Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed (101 page)
Read Windows Server 2008 R2 Unleashed Online
Authors: Noel Morimoto

domain controller can either be turned back on and demoted, or simply be deleted and
cleaned from the domain.
Performing an Upgrade on a Single Domain Controller Server
After all various considerations regarding applications and hardware compatibility have
been thoroughly validated, a standalone server can be upgraded.
The health of the domain controllers should be verified prior to upgrading the domain
controllers. In particular, the Domain Controller Diagnostics (DCDIAG) utility should be
run and any errors fixed before the upgrade. The Windows Server 2003 DCDIAG utility is
490
CHAPTER 16
Migrating from Windows Server 2003/2008 to Windows Server
2008 R2
part of the Support Tools, which can be found on the installation media under
\support\tools\. The Support Tools are installed via an MSI package named
SUPTOOLS.MSI in Windows Server 2003. After installing the tools, the DCDIAG utility
can be run. The same utility is included in Windows Server 2008 with no additional
installs required. Execute the tool and verify that all tests passed.
The Active Directory Domain Services forest and the domain need to be prepared prior to
the upgrade. This installs the schema updates that are new to Windows Server 2008 R2
Active Directory. The following steps should be run on the Flexible Single Master
Operations (FSMO) role holder(s), specifically the schema master for forestprep and the
infrastructure master for domainprep. In a small environment or a single domain, all these
roles are typically on the same domain controller. To prepare the forest and domain,
execute the following steps on the domain controller with the roles:
1. Insert the Windows Server 2008 R2 DVD into the drive. If the Install Windows
autorun page appears, close the window.
NOTE
When preparing the forest, be sure to log on to the schema master as a member of
the Schema, Enterprise, and Domain Admins group.
ptg
2. Select Start, Run.
3. Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe /forestprep and click OK, where d: is the
DVD drive.
4. A warning appears to verify that all Windows 2000 domain controllers are at Service
Pack 4 or later. Enter C and press Enter to start the forest preparation.
5. Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe /domainprep /gpprep and click OK.
6. Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe /rodcprep and click OK. This update allows
Read-Only Domain Controllers.
Now that the schema updates have been installed and the domain preparation is done,
the domain is ready to be upgraded. The FSMO role holder should be the first Windows
Server 2003/2008 domain controller to be upgraded. Follow these steps to upgrade:
1. Insert the Windows Server 2008 R2 DVD into the DVD drive of the server to be
upgraded.
2. The Install Windows page should appear automatically. If not, choose Start, Run and
then type d:\Setup, where d: is the drive letter for the DVD drive.
3. Click Install Now.
4. Click the large Go Online to Get the Latest Updates button. This ensures that the
installation has the latest information for the upgrade.
5. Enter your product key and click Next.
6. Select the I Accept the License Terms option on the License page, and click Next
to continue.
Phased Migration
491
7. Click the large Upgrade button.
8. Review the compatibility report and verify that all issues have been addressed. Click
Next to continue.
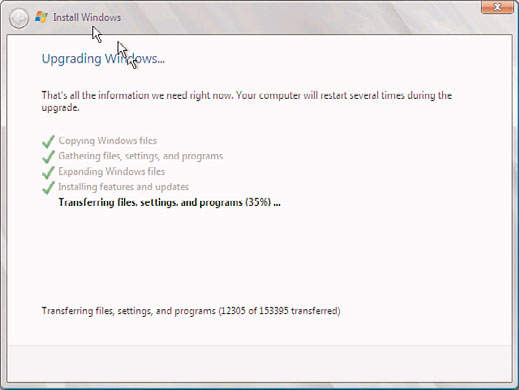
9. The system then copies files and reboots as a Windows Server 2008 R2 server,
continuing the upgrade process. After all files are copied, the system is then
upgraded to a fully functional install of Windows Server 2008 R2 (see Figure 16.1)
and will then reboot again. All this can take some time to complete.
ptg
16
FIGURE 16.1
Big Bang upgrade.
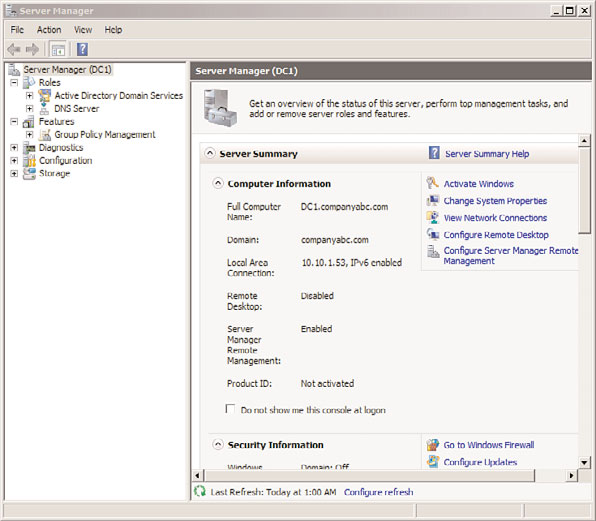
10. After the final reboot, the domain controller will be at the familiar Ctrl+Alt+Del
screen. After logon, the domain controller will open to the Server Manager console,
as shown in Figure 16.2. The domain controller upgrade is complete.
The upgrade process shown in steps 1 through 10 is then repeated for each of the remain-
ing Windows Server 2003/2008 domain controllers.
