authentication.
Security can be administered for a web server, website, or a specific page.
Authentication such as Anonymous, ASP.NET Impersonation, Basic Authentication,
Digest Authentication, Forms Authentication, and Windows Authentication can be
configured. Take note as Anonymous authentication is enabled by default and might
have to be disabled before a different authentication method can be used. In the
past, these authentication types existed out of the box. However, with the modular-
ized installation approach, each element now needs to be selected separately during
the installation process.
Installing and Configuring Websites
395
12
FIGURE 12.8
Viewing the SMTP E-Mail feature page.
ptg
.
Authentication Rules feature page—
Use this page to enforce control of web
content access by utilizing Allow or Deny rules. Other IIS features such as Users and
Roles are associated with this feature as you can specify Allow and Deny rules to
already created users and roles.
.
CGI feature page—
IIS 7.5 supports CGI applications. This page is used to configure
CGI properties, which allows these applications to run on an IIS 7.5 web server.
Additional elements on this page control other aspects of CGI applications, includ-
ing CGI timeout values, whether or not a CGI application runs in its own console,
and, finally, the security context the application will utilize.
.
Compression feature page—
There are two options available on this page that
enhance transmission times between the server and browsers. The compression
elements that can be configured consist of compressing static content and compress-
ing dynamic content.
NOTE
For clients to leverage this feature, they must use a web browser that supports com-
pression, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 7.0. In addition, the use of dynamic com-
pression can increase processor utilization.
.
Default Document feature page—
Similar to the concept in earlier versions of IIS,
the Default Document page is used to select the default web page that appears when
396
CHAPTER 12
Internet Information Services
a user connects to a site. An example is default.htm. This feature can be enabled or
disabled via the Actions pane.
.
Directory Browsing feature page—
This feature is disabled out of the box. By
selecting the Enable task in the Actions pane, this page can be used to configure
directory browsing functionality. The elements that can be selected include Time,
Size, Extension, Date, and Long Date.
.
Errors feature page—
The Errors feature page is similar to the Cluster Errors tab on
earlier versions of IIS. An administrator can use this page to create custom error
messages for web server clients. It is possible to edit a default error or create a new
error page.
.
Failed Request Tracing Rules feature page—
This setting is used to manage a list
of tracing rules for failed requests. The Failed Request Tracing Rules Wizard is
invoked by clicking Add in the Actions pane. The wizard walks you through the
creation of the trace by first requesting information on what will be traced. The
options include All Content, ASP.NET, ASP, and Custom Creation. Trace Conditions
are defined on the next page. Conditions include Event Severity, Status Codes, or
Time Taken in Seconds. The final page is utilized to select the trace providers.
NOTE
ptg
When configuring Failed Request Tracing Rules for a site, logging of failed requests
must be enabled for the site at the server scope. If it is not, Failed Request Tracing
Rules will not be available for a site.
.
Handler Mappings feature page—
Use this page to specify resources that will
handle responses for specific request types. Actions include Add Managed Handler,
Add Script Map, and Add Module Mapping.
.
HTTP Redirect feature page—
There will be times when there is a need to redirect
incoming requests to an alternate uniform resource locator (URL) or website file. To
achieve this goal, the HTTP Redirect page can be used to redirect requests to a
specific destination.
.
HTTP Response Headers feature page—
This feature should be used to configure
HTTP headers based on entering name and values to responses from the web server.
.
IP Address and Domain Restrictions feature page—
This page is used to create
and manage rules that allow computer networks and IP addresses the opportunity to
either gain access or be denied to specific web content. The rules available consist of
Allow or Deny and it is possible to enter a single IP address, range of IP addresses, or
domain name. Finally, rules can be added to a page, site, or inherited from the
parent.
.
ISAPI Filters feature page—
ISAPI filters are programs that respond to certain
events during HTTP request processing. You can add, enable, and disable filters for a
website on this page.
Installing and Configuring FTP Services
397
.
Logging feature page—
The Logging feature page configures how IIS log requests
will be handled for the web server. For more information on logging, see the section
“Using IIS Logging” toward the end of the chapter.
.
MIME Types feature page—
The MIME Types feature page is utilized for managing
a list of Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (MIME) types for the web server or
12
website. When creating or managing MIME types, the following elements need to be
entered: Extension, MIME Type, and Entry Type.
.
Modules feature page—
This feature should be used when managing or adding
managed modules and adding native modules to a web server or website.
Authentication and compression are examples of native code modules.
.
Output Caching feature page—
The Output Caching features page is leveraged
when defining a set of rules associated with caching content. Some of the cache
settings include defining file extensions, maximum cache response sizes, and cache
size limit in MB.
.
Request Filtering feature page—
The page is used to configure filtering rules for a
website or application.
.
SSL Settings feature page—
This page helps an administrator create, manage, and
assign certificates for the web server. For more information on creating certificates
ptg
and assigning them to a website, review the section “Using SSL Certificates.”
.
WebDav Authoring Rules feature page—
This feature page is used for managing a
list of authoring rules that control access to content.
IIS 7.5 Features Associated with Management
The following bullets highlight the feature icons and respective configuration pages associ-
ated with Management configurations:
