Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (79 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

Prognosis
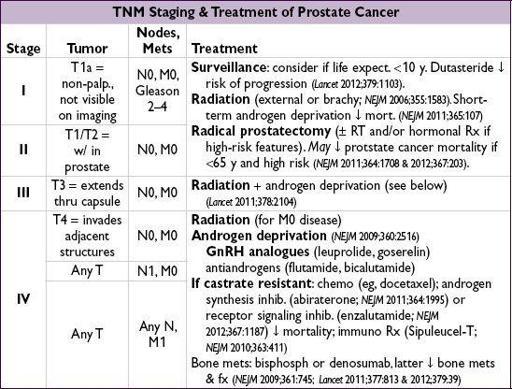
• PSA level, Gleason grade and age are predictors of metastatic disease • In surgically treated Pts, 5-y relapse-free survival >90% if disease confined to organ,
75% if extension through capsule, and
40% if seminal vesicle invasion • PSA doubling time, Gleason, & time to biochemical recurrence predict mortality following recurrence. For local recurrence following RP, salvage RT may be beneficial if low PSA.
• Metastatic disease: median survival ~24–30 mo; all become castrate resistant (in 15–20% discontinuation of antiandrogens results in paradoxical ↓ in PSA) • Long-term consequences of antiandrogen therapy include osteoporosis
Prevention
• Finasteride and dutasteride ↓ total prostate cancers detected by bx, but ↑ number of high Gleason grade tumors (
NEJM
2003;349:215 & 2010;362:1192)
COLORECTAL CANCER (CRC)
Epidemiology and risk factors
(
Lancet
2010;375:1030;
CA Cancer J Clin
2011;61:212)
• 4th most common cancer in U.S. men & women; 2nd leading cause of all cancer death • Rare before age 40, w/ 90% of cases occurring after age 50. ~75% are sporadic.
•
Family history
: up to 25% of Pts haveFHx. Risk depends on # of 1st-degree relatives (w/ CRC
or
polyp) and their age at dx; ~5% have an identifiable germline mutation
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
: mutation in
APC
gene → 1000s of polyps at young age → ~100% lifetime risk; ↑ risk of thyroid, stomach, small bowel cancers
Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC)
: most common hereditary CRC (~3% of all CRC;
NEJM
2003;348:919); mutations in DNA mismatch repair genes (eg,
MSH2
,
MLH1
) →
microsatellite instability (MSI)
→ ↑ tumor progression → ~80% lifetime risk; predom.
right-sided
tumors; ↑ risk of
endometrial
, ovarian, stomach, urothelial, small bowel and pancreatic cancers.
Amsterdam criteria: ≥3 family members w/ HNPCC-related cancer, one of which is dx before age 50, affecting 2 successive generations.
•
Inflammatory bowel disease
: ↑ risk with ↑ extent and duration of disease • Other factors a/w ↑ risk of CRC: diet rich in animal fat, ? smoking, ? diabetes/obesity •
COX-2
: ↓ risk of adenomas w/ ASA & NSAIDs. ASA assoc. w/ ↓ CRC incidence, mets and mortality (
Lancet
: 2010;376:1741; 2012;379:1591 & 1602). ↓ COX-2-expressing CRC after prolonged ASA (
NEJM
2007;356:2131). ASA effect limited to
PIK3CA
-mut CRC (
NEJM
2012;367:1596). COX-2 inhib. effective but ↑ bleeding & CV events (
NEJM
2006;355:873 & 885).
Pathology and genetics
(
NEJM
2009;361:2449;
Nature
2012;487:330)
•
Adenoma
→
carcinoma sequence
reflects accumulation of multiple genetic mutations. ↑ risk of malig. w/ large (>2.5 cm), villous, sessile adenomatous polyps. Adenomas typically observed ~10 y prior to onset of cancer (both sporadic & familial).
• Genetic profile in sporadic CRC:
APC
(~80%),
KRAS
(~40%),
TP53
(50–70%),
DCC
or
SMAD4
, or
BRAF
(~15%); chrom instability (majority) or mismatch repair defic (10–15%) • Upfront genotyping may guide Rx; eg, benefit of anti-EGFR Ab cetuximab greater in
KRAS
wild-type than KRAS mutant (
NEJM
2008;359:1757).
BRAF
mutation may guide clinical trials.
