Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness (214 page)
Read Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness Online
Authors: Anne Waugh,Allison Grant
Tags: #Medical, #Nursing, #General, #Anatomy

Metaphase
Second phase of mitosis
Metastasis (pl. metastases)
Secondary deposits from a primary malignant tumour
Microbe
Micro-organism, e.g. a fungus, bacterium or virus
Micturition
Passing urine
Mitosis
Cell division giving two identical daughter cells
Mole
In chemistry, the quantity of a substance representing its molecular weight in grams
Motor nerve or neurone
An efferent nerve that carries impulses from the central nervous system to muscles or glands
Mucosa
Lining of body tracts (also mucous membrane)
Necrosis
Cell death following loss of oxygen supply
Negative feedback [system]
A physiological control mechanism that corrects deviations from a normal range
Neoplasm
A new growth which may be benign or malignant
Nephron
The structure in the kidneys responsible for the formation of urine
Neuromuscular junction
The synapse between a motor nerve and a skeletal muscle cell
Neurone
Nerve cell
Neurotransmitter
Chemical that transmits an impulse between one nerve and the next, or between a nerve and the neuromuscular junction
Non-specific defence
The defence mechanisms of the body that are effective against different types of threat, e.g. the skin, inflammation, complement
Norepinephrine
Alternative name for noradrenaline
Nucleotide
Building block of nucleic acids
Nutrient
Any substance that is digested, absorbed and used to promote body function
Oedema
Tissue swelling due to collection of fluid in the intercellular spaces
Olfaction
Sense of smell
Oncogenic
Cancer-causing
Organ
Body part, composed of different tissues, that carries out a specific body function
Organelle
Intracellular structure that carries out a specific function
Organic
A molecule or substance containing carbon
Origin
Point of attachment of a muscle to a bone that moves least during muscle contraction
Osteon
Structural unit of compact bone
Osmoreceptors
Specialised sensory receptors sensitive to solute concentration
Osmosis
Movement of water down its concentration gradient across a semipermeable membrane
Osmotic pressure
The pressure exerted by water in a solution
Ossicles
Bones of the middle ear: hammer, anvil and stirrup
Ossification
The production of bone tissue
Ovulation
The release of a mature ovum from the ovary
Oxidative phosphorylation
The aerobic high energy-generating metabolic process of cellular respiration
Oxyhaemoglobin
The oxygenated form of haemoglobin
Parasympathetic nervous system
Division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for ‘rest and repair’
Parietal layer
A layer of serous membrane lining a body cavity (cf. visceral layer)
Parturition
Childbirth
Passive transport
Any form of transport within the body that does not require the use of energy
Pathogen
Micro-organism capable of causing disease
Peptidase
An enzyme that breaks down protein
Peripheral nervous system
Nervous tissue that is not part of the brain or spinal cord
Peripheral resistance
The force against which the blood has to push to move through the arterial circulation, determined mainly by the diameter of the arterioles
Peristalsis
Rhythmical contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of hollow organs and tubes, e.g. the alimentary canal
pH scale
Scale of measurement of acidity or alkalinity
Phagocytosis
Defence mechanism by which body cells consume and destroy foreign materials, ‘cell eating’
Phenotype
The expression of the genes in an individual, e.g. hair colour, height, etc.
Phospholipid
Fat-based molecule containing phosphate, essential to the structure of the cell membrane
Pinocytosis
Ingestion of small vacuoles into a cell, ‘cell drinking’
Plasma
Clear, straw coloured liquid portion of the blood
Plasma protein
Any one of a group of important proteins synthesised by the liver and carried in the plasma, with diverse physiological functions, e.g. as antibodies or clotting proteins
Platelet (thrombocyte)
Small cell fragments involved in blood clotting
Polymophonuclear leukocyte
A general term for a white blood cell with an irregular nucleus (i.e. basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils)
Polyuria
Production of large quantities of urine
Positive feedback [system]
Physiological control mechanism that causes progressive deviation from normal limits; examples are limited, but include the progressive stimulation of the uterine muscle during childbirth
Posterior (dorsal)
Lying to the back of the body
Preload
The amount of blood in the ventricle just prior to ventricular contraction, determined mainly by venous return
Pressure ulcer
Damage to superficial tissues caused by prolonged pressure and interrupted blood supply, usually over a bony prominence
Primary wound healing
Simple repair of relatively minor tissue damage
Prognosis
Likely outcome of a disease
Prophase
First phase of mitosis
Pronation
The turning of the palms to face backwards
Proximal
Nearer the origin of a body part or point of attachment of a limb
Puberty
The stage of life in males or females where reproductive maturity is achieved
Pulmonary
Of the lungs
Pulse
