I Have Landed (30 page)
Authors: Stephen Jay Gould

All the traditions that I have discussed in this essayâfrom airline listings to bibliographies and constitutional definitionsârepresent taxonomies, or classifications of related objects into an order that either helps us to retrieve information (the basic utilitarian reason for erecting taxonomies) or purports to explain the basis of variation (the scientist's more general rationale for devising systems of classification). My examples from the Constitution of the United States, discussed just above, illustrate this principle well. All the claims that now seem either cruel or merely senseless pose arbitrary answers to questions about categories and classifications: Who shall vote? How shall we count people for the census? How shall “true blue” be defined as a criterion for ultimate leadership?
I emphasize this principle because false taxonomiesâbased on sensible criteria at first but then persisting as traditions that can only be deemed arbitrary (at best) or harmful (at worst)âform a potent category of mental biases that becloud our view of empirical nature and our moral compass as well. My fellow
scientists seem particularly subject to this species of blindness because we have been trained to think that we see the world objectively. We therefore become specially subject to delusion by taxonomic schemes implanted in our minds by cultural traditions of learning but falsely regarded as expressing an objective natural reality.

Becher's bibliography of 1671, now sensibly ordered by last names
.
To present an example of tradition's power to reach forward from arbitrary beginnings by imposing false taxonomies upon human thought, let me return to the Bauhinsâthis time, to the brother hidden by Caspar among his Johns. Strange as this fact may sound to modern ears, the first half-century of modern paleontologyâfrom Agricola's first printed treatise of 1546 up to 1600âincluded virtually no illustrations of fossils in published sources, although botanical traditions for illustration had already led to the production of several elaborate, lavishly illustrated herbals. Agricola's long and elegantly printed treatise included no picturesâand neither did the great source from antiquity, Pliny's
Natural History
. I can think of only four or five sixteenth-century sources that printed any illustrations of fossils at all, and only two of these works feature series of drawings that could be called either extensive or systematicâ
De Rerum Fossilium
, the 1565 treatise by the great Swiss polymath Conrad Gesner, and a 1598 monograph on the medicinal waters and surrounding natural environments of the German fountains at Boll by Jean Bauhin (who as a young man had studied and then collaborated with Gesner).
Gesner's work presents a general exemplification, not a report about a specific collection from a particular place. Gesner therefore provided simple woodcut illustrations for one or two specimens from each major group of “fossils” then known in Europe (a heterogeneous assemblage by modern standards, including paleolithic hand axes then interpreted as stones that fell from the sky in thunderstorms, and sea urchins then interpreted by some scholars as serpents' eggs).
Bauhin's treatise, on the other hand, represents a true beginning for an important tradition in science: the depiction not only of characteristic forms or representative specimens, but an attempt to present the full range of variety found in a particular faunaâin other words, to “draw 'em all just as one sees 'em,” without any confusing selection or interpretation. In fact, in his very few paragraphs of introductory text, Bauhin tells us that he will simply show what he sees and not enter the brewing debate about the meaning of fossils. For that fascinating but (for his purposes) diversionary activity, readers will have to consult (he pointedly tells us) the aforementioned scholarly works of Agricola and Gesner. He, Jean Bauhin, nature's humble servant, will simply draw the fossils he has found and let readers draw their own conclusions.
Bauhin's fifty-three pages and 211 drawings therefore mark the first printed presentation of a complete set of fossil specimens from a particular place. In consulting his treatise, we are truly “present at the creation” of an important tradition in the depiction and classification of nature's bountiful variety. But however much we appreciate the privilege, and however appropriately we admire Bauhin's originality, we should also bear the theme of this essay in mind and ask some crucial questions about cultural practices: What conventions did Bauhin invent in creating this genre? Did his rules and customs make sense in his day? Did they then become arbitrary impediments to increasing knowledge, masquerading as an “obvious” way to present “objective” facts of nature?
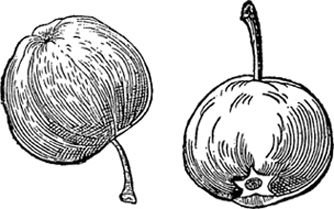
Bauhin's attempt to devise an iconographic convention for distinguishing apples from pears, by drawing apples with stems down and pears with stems up, from his 1598 treatise
.
As a striking proof that our iconographic traditions may originate as arbitrary inventions of idiosyncratic beginners, we need only consider the chapter following the opening section on fossils in Bauhin's 1598 treatiseâhis discussion of variation in local pears and apples. The average apple couldn't be confused with the average pear, but so many forms of both fruits had been developed in this region of Germany that extensive overlap could lead to uncertainties for dumpy and elongated apples or for compressed and top-heavy pears. Bauhin therefore invented the practice of drawing all the apples stem down and all the pears stem up!
