Stockwin's Maritime Miscellany (13 page)
Read Stockwin's Maritime Miscellany Online
Authors: Julian Stockwin

During his voyage around the great continent Flinders had noted abnormal behaviour of the compass needle, and to correct for this he proposed that a length of iron bar be let into the deck, with its upper end level with the compass card in the binnacle. Although such compensating devices were not used until the second half of the nineteenth century they are called Flinders bars in his honour and are an integral part of ships’ compasses even today.
When Flinders returned to England he had not seen his wife Anne for nine years and was in poor health as the result of his imprisonment.
However
, he immediately began work on
A Voyage to Terra Australis
, which became widely read and gave the name Australia, which Flinders favoured, general currency. The governor of New South Wales used it in his dispatches to England and recommended to the Colonial Office that it be officially adopted. In 1824 the Admiralty decreed that the continent should officially be thus known, but Flinders did not live to see this as he died, just 40 years old, the day after his seminal work was published in 1814.
 HM sloop
HM sloopInvestigator
, in which Flinders circumnavigated Australia
.
‘H
E VANISHED TRACKLESS INTO THE BLUE IMMENSITY
’
In 1785 Louis XVI of France commissioned a great voyage of exploration, a four-year expedition across the Atlantic Ocean and into the Great South Sea, as the Pacific Ocean was then known, before returning to France. It was to be led by Jean-François de Galaup, Comte de La Perouse, one of the country’s most eminent naval officers. The project was heralded as France’s most ambitious maritime endeavour; during its circumnavigation every field of science was to be studied. Louis wanted to secure a rank for France alongside Britain, then the world’s leading seafaring nation, and personally gave instructions, specifying the itinerary and objectives.
No efforts were spared in provisioning the expedition’s two frigates
La Boussole
and
L’Astrolabe
. As well as charts and navigation instruments they took a portable observatory and gifts for natives including 570 kg of glass beads and 50,000 sewing needles. Competition was keen for the 400 berths. Among the applicants was a 16-year-old second lieutenant from the military academy at Paris, a Corsican named Napoleone di Buonaparte; he was not selected.
Although most of La Perouse’s naval career had been spent fighting the British, as an explorer he received their support and cooperation thanks to an act of humanity during the American War of Independence. La Perouse had destroyed the British forts in Hudson Bay but spared the lodgings of the British fur traders, leaving them food to survive the harsh winter. His actions were not forgotten, and when he was about to launch his expedition the British agreed to cooperate in his scientific quest. A French go-between was given access to James Cook’s charts and surveys. When La Perouse left France he carried with him two compasses that had gone around the world with Cook, a gift of the Royal Society. He treated them with great veneration as he was a huge admirer of Cook.
La Perouse set sail for South America in August 1785 and entered the Pacific in early 1786. In September 1787 he stopped to take on water at Samoa, where natives killed 12 of his men including the captain of
L’Astrolabe
.
The two frigates sailed into Botany Bay at the end of January 1788 where La Perouse was surprised to find a British squadron – they had just founded Australia’s first colony. La Perouse took the opportunity to send reports and letters home with some of the departing English ships.
On 10 March
La Boussole
and
L’Astrolabe
left Australia heading northeasterly. They were never seen again. The Scottish essayist Thomas Carlyle later wrote of La Perouse: ‘He has vanished trackless into the blue immensity.’
In September 1791, six years after La Perouse had left, Rear Admiral d’Entrecasteaux came looking for him with two ships. They combed the Pacific and in May 1793 spotted smoke rising from the interior of an island to the northeast of Australia. D’Entrecasteaux was convinced he had found survivors of the expedition, but treacherous reefs forced him to leave without sending a search party ashore. D’Entrecasteaux died shortly after, and revolutionary France had other concerns: she was locked in war with much of Europe. No further rescue expedition was sent by the French. Louis XVI while being led to the guillotine is said to have asked whether there was any news of La Perouse.
It was not until 1826 that Peter Dillon, an Irish captain, found enough evidence to piece together the events of the tragedy, which was confirmed
by
the later investigation of the underwater remains of
La Boussole
. Both ships had been wrecked on the reefs off the island of Vanikoro, southeast of New Guinea,
La Boussole
first.
L’Astrolabe
had been unloaded and taken apart. One group of men, probably from
La Boussole
, were massacred by the local inhabitants. Some of the surviving sailors built a two-masted craft from the wreckage of
L’Astrolabe
and left westward about nine months later, but what happened to them is unknown. Two men, one a ‘chief’ and the other his servant, had remained behind, but their fate was never established.
LOSE YOUR BEARINGS – not know where you are.