In many cases, the Windows Server 2003/2008 environment that will be migrated includes
one or many Active Directory domains and forests. Because Active Directory is one of the
most important portions of a Microsoft network, it is subsequently one of the most impor-
tant areas to focus on in a migration process. In addition, many of the improvements
made to Windows Server 2008 R2 are directly related to Active Directory, making it even
more appealing to migrate this portion of an environment.
The decision to upgrade Active Directory should focus on these key improvement areas. If
one or more of the improvements to Active Directory Domain Services justifies an upgrade,
492
CHAPTER 16
Migrating from Windows Server 2003/2008 to Windows Server
2008 R2
ptg
FIGURE 16.2
Server Manager console after upgrade.
it should be considered. Improvements were introduced in Windows Server 2003 and
Windows Server 2008, and yet more improvements were made in Windows Server 2008 R2.
The following list details some of the many changes made to Active Directory in Windows
Server 2003 that improved on the original Windows 2000 Server Active Directory:
.
Domain rename capability—
Windows Server 2003 Active Directory supported the
renaming of either the NetBIOS name or the LDAP/DNS name of an Active Directory
domain. The Active Directory domain rename tool can be used for this purpose, but
only in domains that have completely upgraded to Windows Server 2003 or later
domain controllers.
.
Cross-forest transitive trusts—
Windows Server 2003 supports the implementation
of transitive trusts that can be established between separate Active Directory forests.
Windows 2000 supported only explicit cross-forest trusts, and the trust structure did
not allow for permissions to flow between separate domains in a forest. This limita-
tion has been lifted in Windows Server 2003 or later.
.
Universal group caching—
One of the main structural limitations of Active
Directory was the need to establish very “chatty” global catalog servers in every site
established in a replication topology, or run the risk of extremely slow client logon
times and directory queries. Windows Server 2003 or later enables remote domain
controllers to cache universal group memberships for users so that each logon
request does not require the use of a local global catalog server.
Phased Migration
493
.
Intersite topology generator (ISTG) improvements—
The ISTG in Windows
Server 2003 was improved to support configurations with extremely large numbers
of sites. In addition, the time required to determine site topology has been notice-
ably improved through the use of a more efficient ISTG algorithm.
.
Multivalued attribute replication improvements—
In Windows 2000 Server, if a
universal group changed its membership from 5,000 users to 5,001 users, the entire
group membership had to be rereplicated across the entire forest. Windows Server
2003 addressed this problem and allowed incremental membership changes to be
replicated.
.
Lingering objects (zombies) detection—
Domain controllers that have been out
of service for a longer period of time than the Time to Live (TTL) of a deleted object
could theoretically “resurrect” those objects, forcing them to come back to life as
zombies, or lingering objects. Windows Server 2003 properly identified these
zombies and prevented them from being replicated to other domain controllers.
.
AD-integrated DNS zones in application partitions—
Replication of DNS zones
was improved and made more flexible in Windows Server 2003 by storing AD-inte-
grated zones in the application partition of a forest, thus limiting their need to be
replicated to all domain controllers and reducing network traffic. Conversely, the
DNS zones could be configured to replicate them to the entire forest if that was
ptg
appropriate.
16
The Windows Server 2008 Active Directory retained all the new features of Windows
Server 2003 Active Directory and adds several key new features, as follows:
.
Fine-grained password policies—
Password policies can be customized to different
users within the same Active Directory domain.
.
Read-Only Domain Controllers—
These domain controllers are designed for
branch offices and for extranet scenarios, in that they allow directory information to
be accessed but not changed. This adds an element of security to scenarios that
require directory services but are not as secure as the corporate data center.
.
Granular auditing—
The Active Directory auditing is much more granular and
allows tracking of some objects but not others. This reduces the volume of security
logs; however, it provides less information for the auditor or analyst to review during
an audit or information acquisition process.
.
Distributed File System Replication (DFSR)—
DFSR is now used for SYSVOL repli-
cation, replacing the File Replication Service (FRS) that is used to replicate SYSVOL
in Windows 2000 Server and Windows Server 2003. This feature provides more
robust and detailed replication of SYSVOL contents and is available when the
domain functional level is raised to Windows Server 2008.
Features introduced with the upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2 include the following:
.
Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell—
The Active Directory
Module for Windows PowerShell is a consolidated group of Windows PowerShell
cmdlets you can use to manage Active Directory.
494
CHAPTER 16
Migrating from Windows Server 2003/2008 to Windows Server
2008 R2
.
Active Directory Administrative Center—
The Active Directory Administrative
Center is a task-oriented AD management console that allows for the management
of users, groups, computers, sites, and domains from one console.
.
Recycle Bin for AD—
Previously deleted objects can now be restored from the
Recycle Bin.
.
Offline Domain Join—
Join Windows machines to the domain, while offline, via
an XML file.
.
Managed Service Accounts—
This feature greatly improves the daunting task of
managing service account passwords by automatically updating all services when the
service account password is changed.
NOTE
For more information on the improvements to Active Directory and the ways they can be
used to determine whether your organization should upgrade, refer to Chapter 4,
“Active Directory Domain Services Primer,” Chapter 5, “Designing a Windows Server
2008 R2 Active Directory,” Chapter 6, “Designing Organizational Unit and Group
Structure,” and Chapter 7, “Active Directory Infrastructure.”
ptg
In the scenario in this section, there are two domains (companyabc.com and asia.compa-
nyabc.com), which are members of the same forest (shown in Figure 16.3). The compa-
nyabc.com domain has all Windows 2000 Server SP4 domain controllers and the
