Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (248 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto

1. Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 domain controller system with an account
with administrator privileges.
2. Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Active Directory
Users and Computers.
3. Select the View menu, and select Advanced Features.
4. In the tree pane, select the Users container.
5. In the right pane, locate the Administrator account, and double-click the user
account to open the property pages.
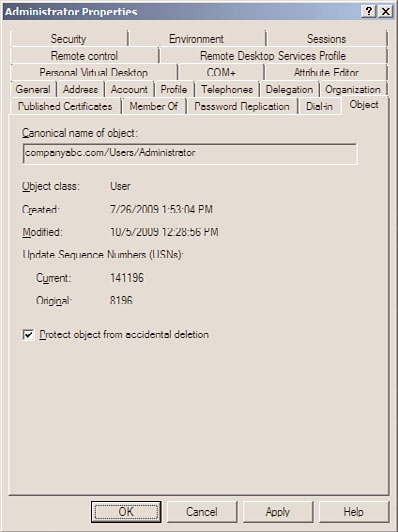
6. Select the Object tab, check the Protect Object from Accidental Deletion check box,
and click OK to apply the changes, as shown in Figure 30.9.
Using the Directory Services Restore Mode Password
When a Windows Server 2008 R2 system is promoted to a domain controller, the
Directory Services Restore mode (DSRM) password is created. This password is used only
when booting into Directory Services Restore mode. Restore mode is used when the Active
Backing Up Windows Server 2008 R2 Role Services
1255
ptg
FIGURE 30.9
Enabling accidental deletion protection on an Active Directory user account.
Directory database is in need of maintenance or needs to be restored from backup. Many
administrators have found themselves without the ability to log on to Restore mode when
necessary and have been forced to rebuild systems from scratch to restore the System State
data. Many hours can be saved if this password is stored in a safe place, where it can be
accessed by the correct administrators. Now with Windows Server 2008 R2, if a full
authoritative restore of the entire Active Directory database and sysvol folder is required,
this can be performed using the Windows Server Backup GUI. To perform the restore, the
domain controller will need to be booted into Directory Services Restore mode. If a single
object or a container with objects within is accidentally deleted, it can be granularly
restored by booting a domain controller in DSRM, restoring the System State, and
performing an authoritative restore of the desired object(s). The issue with this is that the
domain controller is offline to client requests during the entire time it is running in
Directory Services Restore mode. To avoid this, Windows Server 2008 R2 has a new feature
30
called the AD Recycle Bin, which allows for object recovery while the domain controller is
online. This is detailed in the next section.
There can still be cases where restores will require booting domain controllers into DSRM
and the DSRM password will be required. To make sure this password is known, the pass-
word can be updated regularly on all domain controllers. The Restore mode password is
server specific and created on each domain controller. If the password is forgotten, and
the domain controller is still functional, it can be changed using the command-line tool
1256
CHAPTER 30
Backing Up the Windows Server 2008 R2 Environment
ntdsutil.exe from the command prompt. To update the DSRM password on a domain
controller named dc1.companyabc.com, perform the following steps:
1. Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 system with an account with administrator
privileges.
2. Click Start, click All Programs, click Accessories, and select Command Prompt.
3. Type cd \ and press Enter.
4. Type NTDSutil.exe and press Enter.
5. Type Set DSRM Password and press Enter.
6. Type Reset Password on Server dc1.companyabc.com and press Enter.
7. Type the new DSRM password, and press Enter.
8. Type the new DSRM password again for confirmation, and press Enter.
9. Repeat the previous three steps for any additional domain controllers that will have
the DSRM password updated. To close out from NTDSutil.exe, type quit, press
Enter, type quit again, and press Enter.
10. Back at the command prompt, type logoff to log off of the domain controller.
Active Directory Recycle Bin
ptg
Windows Server 2008 R2 includes a feature that can be enabled called the Active Directory
Recycle Bin. When enabled, this feature can allow for a deleted Active Directory object to
be restored without having to restore the System State of a domain controller and boot to
Directory Services Restore mode to perform a selective authoritative restore of that object.
Enabling the Active Directory Recycle Bin requires that all domain controllers are running
Windows Server 2008 R2, the forest functional level must be set to Windows Server 2008
R2, and then functionality can be enabled manually. To enable the Active Directory
Recycle Bin, perform the following steps:
1. Log on to a Windows Server 2008 R2 domain controller in the forest root domain
with an account with domain administrator privileges.
2. Click Start, click All Programs, click Accessories, click the Windows PowerShell
folder, right-click on Windows PowerShell, and select Run As Administrator.
3. Type cd \ and press Enter.
4. Type Import-Module ActiveDirectory and press Enter.
5. Type Get-ADForest and press Enter. Review the ForestMode value, which should be
set to Windows2008R2Forest.
6. If the ForestMode is not set to Windows2008R2Forest, for a forest named compa-
nyabc.com as an example, type Set-ADForestMode –Identity companyabc.com -
ForestMode Windows2008R2Forest and press Enter. Type a Y and press Enter to
confirm the change.
7. Once the forest functional level is confirmed to be at the Windows Server 2008 R2
level, type in Get-ADOptionalFeature –Filter * and press Enter. This returns the
list of optional features, including the Active Directory Recycle Bin. If this feature is
enabled, the EnabledScopes setting will have a value.