DERIVATION
: before modern navigation aids arrived, a ship’s position when in sight of land was determined by the intersection of the compass bearings of two objects ashore. If one of these points of reference was obscured, the position of the ship would be unknown.
 H
HOW FAST ARE WE GOING
?
During the great voyages of discovery by Columbus and others, sailors would arrive at a measure of their speed by dropping a chip of wood or some other material into the water and counting in seconds how long it took the ship to pass by it and then looking up special conversion tables. This method was still used on some Dutch ships at the end of the eighteenth century.
A more precise method came with the invention of the common log in the 1570s. This was a triangular piece of wood called the log-ship attached to a long line, knotted at regular intervals, which a sailor threw overboard, counting the number of knots that ran out within 30 seconds. This provided a record of the ship’s speed in ‘knots’, a measure used to this day. A knot is 1.852 km per hour.
Various other improvements were tried, but it was not until 1802 that the first successful self-recording log was patented by Edward Massey, a clock and watchmaker in Newcastle. Massey’s log recorded the distance travelled on a series of dials which could be read when the log and its line were retrieved from the sea. It proved very accurate and was used extensively at sea for much of the nineteenth century.
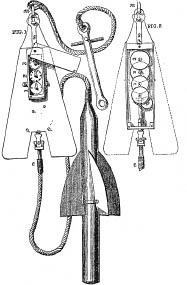 Massey’s log
Massey’s logThe instrument was based on a small rotator dragged in the water; motion was transmitted to a recording mechanism on the ship’s rail
.
T
WO STORMS, TWO MEN
The inhabitants of coastal communities commonly witnessed the fury of the sea when sailing ships snapped their anchor cables in gales and broke up, their doomed passengers often tantalisingly close to the safety of the shore.
Two storms in 1807 were the catalysts to the work of the pioneers of ship-to-shore rescue, Englishmen George Manby and Henry Trengrouse. They lived at opposite ends of the country – Trengrouse in Cornwall and Manby in Norfolk.
On 18 February the gun-brig
Snipe
foundered off Great Yarmouth. The ship was carrying French prisoners and women and children. George Manby was among the helpless onlookers trying to shut out the screams of the drowning as the waves crashed over the ship. Sixty-seven perished within 55 m of the shore and more bodies were picked up along the coast. In the same year, on 29 December, Henry Trengrouse witnessed the fate of the doomed HMS
Anson
in Mount’s Bay, Cornwall. She had been sailing to France to join a blockade of the French fleet when she ran aground in a storm only 90 m from shore. People along the shore watched as some 270 sailors made it to safety using the ship’s masts as bridges to the beach, but to the horror of the onlookers more than 60 of the crew, including her captain, drowned.
Appalled at the loss of life so close to shore, both men came up with proposals for rescue apparatus; the ideas were similar but used very different methods to propel a line from shore to ship. Manby used a mortar to fire a lead ball with a line attached which would enable a rescue boat to be hauled between ship and shore. He subsequently replaced the recovery boat with a canvas cot and then developed a lightweight mortar which enabled apparatus to be carried on horseback. Trengrouse used a rocket rather than a mortar.
The first recorded rescue using the Manby contraption took place on 18 February 1808, when a party commanded by Manby himself saved the crew of the brig
Elizabeth
140 m off Great Yarmouth. The Navy Board began to supply it to various stations around the coast, and 239 lives were recorded to have been saved with the device.
In 1818 Trengrouse demonstrated his apparatus to the Admiralty, who found his model superior to Manby’s for ship-to-shore rescue work. They suggested that a specimen apparatus be placed in every dockyard, so that naval officers might become familiar with it. In the same year Trinity House recommended that it be carried on all its vessels. The government ordered 20 sets but then decided to have the Ordnance Board manufacture them. Trengrouse was paid £50 compensation and received a personal letter from Alexander I of Russia in recognition of the usefulness of his apparatus. He was awarded several medals and received 30 guineas from the Society of Arts, but apart from that no financial reward for his invention.
Improved rockets were later invented by John Dennett and Colonel Boxer, and the rocket completely superseded the mortar. To this day it still plays a role in ship-to-shore rescue.
 Engraving depicting a stranded Indiaman, along with different rescue techniques of the nineteenth century
Engraving depicting a stranded Indiaman, along with different rescue techniques of the nineteenth century.
TAKEN ABACK – jolted by unpleasant news, at a momentary loss.
DERIVATION
: a very real danger for a sailing ship was a sudden shift in the wind or an unexpected squall striking the ship from a different direction. The sails could be blown back against the masts, resulting in serious damage, possibly even leaving the ship helpless.
