Pediatric Examination and Board Review (195 page)
Read Pediatric Examination and Board Review Online
Authors: Robert Daum,Jason Canel

(E) cardiopulmonary resuscitation is known to cause retinal hemorrhage
3.
A head CT is performed and the results show an acute (high-intensity signal) subdural hemorrhage along the right cerebral convexity (see
Figure 109-1
). You provide this information to your colleague. In the process of obtaining more history, your colleague shares with you that the child fell off the bed 3 days ago. Which of the following is true?
(A) subdural hematomas are pathognomonic for inflicted head trauma
(B) household falls from furniture most commonly result in subarachnoid and parenchymal bleeding
(C) a CT scan is superior to MRI to detect acute subarachnoid bleeding
(D) MRI is the study of choice to detect a skull fracture
(E) epidural hematomas occur because of rotational forces on the skull, most prominently in the occipital region
4.
A skeletal survey has been performed. Which statement is incorrect?
(A) a skeletal survey includes 14-19 views of the skeletal system
(B) a “babygram” is sufficient as a screening tool for abuse
(C) a skeletal survey is indicated for children who are younger than 2 years of age with suspicion of child maltreatment
(D) a bone scan is inferior to a skeletal survey to age skeletal trauma
(E) radiograph images of the hands and feet are not warranted in children younger than 1 year of age
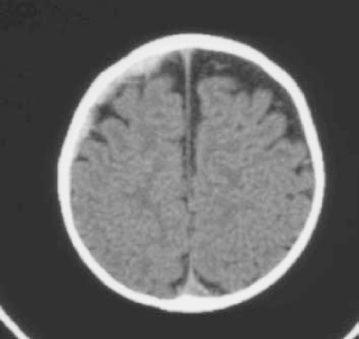
FIGURE 109-1.
Head CT of 8-month-old with irritability.
5.
Which statement about inflicted traumatic brain injury is false?
(A) inflicted head trauma is the most common cause of death in traumatically injured infants
(B) in the US, about 2000 cases of traumatic brain injury annually are because of inflicted injury
(C) the peak incidence of inflicted traumatic brain injury coincides with the peak incidences of colic, from 6 weeks to 4 months
(D) female babysitters are the most common perpetrators of inflicted head trauma
(E) physicians can “miss” a diagnosis of traumatic brain injury because of the lack of external evidence of trauma
6.
Which is not a predisposing factor for inflicted head trauma?
(A) the relatively large head size of an infant in proportion to the rest of the body
(B) open anterior fontanel
(C) high water content of the brain
(D) disparity of size between caretaker and child
(E) helplessness of the baby
7.
A skeletal survey is performed on the patient and callus formation is seen on 3 ribs. Which of the following is true?
(A) the time to form callus observable on radiograph is 7-10 days
(B) acute rib fractures are easily visualized by radiograph
(C) bone scan can assist in aging the fractures
(D) rib fractures are a common form of birth trauma seen in children delivered by cesarean
(E) the rib injuries and head trauma occurred at the same time
8.
Which is a true statement about classic metaphyseal fractures?
(A) treatment includes provision of a posterior mold and rest
(B) they are painful with movement, and swelling is detected in inspection
(C) they occur in soccer and hockey players
(D) they result from a planar fracture through the region of the metaphysis where it is contiguous to the physis
(E) high-risk locations for metaphyseal lesions are the wrist and hand joints
9.
Of the injuries listed below, which bone fracture is the most suspicious for abuse and always warrants an investigation?
(A) a healing rib fracture found on radiograph of a premature baby in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU)
(B) a spiral femur fracture in a 5-year-old
(C) a skull fracture in an 8-month-old after a witnessed fall
(D) an unwitnessed buckle or torus fracture of the distal radius of a 7-year-old
(E) a 6-month-old with a humeral fracture that occurred after being dropped by a sibling
10.
Select the factor that would not raise concern that an injury is more likely inflicted
(A) delay in seeking care
(B) discrepancies in the history provided by caretakers
(C) inconsistency between the history and the child’s developmental abilities
(D) parent smells of alcohol or appears intoxicated
(E) injury was said to be caused by a sibling or self-inflicted
11.
You inform your colleague that your diagnosis is inflicted head trauma and skeletal injuries. Which of the following steps is not necessary?
(A) contact the regional child welfare system and report this as a case of suspected child abuse
(B) document in the medical record your history, physical, results of studies, and your impression
(C) restrict all visitation to the child until the investigation is completed to protect the child from further potential harm
(D) provide materials to investigational authorities according to your hospital protocols and state law
(E) offer the child welfare system and police investigators assistance in assessing other children in the current caretaker’s environment
12.
