Pediatric Examination and Board Review (145 page)
Read Pediatric Examination and Board Review Online
Authors: Robert Daum,Jason Canel

A newborn is evaluated for a heart murmur and found to have a VSD. History is notable for a lack of prenatal care. At the time of delivery, ultrasound evaluation showed intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR).
On examination, the child is noted to have symmetric growth retardation, small palpebral fissures, thin upper lip, and underdeveloped philtrum.
SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER
1.
The most likely diagnosis to explain these features is
(A) chromosome anomaly
(B) diabetic embryopathy
(C) fetal alcohol syndrome
(D) maternal smoking
(E) sporadic heart defects with familial features
2.
Which of the following are common features of fetal alcohol syndrome?
(A) hypoplastic philtrum with thin upper lip
(B) microcephaly and midface hypoplasia
(C) mild to moderate mental retardation
(D) short palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, ptosis, strabismus
(E) all of the above
3.
A child has a VSD, sacral agenesis, rib and vertebral anomalies, femoral hypoplasia, and a renal malformation. Which of the following diagnoses best explains these clinical features?
(A) chromosome abnormality
(B) diabetic embryopathy
(C) fetal alcohol syndrome
(D) folic acid deficiency
(E) warfarin embryopathy
4.
Which of the following are features of the fetal phenytoin sodium syndrome?
(A) caudal regression, sacral agenesis, renal defects, cardiac defects
(B) spina bifida, craniofacial abnormalities
(C) hypoplasia of midface, low nasal bridge, ocular hypertelorism, cleft lip and palate, and hypoplasia of distal phalanges with small nails
(D) IUGR, microcephaly, mental retardation, birth defects such as congenital heart defects, and vertebral anomalies
5.
Severe nasal hypoplasia, choanal atresia, microcephaly, optic atrophy, lag in skeletal maturation, and stippling of epiphyseal growth centers is characteristic of prenatal exposure to
(A) antihistamine
(B) heparin
(C) hydantoins (eg, phenytoin)
(D) isotretinoin
(E) warfarin
6.
A newborn is treated for a myelomeningocele. Counseling of the family regarding neural tube defects should include which of the following statements and recommendations?
(A) there is no increased risk of recurrence for future children
(B) mom should use prenatal vitamins during all subsequent pregnancies
(C) there is a 25% risk of recurrence for future children. Additionally, you recommend use of prenatal thiamine
(D) 3-4% risk of recurrence for future children and use of 4 mg folate per day starting before conception
(E) 50% recurrence risk and use of 0.4 mg folate per day during pregnancy
7.
Strands of amniotic membrane (amniotic bands) may become dislodged and cause which of the following birth defects?
(A) amputations of digits
(B) cleft lip and/or palate
(C) clefts of the face and eye
(D) ring-like constriction of the limbs
(E) all of the above
8.
Which of the following definitions is incorrect?
(A) association: relationship between a birth defect and a prenatal infection
(B) malformation: morphologic defect of an organ from an intrinsically abnormal developmental process (eg, congenital heart defect)
(C) disruption: extrinsic destructive process that interferes with previously normal development (eg, amniotic bands that cause amputation of a finger)
(D) deformation: extrinsic mechanical force that causes asymmetric abnormalities (eg, breech position causing tibial bowing and club foot)
(E) dysplasia: abnormal cellular organization or function that generally affects only a single tissue type (eg, a cartilage abnormality that results in achondroplasia)
9.
A newborn is noted to have frontal bossing, midfacial hypoplasia, and ptosis suggestive of craniosynostosis. The child also has fusion (syndactyly) of all of the digits on each hand. The most likely diagnosis is
(A) Apert syndrome
(B) Crouzon syndrome
(C) Pfeiffer syndrome
(D) Saethre-Chotzen syndrome
(E) none of the above: sporadic craniosynostosis
10.
A newborn with vertebral anomalies, anal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula, radioulnar synostosis, and horseshoe kidney most likely has
(A) CHARGE association
(B) DiGeorge syndrome
(C) MURCS association
(D) Poland anomaly
(E) VATER association
11.
A newborn with coloboma of the eye, heart defect, choanal atresia, and ambiguous genitalia most likely has
(A) CHARGE association
(B) DiGeorge syndrome
(C) MURCS association
(D) Poland anomaly
(E) VATER association
12.
A newborn with evidence of fetal compression leading to a squashed, flat face, clubbing of the feet, pulmonary hypoplasia, and breech presentation should have a detailed evaluation of which of the following organ systems?
(A) cardiovascular
(B) central nervous system (CNS)
(C) dermatologic
(D) genitourinary system
(E) peripheral nervous system
13.