The pressure wave generated by the heart, felt along an arterial wall where that artery lies close to the body surface
Pulse pressure
Diastolic blood pressure subtracted from the systolic value
Pyrexia
Fever
Pyrogen
A substance that causes fever
Radiation
The transmission of energy in waves
Receptor
A molecule, usually on the cell surface, that detects and responds to chemicals in the cell’s external environment, e.g. a neurotransmitter. Also, a sensory nerve ending that detects physical changes in the local environment, e.g. a baroreceptor measuring pressure
Recessive
Genetically, a form of a gene that can only be expressed if it is present as two identical forms on the chromosome pair
Refraction
The bending of light rays as they pass through a lens, e.g. the lens of the eye
Renal
Of the kidneys
Resistance vessel
A blood vessel, usually an arteriole, with a thick layer of smooth muscle in its tunica media, that constricts or dilates to regulate blood flow and blood pressure
Reticulocyte
Immature red blood cell
Retroperitoneal
Lying behind the peritoneum
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Molecule used to transfer genetic instructions from DNA to cytoplasmic ribosomes
Rotation
The movement of a body part around its long axis
Rugae
Folds in the internal surface of a hollow organ when the organ is relaxed
Salt
The product of a reaction between an acid and a base
Saltatory conduction
The ‘jumping’ of a nerve impulse along a myelinated nerve axon, from one node of Ranvier to the next
Scar tissue
The nonfunctional tissue that replaces damaged tissue
Secondary wound healing
Repair of tissue after extensive damage; a more complex and intense process than primary wound healing
Semipermeability (selective permeability)
A property of cell membranes that allows passage of some substances but not others
Sensory nerve or neurone
An afferent nerve that carries impulses to the central nervous system
Sex chromosome
The X or Y chromosome (pair 23)
Sign
An abnormality observed by people other than a patient
Simple propagation
The continuous conduction of an impulse along an non-myelinated nerve fibre
Specific defence mechanisms
Immunity; body’s protective mechanisms raised against a specific threat or antigen
Sphincter
Circle of muscle surrounding an internal passageway or orifice, used to regulate passage through the opening
Spinal reflex
Involuntary, usually protective, action controlled at the level of the spinal cord (i.e. independent of the brain)
Stroke volume
The volume of blood ejected by the ventricle when it contracts
Superior
Towards the upper part of the body
Supination
Turning the palm to face forwards
Sympathetic nervous system
Division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’
Symptom
An abnormality described by a patient
Synapse
The junction between a nerve and the cell it supplies
Syndrome
A collection of signs and symptoms that tend to occur together
Systemic circulation
The blood supply to all body organs except for the pulmonary arteries and veins
Systole
Contraction period of the heart or its individual chambers
Systolic blood pressure
The pressure recorded in the systemic circulation (often at the arm) when the pressure is at its highest, immediately following ventricular contraction; the higher of the two measurements used to denote a blood pressure recording
Tachycardia
Abnormally fast heart rate
Telophase
Fourth (final) phase of mitosis
Thrombosis
The inappropriate, pathological formation of stationary blood clots within blood vessels
Thrombus (pl. thrombi)
Stationary blood clot (clots)
Tissue fluid
Fluid between body cells, also known as interstitial fluid
Tract
A bundle of axons in the central nervous system
Transcription
Production of mRNA from DNA
Translation
Production of protein from mRNA
Trophic hormone
Hormone released that causes the release of a second hormone
Tumour
Mass of cells growing outwith the body’s normal control mechanisms
Tunica adventitia
The outer, supportive lining of blood vessels
Tunica intima
The lining of blood vessels (also called endothelium)
Tunica media
The middle layer of tissue in larger blood vessels
Urine
Liquid waste product made in the kidneys
Vasoconstriction
Decrease in diameter (narrowing) of a blood vessel
Vasodilation
Increase in diameter (widening) of a blood vessel
Vein
A blood vessel that carries blood towards the heart
Venule
A small vein
Virus
Non-living particle, which may be capable of causing disease
Visceral layer
A layer of serous membrane covering a body organ
Voluntary control
Conscious control of a body function
Zygote
Fertilised egg formed by fusion of an ovum and spermatozoon
Normal values
Note.
Some biological measures have been extracted from the text and listed here for easy reference. In some cases slightly different ‘normals’ may be found in other texts and used by different medical practitioners.
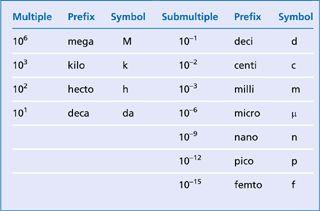
Metric measures, units and SI symbols
| Name | SI unit | Symbol |
|---|---|---|
| Length | metre | m |
| Mass | kilogram | kg |
| Amount of substance | mole | mol |
| Pressure | pascal | Pa |
| Energy | joule | J |
Decimal multiples and submultiples of the units are formed by the use of standard prefixes.