Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (44 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
6.37Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
•
Acute workup
:
toxins
(EtOH, acetaminophen);
vascular abnl
(U/S w/ Doppler);
viral tests
: IgM anti-HAV, HBsAg, IgM anti-HBc, HBV DNA, HCV RNA, anti-HEV, ± EBV, CMV, HSV, VZV;
autoimmune
(ANA, ASMA, ALKM);
ceruloplasmin
•
Chronic workup
: HBsAg, anti-HCV; Fe, TIBC; glc, HbA1c, TG; ANA, ASMA, ALKM; anti-tissue transglutaminase; ceruloplasmin & ɑ1-AT; TSH; vascular abnl (U/S w/ Doppler)
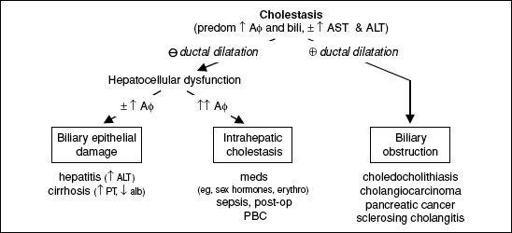
Figure 3-4
Approach to abnormal liver tests with cholestatic pattern
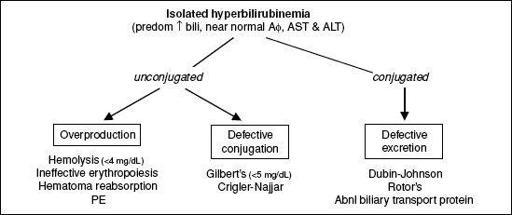
Figure 3-5
Approach to abnormal liver tests with isolated hyperbilirubinemia
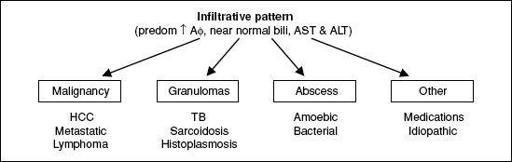
Figure 3-6
Approach to abnormal liver tests with infiltrative pattern
Abnormal liver tests in asymptomatic patients
(
Clin Liver Dis
2009;13:167)
• Careful review of history (
meds, EtOH
/drug use, exposures, risk factors for liver disease) and physical exam. Evaluate for any clues to etiology 1st (eg, d/c med and repeat LFTs).
• Confirm hepatic source: if primarily ↑ AΦ (✓ GGT) or AST > ALT (✓ CK, aldolase, TFT) •
Hepatocellular
Evaluate for most common causes: hepatitis A/B/C, hemochromatosis; screen for evidence of chronic liver disease (platelets, PT/INR, albumin)
Ifevaluation → lifestyle modification (wt loss, DM control) + repeat test 6 mo
If evidence of chronic liver disease or persistent lab abnl, screen for less common causes: AIH, Wilson’s, celiac, ɑ
1
-AT; ✓ U/S & consider liver bx
If still→ liver bx if ALT or AST >2× ULN for >6 mo; o/w observe
•
Cholestatic
: ✓ RUQ U/S, AMA
if biliary dilatation or obstruction → MRCP
if AMAand U/S
, or AMA
and U/S w/ abnl parenchyma → liver bx
if AMA & U/S: AΦ >1.5× ULN → consider bx; AΦ <1.5× ULN → observe
•
Isolated hyperbilirubinemia
: ✓ conjugated vs. unconjugated
conjugated → perform abdominal U/S → MRCP if dilatation or obstruction; if nl ultrasound ✓ AMA and consider MRCP or liver bx
unconjugated → ✓ Hct, retic count, smear, LDH, haptoglobin
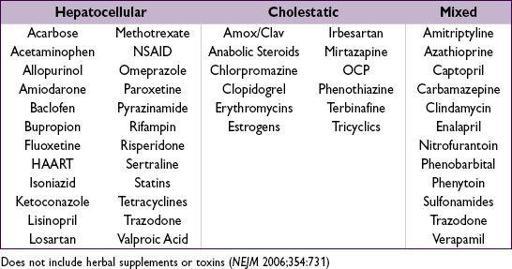
Common medications that cause abnormal liver tests
(
http://livertox.nlm.nih.gov
)
HEPATITIS
VIRAL
Hepatitis A
(ssRNA; 30–45% of acute viral hepatitis in U.S.)
• Transmission: fecal–oral route; contaminated food, water, shellfish; daycare ctr outbreaks • Incubation: 2–6 wk; no chronic carrier state
• Sx: ↓ appetite, malaise, fever, N/V, RUQ pain, ± jaundice; rarely fulminant
• Diagnosis: acute hepatitis =IgM anti-HAV; past exposure =
IgG anti-HAV (
IgM) • Treatment for acute HAV supportive. Prevention: vaccinate children & Pts w/ chronic HBV, HCV (? if cost-effective) or other chronic liver disease (2 doses at 0, 6–12 mo) • Postexposure ppx: age 1–40 y → vaccine; age <1 or >40 y or immunosupp → Ig
Other books
Consumed by a Stranger (Craved Series #4) by Kelly, Hazel
Captivity by James Loney
Gifted Curse (Curse Trilogy) by Owens, C.M.
The Beast of the North by Alaric Longward
Breaking (Fall or Break #2) by Barbara Elsborg
Doctor's Wife by Brian Moore
Tainted by Christina Phillips
Big Road Machines by Caterpillar
Dirty Deals: Olesia Anderson Thriller #1 Free Epub Edition by D. D. Marks