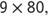Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 (9 page)
Read Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 Online
Authors: Judith A. Muschla,Gary Robert Muschla,Erin Muschla-Berry
Tags: #Education, #Teaching Methods & Materials, #Mathematics, #General

Number and Operations in Base Ten: 3.NBT.3
“Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic.”
3. “Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10–90 (e.g.,) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.”
Background
Knowledge of the products of two one-digit numbers makes multiplication of multiples of 10 by one-digit whole numbers a simple process.
For example,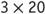 can easily be found if students know that
can easily be found if students know that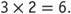 They can use a shortcut to find the product by adding a zero in the ones place. Be sure, however, that your students understand why the shortcut can be used. For example, modeling problems such as 3 groups of 20 and finding the sum can help them understand why
They can use a shortcut to find the product by adding a zero in the ones place. Be sure, however, that your students understand why the shortcut can be used. For example, modeling problems such as 3 groups of 20 and finding the sum can help them understand why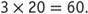
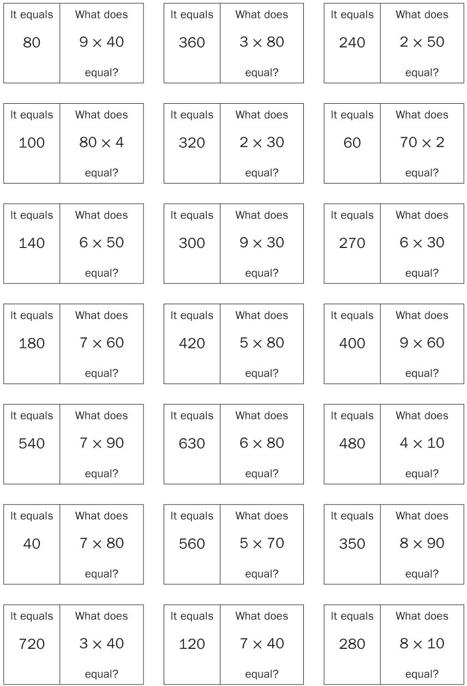
Activity: What Does It Equal?
Students will work individually or in pairs for this activity. They will be given a slip of paper that contains a product and a multiplication problem. They will identify the product, based on the problem.
Materials
One copy of reproducible, “Products and Problems,” for the class and one copy for the teacher; scissors for the teacher.
Preparation
After making two copies of the reproducible, cut out each two-part box from one copy so that you have a total of 21 slips of paper. (Each student or pair of students will receive one slip.) Keep the other copy of the reproducible to refer to during the activity. Note that the slips are arranged in order, each providing the correct answer to the multiplication problem written on the preceding slip. The first answer, “It equals 80,” is the answer to the last problem on the reproducible.
Procedure
1.
Before passing out the 21 slips of paper to your students, mix the slips up.
2.
Hand out one slip of paper to each student (or a slip to a pair of students). For a small class, you may give some students two slips. You must distribute all 21 slips.
3.
To start, choose a student to read the problem written on the right side of his or her slip. If necessary, have the student read the problem twice. All students should check their slips to see if the slips contain the product. Because of the way the slips are designed, only one will contain the correct product. The student who has the slip with the correct product should say “It equals …” and then provide the answer. If the student is correct, he then reads the question written on the right side of his slip. If he is incorrect, point out his error. Another student should then provide the correct product from the left side of her own slip.
4.
Continue the process until the student who read the first question has the correct response to the last question.
Closure
Discuss the activity. Ask your students to explain how knowing the basic multiplication facts helped them multiply whole numbers by multiples of 10.
Products and Problems
Number and Operations—Fractions: 3.NF.1
“Develop understanding of fractions as numbers.”
1. “Understand a fractionas the quantity formed by 1 part when a whole is partitioned into
equal parts; understand a fraction
as the quantity formed by
parts of size
”