Clinical manifestations
• Distal colon: Δ
bowel habits
,
obstruction
, colicky abdominal pain,
hematochezia
• Proximal colon:
iron defic. anemia
, dull vague abd pain; obstruction atypical due to larger lumen, liquid stool and polypoid tumors (
vs
. annular distal tumors) • Metastases: nodes,
liver
, lung, peritoneum → RUQ tenderness, ascites, supraclavicular LN
• Associated with
Streptococcus bovis
bacteremia and
Clostridium septicum
sepsis
Screening
(
NEJM
2009;361:1179)
•
Average risk
: colonoscopy starting at age 50 & repeat q10y strongly preferred method • ↑
risk
: earlier and/or more frequent screening.FHx: age 40 or 10 y before index dx, then q5y. IBD: 8–10 y after dx, then q1–2y. Known or suspected familial syndrome: genetic counseling & very early screening (eg, age 20–25 y), then q1–2y.
•
Imaging
Colonoscopy
: test of choice as examines entire colon; 90% Se for lesions >1 cm. Flex sig less Se vs. colo and CTC (
Gut
2009;58:241). If polyp found, re ✓ in 3–5 y. Removal of adenomatous polyps associated with lower CRC mortality (
NEJM
2012;366:687).
Sigmoidoscopy
: 21% ↓ incidence in CRC & 26% ↓ mortality in distal CRC (
NEJM
2012;366:2345). Benefit may also be seen w/ 1-time flex-sig (
Lancet
2010;375:9726).
CT colonography (CTC)
: c/w colonoscopy, ~90% Se for lesions ≥1 cm but considerably less for smaller lesions (
NEJM
2008;359:1207). In high-risk Pts, Se only 85% for advanced neoplasia ≥6 mm (
JAMA
2009;301:2453). At population level, ↑ participation w/ CTC, but ↓ yield vs. colonoscopy; ∴ similar screening overall (
Lancet
2012;13:55).
•
Biochemical fecal testing
Occult blood
(FOBT): ↓ mortality (
NEJM
1993;328:1365 & 2000;343:1603); 3 card home testing more Se (24% vs. 5%) than DRE/FOBT (
Annals
2005;142:81). Repeat q1y.
Immunohisto for Hb
: Se ~35% & ~80% for adv neoplasia & CRC (
AJG
2012;107:1570)
DNA
: ↑ Se,Sp c/w FOBT, but less Se than colonoscopy (
NEJM
2004;351:2704)
Staging
(
AJCC Cancer Staging Manual
, 7th ed, 2010)
• TNM staging: Size/depth of primary (T), locoregional nodes (N), distant metastases (M). Staging is complex and based on pathologic correlation with observed survival data.
•
Colonoscopy + biopsy/polypectomy + intraoperative
and
pathologic
staging essential for evaluating extracolonic spread • CT scans of chest and abdomen/pelvis (inaccurate for depth of invasion & malignant LN) • Baseline
CEA
in Pt
with known CRC
has prognostic significance and is useful to fol-low response to therapy and detect recurrence;
not
a screening tool
• Chemotherapy
FOLFOX (
5-FU + leucovorin + oxaliplatin
), FOLFIRI or CapeOx (
NEJM
2004;350:2343)
±
Bevacizumab (anti-VEGFA mAb,
NEJM
2004;350:2335) or cetuximab (anti-EGFR mAb,
NEJM
2004:351:337; benefit limited to Pts w/o
KRAS
mutation;
NEJM
2008;359:1757)
Regorafenib (multikinase inhib.) ↑ survival in Pts w/ progressive metastatic CRC (
Lancet
2013;381:303).
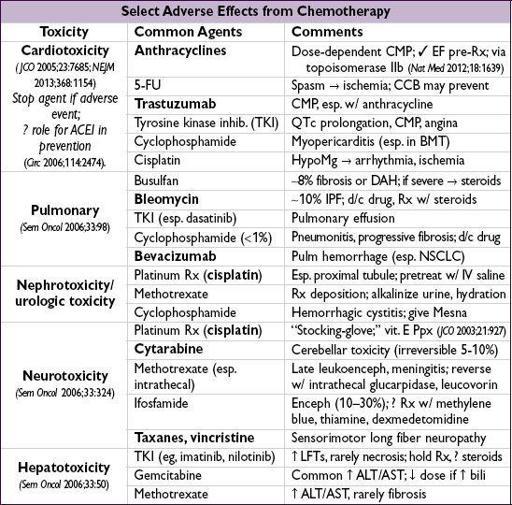
CHEMOTHERAPY SIDE EFFECTS