Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (999 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
7.8Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
IgA makes up the majority of immunoglobulin in mucosal secretions, including nasal and pulmonary secretions, saliva and intestinal fluids, tears, and secretions of the genitourinary tract. IgA is important in preventing attachment or penetration of the body surfaces by microorganisms, and in protection against respiratory, GI, and GU infections. IgA cannot cross the placenta. It can be produced by infants, and their secretions tend to be typically low. IgA is the second most frequent type of monoclonal immunoglobulin identified in multiple myeloma.

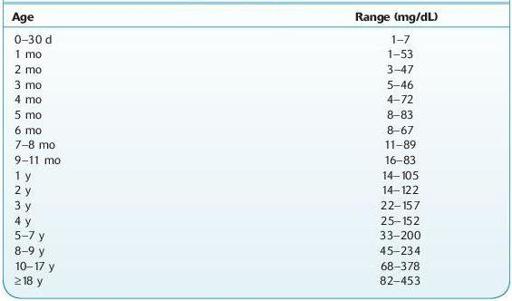
Normal ranges:
see Table 16.41.
TABLE 16–41. Normal Ranges for IgA by Age
Use
Detection or monitoring of monoclonal gammopathies and immune deficiencies
Assist in the diagnosis of multiple myeloma
Monitor therapy for multiple myeloma
Evaluate patients suspected of IgA deficiency prior to transfusion
Evaluate anaphylaxis associated with the transfusion of blood and blood products (anti-IgA antibodies may develop in patients with low levels of IgA, possibly resulting in anaphylaxis when donated blood is transfused)
Interpretation
Increased In
Polyclonal:
Cirrhosis of the liver
Chronic infections
Other books
El hombre equivocado by John Katzenbach
One More Time by RB Hilliard
The Treasure by Jennifer Lowery
Imprudence by Gail Carriger
One Night in Mississippi by Craig Shreve
Eric S. Brown by Last Stand in a Dead Land
Gracie's Touch Zion Warriors 1 by S E Smith
The Turncoats (The Thirteenth Series #2) by G.L. Twynham
Summer Sin (The Anthology Novella Series Book 2) by Darlene Kuncytes
Grounded by Neta Jackson
