Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (53 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

BOOK: Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine
6.63Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
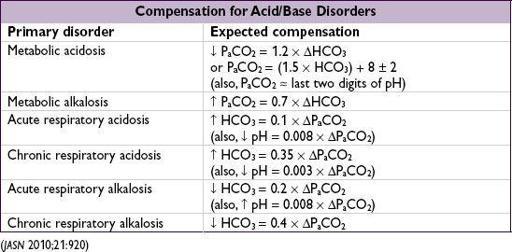
Mixed disorders
(more than one primary disorder at the same time)
• If compensation less or greater than predicted, may be 2 disorders:
P
a
CO
2
too low → concomitant 1° resp. alk.
P
a
CO
2
too high → concomitant 1° resp. acid.
HCO
3
too low → concomitant 1° met. acid.
HCO
3
too high → concomitant 1° met. alk.
• Normal pH
but
…
↑ P
a
CO
2
+ ↑ HCO
3
→ resp. acid. + met. alk.
↓ P
a
CO
2
+ ↓ HCO
3
→ resp. alk. + met. acid.
normal P
a
CO
2
& HCO
3
,
but
↑ AG → AG met. acid. + met. alk.
normal P
a
CO
2
, HCO
3
, & AG → no disturbance
or
non-AG met. acid. + met. alk.
•
Cannot
have resp. acid. (hypoventilation) and resp. alk. (hyperventilation) simultaneously
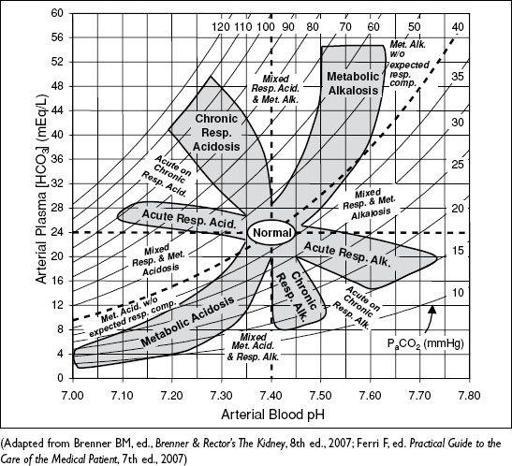
Figure 4-1 Acid-base nomogram
•
ABG vs. VBG
: concordant for pH (~0.04), HCO
3
(~2 mEq) but
not
P
a
CO
2
(~8±17 mmHg) VBG can be used to
screen
for hypercarbia w/ P
a
CO
2
cutoff ≥45 mmHg (100% Se),
but
does not accurately assess
degree
of hypercarbia (
Am J Emerg Med
2012;30:896)
METABOLIC ACIDOSIS
Initial workup
(
Nat Rev Nephol
2010;6:274)
• ✓
anion gap
(AG) = Na+ – (Cl
-
+ HCO
3
-
) = unmeasured anions - unmeasured cations
if ↑ glc, use measured
not
corrected Na
expected AG is [albumin] × 2.5 (ie, 10 if albumin is 4 g/dL, 7.5 if albumin is 3 g/dL)
↑ AG → ↑ unmeasured anions such as organic acids, phosphates, sulfates
↓ AG → ↓ alb or ↑ unmeasured cations (Ca, Mg, K, Li, bromine, immunoglobulin)
• If ↑ AG, ✓
delta-delta
(ΔΔ = DAG/DHCO
3
) to assess if there is an additional metabolic acid-base disturbance; DAG = (calculated AG – expected AG), DHCO
3
= (24 – HCO
3
)
ΔΔ = 1–2 → pure AG metabolic acidosis
ΔΔ < 1 → AG metabolic acidosis
and
simultaneous non-AG acidosis
ΔΔ > 2 → AG metabolic acidosis
and
simultaneous metabolic alkalosis
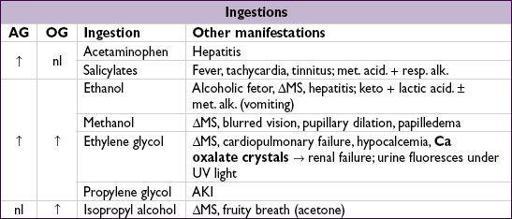
Workup for AG metabolic acidosis
• ✓ for
ketonuria
(dipstick acetoacetate) or plasma b-hydroxybutyrate (bOHB) nb, urine acetoacetate often not present in early ketoacidosis due to shunting to bOHB; ∴ acetoacetate may later turn, but does not signify worsening disease
• Ifketones, ✓
renal function
,
lactate
,
toxin screen
, and
osmolal gap
•
Osmolal gap
(OG) = measured osmoles – calculated osmoles
calculated osmoles = (2 × Na) + (glucose
18) + (BUN
2.8) (can + [EtOH/4.6] if have EtOH level and want to test if other ingestions)
OG >10 → suggests ingestion (see below)
for methanol/ethylene glycol: early on, OG precedes AG; later OG may be nl withAG
Workup for non-AG metabolic acidosis
(
CJASN
2012;7:671)
• Evaluate history for causes (see above)
• ✓
urine anion gap
(UAG) = (U
Na
+ U
K
) – U
Cl
UAG = unmeasured anions – unmeasured cations; as NH
4
+ is primary unmeasured cation, UAG is indirect assay for renal NH
4
+ excretion (
NEJM
1988;318:594)
•UAG → ↑ renal NH
4
+ excretion → appropriate renal response to acidemia Ddx: GI causes, proximal RTA, ingestions or dilutional
Other books
Evil Relations by David Smith with Carol Ann Lee
Her New Worst Enemy by Christy McKellen
These Dead Lands: Immolation by Stephen Knight, Scott Wolf
His Millionaire Maid by Coleen Kwan
Unknown Futures by Jessica E. Subject
A Handful of Time by Rosel George Brown
Fatal Remedies by Donna Leon
Marja McGraw - Bogey Man 03 - They Call Me Ace by Marja McGraw
Second Time's the Charm by Melissa J. Morgan
A Dangerous Age by Ellen Gilchrist