Bauhin's convention did not take hold, so we tend to view his illustrations as rather quaintâand the purely arbitrary character of his decision stands out clearly to us today. But suppose that his practice had endured. Wouldn't we be wondering today why Delicious goes down and Bartlett goes up? Or, more interesting to contemplate, would we be pondering this issue at all? Perhaps we
would simply be accepting a printed orientation that we had seen throughout life, never bothering to question the evident discrepancy with nature's obedience to gravity, where both fruits hang
down
from stems. (Or perhaps, as city folks dwelling in concrete jungles, we would never even realize that nature works differently from art. Honest, growing up as a New York City street kid, I really didn't know for a long time that milk came out of cows' teatsâyuck!ârather than from bottles
ab initio
.)
This example may strike readers as silly. But we follow similarly arbitrary conventions and mistake them for natural reality all the time. Anglophone publications, for example, always draw snails with the apex (the pointy end) on top and the aperture at the bottom. This orientation seems so obviously natural to meâapex up, aperture down. Of courseâhow else could a snail be? But French publicationsâand I do not know how or why the differences in practice beganâusually draw snails in the opposite orientation, with the apex pointing down and the aperture up. So millions of Frenchmen must be wrong,
n'est-ce pas?
But when you learn about the difference and then allow yourself to consider the issue for the first time, you suddenly realizeâand the insight can be quite salutaryâthat the French and English solutions might as well be Bauhin's pears and apples. Neither mode can possibly be called correct by cor-respondence to nature. Most snails crawl horizontally along the substrate. Both ends of the shell lie basically parallel to the sea floor. Neither can be labeled as intrinsically up or down.
In another example that caused me some personal embarrassment but also taught me something important about convention versus nature, I once wrote that the North Pole pointed up and that our planet rotated counterclockwise around this axis (viewed, as by God or an astronaut, from above). An Australian reader wrote me a letter, gently pointing out the absence of absolute “up” or “down” in the cosmos and reminding me that our cartographic convention only reflects where most map-making Europeans live. From his patriotic vantage (and accepting another dubious convention that equates “up” with “good”), the Antarctic Pole points up, and Earth rotates clockwise around this southern standard.
The situation becomes even more complicated, and even more evidently ruled by convention, when we consider the history of cartography. In many medieval maps, drawn under the Ptolemaic notion of a central and nonrotating Earth, eastâthe direction of the rising Sunâoccupies the top of the map. The word
orient
âmeaning “east,” but with an etymology of “rising” in reference to the sunâgained the additional and more symbolic definition of “locating one's position,” because east once occupied this favored top spot on our
standard maps. (The Chinese used to be called Orientals for the same reason, before the term lapsed from political correctness, while Europeans became Occidentals, or westerners, in literal reference to the “falling down,” or setting, of the Sun.)
When we survey Bauhin's more than two hundred fossil drawings, the largest single cache of sixteenth-century paleontological illustrations, we note the origin of several conventions that, although superseded today (and therefore unknown to most modern scientists), seriously impeded, for nearly two centuries, a proper understanding of the nature of fossils and the history of life. Consider just three classes of examples, all based on the taxonomic conventions of sixteenth-century paleontology. The recognition of Bauhin's illustrations as conventional rather than natural, and their replacement, by the end of the eighteenth century, with “modern” figures that clearly depict fossils as ancient organisms, virtually defines the primary shift in understanding that led to our greatest gain in knowledge during the early history of paleontology.
1.
Conflation of categories
. In Bauhin's day, the word
fossil
âderived from the past participle of the Latin verb
fodere
, meaning “to dig up”âreferred to any object of distinctive form found within the earth, thus placing the remains of ancient organisms in the same general category as crystals, stalactites, and a wide range of other inorganic objects. Until organic remains could be recognized as distinctive, placed in a category of their own, and properly interpreted as the products of history, modern geology, with its central concept of continuous change through deep time, could not replace the reigning paradigm of an Earth only a few thousand years old and created pretty much as we find it today, with the possible exception of changes wrought by Noah's universal flood.
If fossils originated within rocks as products of the mineral kingdom, just as crystals grow in mines and stalactites form in caves, then a petrified “shell” may just denote one kind of inorganic object manufactured in its proper place within the mineral kingdom. Thus, when Bauhin places his drawing of a fossil snail shell right next to a conical mound of crystals because both share a roughly similar shape and supposed mode of inorganic origin, this taxonomic convention does not merely record a neutral “fact” of pure observation, as Bauhin claimed. Rather, his juxtaposition of two objects now viewed as fundamentally different in origin and meaning expresses a theory about the structure of nature and the pattern of historyâa worldview, moreover, that stood firmly against one of the great revolutions in the history of scientific understanding: the depth of time and the extent of change.

