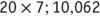Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 (63 page)
Read Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 Online
Authors: Judith A. Muschla,Gary Robert Muschla,Erin Muschla-Berry
Tags: #Education, #Teaching Methods & Materials, #Mathematics, #General

Number and Operations in Base Ten: 5.NBT.5
“Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths.”
5. “Fluently multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.”
Background
In mathematics, an algorithm is a procedure or method for solving a problem. Understanding the standard multiplication algorithm is essential for students to multiply fluently. Following are the steps for multiplying
For larger numbers, the same process is followed for each place value in the multiplier before all the partial products are summed.
Activity 1: Modeling Multiplication
Students will go to a Web site where they will create multiplication problems using the standard algorithm. The computer will help them to model these problems.
Materials
Computers with Internet access for students; computer with Internet access and digital projector for the teacher.
Procedure
1.
Instruct your students to go to
http://nlvm.usu.edu/
. They should click in the grades “3–5” column on the “Numbers and Operations” row and then scroll down to and click on “Rectangle Multiplication.” They will see a grid that models multiplication.
2.
Demonstrate how to use this Web site. Click on “Common” on the bottom of the screen. A problem will appear, and the computer will model the standard algorithm for multiplication on a grid.
3.
Do a few examples as a class. Explain that the numbers in the problem are shown in different colors on the grid. Moving the buttons on the side and on the bottom of the grid changes the problem. With each change the computer models the problem for students and provides the steps for multiplication using the standard algorithm. Make sure students are comfortable with the procedure before allowing them to work independently.
4.
Allow your students time to explore multiplication on the Web site by creating at least three problems of their own.
5.
Next, instruct them to find the products of three problems that you provide. Because of the limitation of the Web site, the factors must be 30 or less. Students are to solve the problems using the standard algorithm, and then check their product on the Web site.
Closure
Have students write an exit ticket explaining the standard algorithm for multiplication.
Activity 2: Finding Errors in Multiplication
Students will find and correct errors on a fictitious quiz that focuses on multiplying multi-digit whole numbers.
Materials
Reproducible, “Multi-Digit Multiplication Quiz,” for each student.
Procedure
1.
Review the standard algorithm for multiplication with your students. If necessary, provide a few example problems.
2.
Hand out copies of the reproducible. Explain that this is a quiz taken by a fictional student named John. He has made several mistakes on his quiz, and it is the task of your students to find his errors and correct his answers. Some answers are correct.
3.
Allow students time to find and correct all the errors.
Closure
Have students check their answers with a partner. Discuss the mistakes they found. Did they find the same mistakes? Did they find all the mistakes? How could they be certain? Did they search for errors in the problems in different ways? If yes, what were the different ways?
Answers
Errors are identified and corrected answers are provided.
(1)
Second partial product should be 840; 882 (
2)
Incorrect addition of partial products; 864
(3)
Correct
(4)
Failure to multiply thefor the first partial product; 2,240
(5)
Correct
(6)
Correct
(7)
Correct
(8)
Failure to regroup when multiplying; 14,350
(9)
Incorrectly multiplying
Name: John
Corrected by
: ______________________________
Multi-Digit Multiplication Quiz
Number and Operations in Base Ten: 5.NBT.6
“Perform operations with multi-digit whole numbers and with decimals to hundredths.”
6. “Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.”
Background
In a division problem, the number that is being divided is called the dividend; the number that divides the dividend is called the divisor; and the answer is called the quotient. There are several ways to solve division problems, including:
- Using long division
- Finding a connection between multiplication and division
- Using rectangular arrays
- Using area models
Activity 1: Piecing Together Division
Students will build division problems from given lists of numbers.
Materials
Reproducible, “Finding Dividends, Divisors, and Quotients,” for each student.
Procedure
1.
Review the process of division and provide some examples.
2.
Distribute copies of the reproducible. Explain that it has eight rows with four numbers in each row.
3.
Instruct your students to work with the numbers in each row. Of the numbers in the row, they are to find three that can form a division problem, identifying the dividend, divisor, and quotient. Explain that there will be no remainders. Also note that one number in the row will not be used. You might also want to mention that because divisors and quotients can be switched, two problems may be found for each row.
Closure
Provide the answers so that students may check their work. Discuss the strategies students used to select the numbers to create the problems. Ask students to write an explanation why two problems result from the numbers in each row.
Answers
Numbers are listed by row in the following order: dividend, divisor, and quotient. The number that is not used is not listed. Note that the divisor and quotient may be switched for each problem.
(1)
1,344; 24; 56
(2)
2,070; 46; 45
(3)
2,997; 37; 81
(4)
216; 72; 3
(5)
2,436; 42; 58
(6)
528; 88; 6
(7)
448; 56; 8
(8)
476; 17; 28