Trigger Point Therapy for Myofascial Pain (23 page)
Read Trigger Point Therapy for Myofascial Pain Online
Authors: L.M.T. L.Ac. Donna Finando

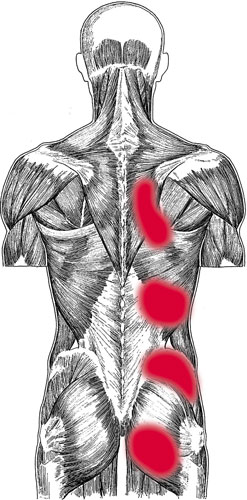
Erector spinae pain pattern
Associated zones, meridians, and points:
Dorsal zone; Foot Tai Yang Bladder meridian;
Iliocostalis thoracis:
BL 11â21, BL 41â50;
Iliocostalis lumborum:
BL 16â26, BL 45â52;
Longissimus thoracis:
BL 11â25, BL 41â52.
Stretch exercises:
- Seated forward stretch: Sit comfortably on a chair with the feet placed flat on the floor. Fold the torso toward the floor, reaching forward and down with the arms. Allow your head and neck to hang loosely. Hold this position for a count of twenty to thirty. Return to the seated position slowly.
- Pelvic tilts: Lie supine. Bend the knees, placing the soles of the feet on the floor. Exhale and slowly drop the lumbar curve of the back toward the floor. Hold for a count of five, then release. Repeat several times. Be certain that the drop of the lumbar arch occurs as a result of the relaxation of the back muscles, not from an anterior tilt of the lower pelvis brought on by contracting the gluteal muscles.
- Cats: Position the body on the hands and knees. Arch the back, lifting both the head and the buttocks toward the ceiling. Hold for a count of five. Then round the back, aiming both the head and the coccyx for the floor. Hold for a count of five. Alternate these two positions three to four times.
Strengthening exercise:
Lie prone, with the hands clasped behind the head. Lift the upper portion of the body from the floor, making sure to keep the buttocks and legs relaxed. Hold for a count of one to three.
Repeat two or three times, increasing frequency and duration as the strength of the back increases.
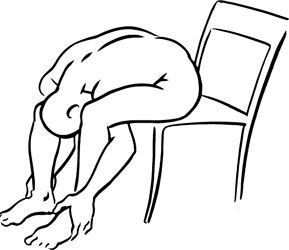
Stretch exercise 1: Erector spinae
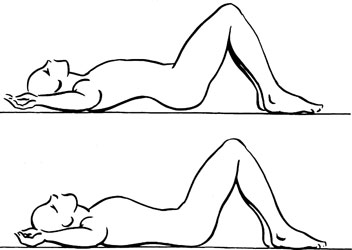
Stretch exercise 2: Erector spinae
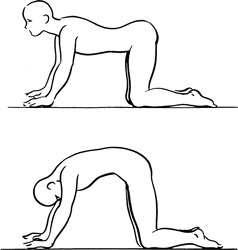
Stretch exercise 3: Erector spinae
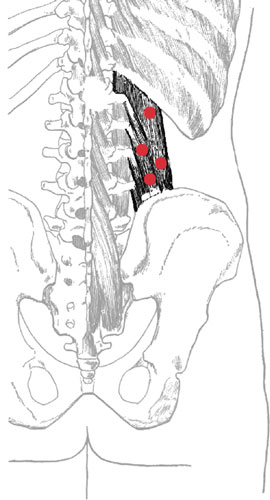
Quadratus lumborum and trigger points
Q
UADRATUS
L
UMBORUM
Proximal attachment:
Medial one-half of the twelfth rib and the transverse processes of L1âL4.
Distal attachment:
Uppermost posterior aspect of the crest of the ilium.
Action:
Acting unilaterally:
stabilizes the lumbar spine in the upright position; laterally flexes the lumbar spine; acts as a hip hiker.
Acting bilaterally:
extends the lumbar spine; acts in forced exhalation, as might occur in coughing; fixes the twelfth rib, facilitating contraction of the diaphragm.
Palpation:
Quadratus lumborum is one of the muscles most commonly involved in lower back pain, yet it is commonly overlooked as a source.
To locate quadratus lumborum, identify the following structures:
- Rib 12âThe bottommost or “floating” rib is the shortest of the twelve ribs. Locate its free anterior border posterior to the midaxillary line, level with the vertebral body of L2.
- Transverse processes of L1âL5
- Iliac crestsâLying on a horizontal line with the junction of L4âL5
Palpate quadratus lumborum with the patient lying prone. Gently depress the area between the iliac crest and the twelfth rib through the soft lateral aspect of the torso, pressing medially and obliquely toward the transverse processes of the lumbar vertebrae (not sagitally into the body). Image the location of quadratus lumborum. As you do so your hand will encounter the lateral bands of quadratus lumborum.
Pain pattern:
Superficial trigger points refer pain to the lateral border of the iliac crest and over the greater trochanter. Deep trigger points refer pain over the region of the sacroiliac joint and deep within the center of the buttock. The patient may be unable to bear standing upright or walking due to deep, aching low back pain. Inability to turn over in bed without pain. Trigger points may produce an apparent leg-length discrepancy.
Causative or perpetuating factors:
Overload stress of simultaneous bending and lift-ing; awkward lifting of heavy objects; sustained and repetitive strain; sudden leg-length discrepancy as might occur with the use of an ankle cast.
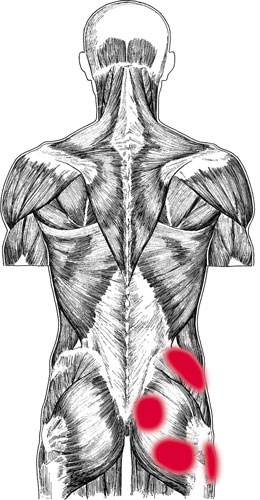
Quadratus lumborum pain pattern
Satellite trigger points:
Gluteus minimus, gluteus medius, thoracolumbar paraspinals, piriformis.
Affected organ system:
Kidney/genitourinary system.
Associated zones, meridians, and points:
Dorsal zone; Foot Tai Yang Bladder meridian, BL 21â24, BL 51 and 52.
Stretch exercises:
- Lying supine with the feet on the floor and the knees bent, cross the leg on the unaffected side over the leg on the affected side. Use the upper leg to gently pull the lower leg toward the floor. Hold for a count of fifteen to twenty.
- Stand with the back approximately 12 inches away from a wall. Twist the upper body to place both palms on the wall. Hold for a count of fifteen to twenty.
- Cross the affected leg behind the unaffected leg, shifting your weight toward the affected hip. Reach both arms above the head, grasping the wrist of the homolateral arm with the opposite hand. Laterally bend the torso toward the unaffected side. Hold this position for a count of ten to fifteen.
Strengthening exercise:
Because quadratus lumborum is a postural muscle, strengthening exercises are generally not necessary.
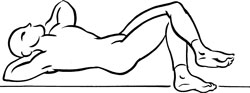
Stretch exercise 1: Quadratus lumborum
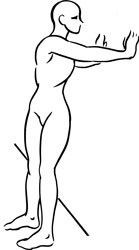
Stretch exercise 2: Quadratus lumborum
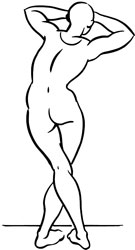
Stretch exercise 3: Quadratus lumborum
