Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 (65 page)
Read Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 Online
Authors: Judith A. Muschla,Gary Robert Muschla,Erin Muschla-Berry
Tags: #Education, #Teaching Methods & Materials, #Mathematics, #General

BOOK: Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5
10.16Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Activity 2: Modeling Multiplication and Division of Decimals
Students will model multiplication and division of decimals on graph paper. They will relate the models to the standard algorithms.
Materials
Ruler; colored pencils; crayons; graph paper for each student.
Procedure
1.
Explain that students will model multiplication and division of decimals.
2.
Instruct them to mark off a 10-by-10 square on graph paper.
3.
Together as a class, work on the following two examples.
- First model
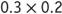 . Instruct your students to use a colored pencil, or crayon, to lightly color 2 tenths vertically within the 10-by-10 square. Note that 2 tenths (2 columns) is equivalent to 20 hundredths (20 graph-paper squares). Students should then use a different color to color 3 tenths on the grid horizontally. Note that 3 tenths (3 rows) is equivalent to 30 hundredths and that the two colors will overlap on 6 squares on the grid. Ask your students what the product is based on their model. They should realize that the product is represented by the region that is colored with both colors. Six squares are shaded with both colors; therefore, the product is 6 hundredths.
. Instruct your students to use a colored pencil, or crayon, to lightly color 2 tenths vertically within the 10-by-10 square. Note that 2 tenths (2 columns) is equivalent to 20 hundredths (20 graph-paper squares). Students should then use a different color to color 3 tenths on the grid horizontally. Note that 3 tenths (3 rows) is equivalent to 30 hundredths and that the two colors will overlap on 6 squares on the grid. Ask your students what the product is based on their model. They should realize that the product is represented by the region that is colored with both colors. Six squares are shaded with both colors; therefore, the product is 6 hundredths. - Instruct your students to mark off another 10-by-10 square on graph paper. Now model a division problem:
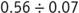 . Students should use a colored pencil, or crayon, to lightly color 56 hundredths vertically on the grid. Next they should use a different color to shade 7 of the 56 squares that they already shaded. After they have shaded 7 hundredths, ask them to shade the remaining 49 hundredths in groups of 7. They may choose to use a different color for each group, or to outline each group more darkly. Ask them to use the model to identify the quotient. The quotient is 8 because there are 8 groups of 7 hundredths in 56 hundredths.
. Students should use a colored pencil, or crayon, to lightly color 56 hundredths vertically on the grid. Next they should use a different color to shade 7 of the 56 squares that they already shaded. After they have shaded 7 hundredths, ask them to shade the remaining 49 hundredths in groups of 7. They may choose to use a different color for each group, or to outline each group more darkly. Ask them to use the model to identify the quotient. The quotient is 8 because there are 8 groups of 7 hundredths in 56 hundredths.
4.
Present these problems to your students: (1); (2)
; (3)
; (4)
. Instruct your students to complete models for these problems on graph paper, showing the solutions. If time permits, add more problems.
Closure
Discuss the answers. Ask questions such as the following: How were the models similar? How were they different? How can you use each type of model to find the corresponding multiplication or division problem? Have students write a reflection on the connection between multiplication and division of decimals.
Answers
(1)
0.72; 72 squares are in the overlapping regions.
(2)
12; 12 groups of 4 hundredths are formed.
(3)
0.30; 30 squares are in the overlapping regions.
(4)
4; 4 groups of 7 hundredths are formed.
Build a Problem
Directions: Follow the clues to create decimal addition and subtraction problems and their answers. Start with problem 1 and work in order. Use the Number Cards to create the problems and answers. Each card will be used only once. Two cards will not be used.
1.
The problem's first addend has 5 ones. The other addend has 4 tenths. The sum has 7 hundredths.
2.
The problem starts with a number that has 3 hundredths. The number that is subtracted has 3 hundredths. The answer has 2 ones.
3.
The problem's first addend has 0 tenths. The other addend has 2 tenths. The sum has 1 hundredth.
4.
The number that starts the problem has 6 hundredths. The number that is subtracted has 4 tenths. The answer has 5 ones.
5.
The problem's first addend has 7 tenths. The other addend has 1 ten. The sum has 1 ten and 3 ones.
6.
The number that starts the problem has 0 ones. The number that is subtracted has 5 hundredths. The answer has 5 tenths.
Number Cards
Number and Operations—Fractions: 5.NF.1
“Use equivalent fractions as a strategy to add and subtract fractions.”
1. “Add and subtract fractions with unlike denominators (including mixed numbers) by replacing given fractions with equivalent fractions in such a way as to produce an equivalent sum or difference of fractions with like denominators.”
Background
To add or subtract fractions, the denominators must be the same. If the denominators are different, students must write equivalent fractions that have the same denominator. For example, to add and
and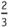 , students must find a common denominator. To find the least common denominator, students should find the least common multiple of 4 and 3, which is 12. They must then change each fraction to an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 12.
, students must find a common denominator. To find the least common denominator, students should find the least common multiple of 4 and 3, which is 12. They must then change each fraction to an equivalent fraction with a denominator of 12.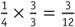 and
and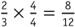 The problem is rewritten as
The problem is rewritten as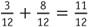 .
.
Other books
Warrior of the Isles by Debbie Mazzuca
Heart Like Mine by Amy Hatvany
I, Claudius by Robert Graves
If Only by Louise J
Sinner's Gin by Ford, Rhys
Last Tales by Isak Dinesen
Zypheria's Call (A Tanyth Fairport Adventure) by Lowell, Nathan
Rescuing the Heiress by Valerie Hansen
To Murder Matt by Viveca Benoir
The Hunt for the Missing Spy by Penny Warner