Backing Up Windows Server 2008 R2 Role Services
1257
8. Assuming that this functionality has not been enabled, as it is not enabled by
default, type Enable-ADOptionalFeature ‘Recycle Bin Feature’ –Scope
ForestorConfigurationSet –Target companyabc.com and press Enter.
9. When prompted that this is an irreversible action, type Y and press Enter to enable
the Active Directory Recycle Bin feature.
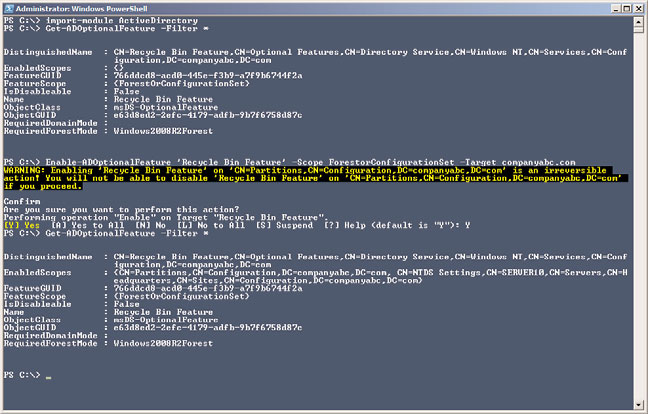
10. After the command completes, type Get-ADOptionalFeature –Filter * and press
Enter. Note that the EnabledScopes setting is now populated with a value, as shown
in Figure 30.10.
ptg
FIGURE 30.10
Enabling the Active Directory Recycle Bin feature.
11. Type exit and press Enter to close the PowerShell window.
After the Active Directory Recycle Bin is enabled, it should be tested with test organiza-
tional units, groups, users, or any desired objects. To perform a restore, the Restore-
ADObject cmdlets will be used along with a few other cmdlets to get the preliminary
information needed to restore. This restore process is detailed in Chapter 31.
Certificate Services
30
When the Active Directory Certificate Services role and role servers are installed on a
Windows Server 2008 R2 system, a Certification Authority is created. The Certification
Authority or CA is used to manage and allocate certificates to users, servers, and workstations
when files, folders, email, or network communication needs to be secured or encrypted.
When the CA allocates a certificate to a machine or user, that information is recorded in
the certificate database on the local drive of the CA. If this database is corrupted or
deleted, all certificates allocated from this server become invalid or unusable. To avoid this
1258
CHAPTER 30
Backing Up the Windows Server 2008 R2 Environment
problem, the certificates and Certificate Services database should be backed up frequently.
Even if certificates are rarely allocated to new users or machines, backups should still be
performed regularly. The certificate authority database is backed up with a full system
backup but can be backed up using the Certification Authority console. To perform a
manual backup of the certificate authority, perform the following steps:
1. Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 Certification Authority server system with an
account with administrator privileges.
2. Click Start, click All Programs, click Administrative Tools, and select Certification
Authority.
3. Double-click on the Certification Authority server to initiate the connection in the
console.
4. Right-click on the server, click All Tasks, and select Back Up CA.
5. When the Certification Authority Backup Wizard opens, click Next on the
welcome page.
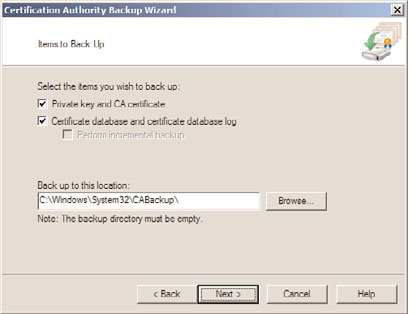
6. On the Items to Back Up page, check both check boxes, and in the Back Up to This
Location text box, type c:\Windows\System32\CABackup\ and click Next, as shown
in Figure 30.11.
ptg
FIGURE 30.11
Specifying the options for the Certification Authority Backup Wizard.
7. A window opens stating that the destination folder does not exist; click OK to create
the folder and continue.
8. On the Select a Password page, enter a password, confirm the password, and click
Next to continue. This password is very important because it will be required to
restore the database should that be necessary—so store this password in a safe place.
Backing Up Windows Server 2008 R2 Role Services
1259
9. On the Completing the Certification Authority Backup Wizard page, review the
settings, and click Finish to create the backup.
10. After the backup completes, the focus is returned to the Certification Authority
console. Close the console.
11. Log off of the server.
Domain Name System
Domain name system (DNS) configuration data is stored in the Registry and is backed up
with the System State backup. For each DNS zone that is hosted on the Windows Server
2008 R2 server that is not an Active Directory-integrated zone, a backup zone file is
created and stored in the %systemroot%\DNS\Backup folder. These files can be backed up
and used to restore a DNS zone to the same server after a restore or they can be used to
create new zones on a different server using these files to import the latest saved records.
For Active Directory-integrated DNS zones, these zones are backed up with the domain
controller System State and can be troublesome to restore. To back up the DNS zones
manually and selectively, perform the following steps:
1. Log on to the Windows Server 2008 R2 domain controller running DNS services
with an account with administrator privileges. These steps also work on primary
ptg
zones that are not Active Directory-integrated and also on non-domain controller