Long-term management of a patient with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome includes
(A) calcium monitoring and replacement
(B) routine serial renal ultrasounds and α-fetoprotein (AFP) measurements
(C) growth hormone replacement
(D) seizure precautions
(E) monitoring for development of cardiomyopathy
14.
The most likely diagnosis in a child with hyperphagia resulting in morbid obesity, micropenis, short stature, small hands and feet, and hypotonia is
(A) Angelman syndrome
(B) Bardet-Biedl syndrome
(C) Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
(D) Prader-Willi syndrome
(E) Sotos syndrome
15.
The clinical features suggestive of a 22q11 deletion (velocardiofacial, DiGeorge syndrome) include all of the following except
(A) conotruncal heart defects
(B) hypoparathyroidism
(C) immune dysfunction
(D) transverse palmar crease
(E) velopharyngeal insufficiency
16.
The best way to diagnose a microdeletion syndrome (eg, Prader-Willi, Williams, or DiGeorge syndrome) is
(A) routine karyotype
(B) FISH
(C) sequencing
(D) PCR (polymerase chain reaction)
(E) none of the above
ANSWERS
1.
(C)
Most teratogenic drugs exert a deleterious effect in a minority of exposed fetuses. The features described are most consistent with fetal alcohol exposure (see
Figure 85-1
). Diabetic embryopathy can cause heart defects but do not lead to the dysmorphic features described or IUGR. Sporadic heart defects do not typically have IUGR. All infants with dysmorphic features and a heart defect without a specific diagnosis should have a chromosome analysis and FISH studies for 22q deletion. But the features noted in this case point toward alcohol exposure. Maternal smoking is associated with IUGR but not with specific heart defects or dysmorphism.
2.
(E)
All of the features listed are frequent in the fetal alcohol syndrome. Additional features include prominent lateral palatine ridges, micrognathia, flat nasal bridge, short and upturned nose, VSD, ASD, pectus excavatum, altered palmar creases, small fifth fingernails, hemangiomas, poor coordination, fine motor impairment, hypotonia, irritability in infancy, and hyperactivity in childhood.
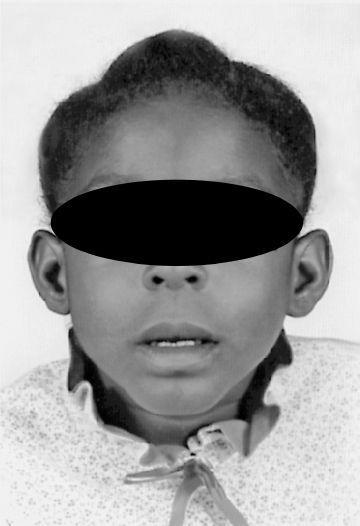
FIGURE 85-1.
Fetal alcohol syndrome: midface hypoplasia, absent philtrum, and microcephaly associated with a ventricular septal defect. (Reproduced, with permission, from Fuster V, O’Rourke RA, Walsh RA, et al. Hurst’s the Heart. 12th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2008: Fig. 12-15.)
3.
(B)
Congenital malformations occur more frequently in infants of diabetic mothers than in the general population, and multiple anomalies may be present. These anomalies include those mentioned and also coarctation, complete transposition, macrosomia, brain malformations (including holoprosencephaly, agenesis of the corpus callosum, and others), and renal malformations.
4.
(C)
The features of the fetal hydantoin (eg, phenytoin) syndrome are seen in approximately 7-10% of exposed infants, and an additional 30% may show lesser effects. In addition to the features listed, the syndrome is characterized by prenatal onset growth failure for weight, length, and head circumference; mental retardation; craniofacial features of wide anterior fontanel; metopic ridging; ocular hypertelorism; broad depressed nasal ridge; short nose with bowed upper lip; major malformations including clefts of the lip and palate; cardiovascular anomalies; and minor limb reduction malformations. The features in answer A are characteristic of maternal diabetes, those in answer B characteristic for valproic acid exposure, and in answer D characteristic for maternal PKU.
5.
(E)
Prenatal exposure to warfarin leads to an increase in abortion, stillbirth, and prenatal growth deficiency. The period of greatest risk is 6-9 weeks postconception. Developmental delay, mental deficiency, hypotonia, and seizures may occur. After 9 weeks, ocular defects and midline CNS malformations may occur. Antihistamine exposure is not known to lead to increased risk of birth defects. Isotretinoin exposure occurs by treatment of acne or other skin disorders, and it leads to features reminiscent of the DiGeorge sequence. Heparin exposure leads to 10-15% risk of stillbirth and a 20% risk for premature birth, but a specific malformation syndrome has not been described. Fetal hydantoin syndrome is reviewed in question 4.
