Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine (111 page)
Read Pocket Medicine: The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Marc Sabatine
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

Secondary
(10–20%)
• Typically >35 y of age; due to
structural
abnl of vessel wall •
Tissue ischemia & injury
(eg, digital ulcers), which is
not
seen in primary Raynaud’s • Etiologies: CTD (abnl nail-fold exam): SSc, SLE, PM-DM, MCTD, Sjögren’s, RA
Arterial disease: periph atherosclerosis, thromboangiitis obliterans (
abnormal pulses
)
Hematologic: cryoglobulinemia, Waldenström’s, antiphospholipid syndrome
Trauma (vibration or repetitive motion injury) & drugs (ergot alkaloids, estrogens, cocaine)
Treatment
(
Curr Opin Rheumatol
2011;23:555;
BMJ
2012;344:e289)
• All: avoid cold, maintain warmth of digits & body; avoid cigarettes, drugs and trauma • Mild–mod:
long-acting CCB
, topical nitrates, SSRI, ARB, ɑ-blockers, ASA/clopidogrel • Severe: PDE inhibitors, anti-ET-1 receptor (if ulcers esp. w/ PHT), digital sympathectomy • Digit-threatening: IV prostaglandins, digital sympathectomy, ± anticoagulation • Others: fish oil (1° RP only; Am J Med 1989;86:158), abx for infected ulceration
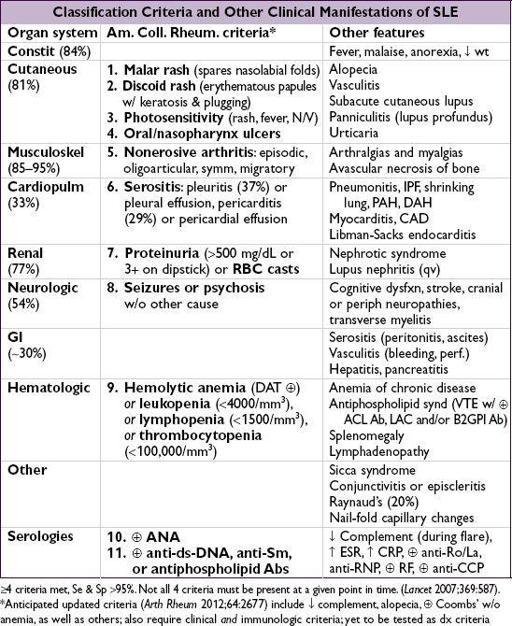
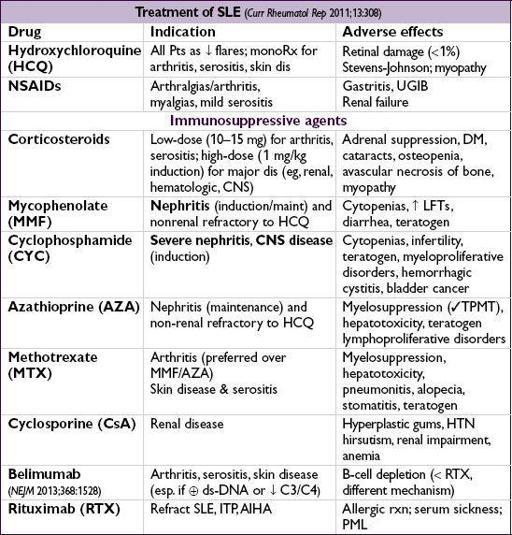
SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS (SLE)
Multisystem inflammatory autoimmune disease with a broad spectrum of clinical manifestations in association with antinuclear antibody (ANA) production
Epidemiology
(
NEJM
2011;365:2110)
• Prevalence 15–50/100,000; predominantly affects women 2nd to 4th decade •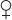 :
: ratio=8:1; African American:Caucasian ratio=4:1
ratio=8:1; African American:Caucasian ratio=4:1
• Complex genetics; some HLA assoc.; rare C1q & C2 defic.
Workup
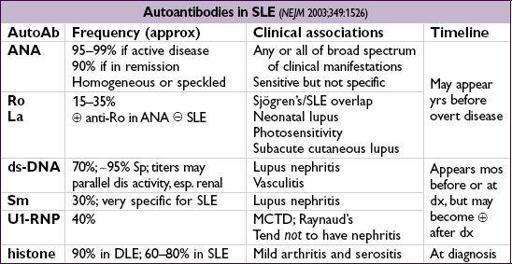
• Autoantibodies: ANA, if→ ✓ anti-ds-DNA, anti-Sm, anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-U1-RNP
• Lytes, BUN, Cr, U/A, urine sed, spot microalb:Cr ratio or 24-h urine for CrCl and protein • CBC, PTT, APLA (in 20–40%; ACL IgG/IgM, B2GP1, lupus anticoagulant), C3, C4
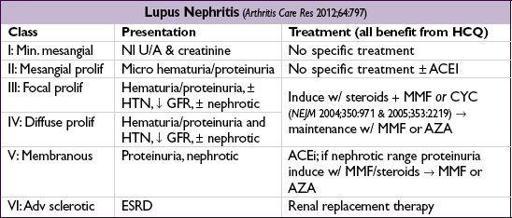
• If ↓ GFR, active sediment, hematuria or proteinuria → renal bx to guide Rx
Prognosis
• 5-y survival rate >90%, 10-y survival rate >80%
• Leading causes of morbidity and mortality:
infection
,
renal failure
, neurologic and cardiovascular events; thrombotic complications (Medicine 2003;82:299)
Drug-induced lupus (DLE)
(
Drug Saf
2011;34:357;
Curr Opin Rheumatol
2012;24:182)
• Many drugs:
procainamide
,
hydralazine
, penicillamine, minocycline, INH, methyldopa, quinidine, chlorpromazine, diltiazem,
anti-TNF
(esp. infliximab), interferons • Idiosyncratic onset; generally mild disease with arthritis, serositis, skin disease •Anti-histone (95%) (may be
in anti-TNF);
anti-ds-DNA (may be
in anti-TNF) & anti-Sm; normal complement levels • Usually reversible w/in 4–6 wk after stopping medication