On further investigation you find out the baby had an admission for gastroenteritis 1 month before this presentation. Choose the most appropriate statement below
(A) children diagnosed with abusive head trauma rarely have episodes of prior traumatic brain injury
(B) further evaluation of this child would include imaging of the GI system
(C) an evaluation for glutaric aciduria is warranted
(D) the most common presentation of inflicted head trauma is cardiopulmonary arrest
(E) the treating physician should obtain consent to review prior medical records to reevaluate the prior and current diagnoses in light of the current findings
13.
Which statement accurately reflects the mechanism of inflicted head trauma?
(A) impact from a fall less than 3 feet can cause serious life-threatening traumatic brain injury
(B) a shearing injury, because of accelerationdeceleration forces, leads to the disruption of bridging veins and development of subdural bleeding; shearing of other tissue interfaces can cause brain damage
(C) lack of impact findings (eg, bruising on examination) rules out an impact injury
(D) tin ear syndrome is caused by an isolated linear impact injury
(E) the force required to cause shaking injuries is mild and within the realm of normal caretaking behavior
14.
Identify the abusive injury
not
associated with violent shaking
(A) retinal hemorrhages
(B) rib fractures
(C) axonal brain injury
(D) diaphyseal fractures of the long bones
(E) subdural hematomas
15.
Which is a true statement about the outcomes for children with inflicted traumatic brain injuries?
(A) mortality is low from abusive head trauma
(B) neurodevelopmental delays are expected and careful follow-up is required
(C) the infant brain is pliable and will regenerate after insult
(D) brain injuries are mostly motor-based impairments
(E) cognitive and behavioral delays are rarely seen in children with significant traumatic brain injury
16.
Which is a true statement regarding the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) system and the assessment of the severity of head trauma in children?
(A) there are 3 categories of head trauma (minor, moderate, and severe), which are based on CT findings
(B) 3 clinical examination categories are the basis for the GCS
(C) the GCS scoring system ranges from 0 to 15
(D) the GCS system uses clinical findings and assigns the same points for adults and children
(E) the GCS system is not widely used for assessment of head trauma in children
17.
Which is an erroneous statement regarding the treatment of serious head trauma?
(A) initial focus on adequate hemodynamics and oxygenation is imperative
(B) intubation and ventilation are indicated for children with a GCS less than 8
(C) cervical spine immobilization should be considered in the initial assessment and ensured in children with a mental status change
(D) immediate imaging of the head should include an MRI to delineate the extent of gray matter injury
(E) maintenance of cerebral perfusion pressure and lowering of high intracranial pressure are the main goals of treatment of a severe head injury
18.
Your colleague, her domestic partner, and the babysitter are being investigated because of your diagnosis of abusive head trauma and skeletal injuries. Which is the best statement regarding outcome from traumatic brain injury?
(A) based on the initial GCS, which was more than 10, her child should have no long-term sequelae from the brain injury
(B) infants and children with brain injury have better outcomes because of the plasticity and myelination of the brain compared with older children with the same injury
(C) long-term cognitive, behavioral, and/or neurologic deficits are common in children who have sustained inflicted head trauma, and they warrant close follow-up care
(D) children who have a normal neurologic examination after serious brain trauma have no longterm effects
(E) prophylactic administration of anticonvulsants seems to correlate with better behavioral outcome in children with serious head trauma
ANSWERS
1.
(B)
This patient’s clinical examination and history lead to a differential diagnosis that includes entities that would cause mental status change in a child. CNS infection, central trauma, ingestion, and dehydration are the most likely causes of her clinical state. On examination she is not significantly dehydrated and her electrolytes are normal. Therefore, there seems to be no metabolic derangement. Because the lumbar taps yielded grossly bloody fluid, and because of the history of tremors, a head CT is warranted. Although the child does not have a classic toxicologic syndrome, a standard toxicology screen is appropriate as is a review of medications in the home. The depressed mental status, irritability, anemia, and grossly bloody lumbar tap put head trauma high on the differential, and a skeletal survey would be indicated even if the initial head CT was negative. The child also seems to be uncomfortable with movement; this paradoxical finding could indicate central nervous system infection or an acute injury (eg, an acute skeletal injury). An abdominal ultrasound does not aid in the evaluation of this child; if abdominal trauma was being considered, ordering liver enzymes, an amylase and lipase, as well as an abdominal CT to rule out a duodenal hematoma or a solid organ injury, would be appropriate.
