The Elements of Computing Systems: Building a Modern Computer from First Principles (7 page)
Read The Elements of Computing Systems: Building a Modern Computer from First Principles Online
Authors: Noam Nisan,Shimon Schocken

BOOK: The Elements of Computing Systems: Building a Modern Computer from First Principles
8.09Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Or
The Or function returns 1 when at least one of its inputs is 1, and 0 otherwise.
The Or function returns 1 when at least one of its inputs is 1, and 0 otherwise.

Xor
The Xor function, also known as “exclusive or,” returns 1 when its two inputs have opposing values, and 0 otherwise.
The Xor function, also known as “exclusive or,” returns 1 when its two inputs have opposing values, and 0 otherwise.

Multiplexor
A multiplexor (figure 1.8) is a three-input gate that uses one of the inputs, called “selection bit,” to select and output one of the other two inputs, called “data bits.” Thus, a better name for this device might have been selector. The name multiplexor was adopted from communications systems, where similar devices are used to serialize (multiplex) several input signals over a single output wire.
A multiplexor (figure 1.8) is a three-input gate that uses one of the inputs, called “selection bit,” to select and output one of the other two inputs, called “data bits.” Thus, a better name for this device might have been selector. The name multiplexor was adopted from communications systems, where similar devices are used to serialize (multiplex) several input signals over a single output wire.


Figure 1.8
Multiplexor. The table at the top right is an abbreviated version of the truth table on the left.
Multiplexor. The table at the top right is an abbreviated version of the truth table on the left.

Figure 1.9
Demultiplexor.
Demultiplexor.

Computer hardware is typically designed to operate on multi-bit arrays called “buses.” For example, a basic requirement of a 32-bit computer is to be able to compute (bit-wise) an And function on two given 32-bit buses. To implement this operation, we can build an array of 32 binary And gates, each operating separately on a pair of bits. In order to enclose all this logic in one package, we can encapsulate the gates array in a single chip interface consisting of two 32-bit input buses and one 32-bit output bus.
This section describes a typical set of such multi-bit logic gates, as needed for the construction of a typical 16-bit computer. We note in passing that the architecture of
n
-bit logic gates is basically the same irrespective of
n
’s value.
n
-bit logic gates is basically the same irrespective of
n
’s value.
When referring to individual bits in a bus, it is common to use an array syntax. For example, to refer to individual bits in a 16-bit bus named data, we use the notation data [0], data [1],..., data[15].
Multi-Bit Not
An
n
-bit Not gate applies the Boolean operation Not to every one of the bits in its
n
-bit input bus:
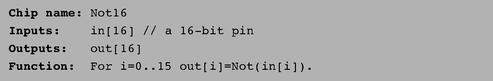
An
n
-bit Not gate applies the Boolean operation Not to every one of the bits in its
n
-bit input bus:

Multi-Bit And
An
n
-bit And gate applies the Boolean operation And to every one of the n bit-pairs arrayed in its two
n
-bit input buses:

An
n
-bit And gate applies the Boolean operation And to every one of the n bit-pairs arrayed in its two
n
-bit input buses:

Multi-Bit Or
An
n
-bit Or gate applies the Boolean operation Or to every one of the n bit-pairs arrayed in its two
n
-bit input buses:

An
n
-bit Or gate applies the Boolean operation Or to every one of the n bit-pairs arrayed in its two
n
-bit input buses:

Multi-Bit Multiplexor
An
n
-bit multiplexor is exactly the same as the binary multiplexor described in figure 1.8, except that the two inputs are each
n
-bit wide; the selector is a single bit.
An
n
-bit multiplexor is exactly the same as the binary multiplexor described in figure 1.8, except that the two inputs are each
n
-bit wide; the selector is a single bit.

Many 2-way logic gates that accept two inputs have natural generalization to multi-way variants that accept an arbitrary number of inputs. This section describes a set of multi-way gates that will be used subsequently in various chips in our computer architecture. Similar generalizations can be developed for other architectures, as needed.
Multi-Way Or
An
n
-way Or gate outputs 1 when at least one of its n bit inputs is 1, and 0 otherwise. Here is the 8-way variant of this gate:

An
n
-way Or gate outputs 1 when at least one of its n bit inputs is 1, and 0 otherwise. Here is the 8-way variant of this gate:

Other books
A Fatal Winter by G. M. Malliet
Flight by Colmer, Siena
The Likeness: A Novel by Tana French
Jared by Teresa Gabelman
The Bridge on the Drina by Ivo Andrić
Devon's Pair: Powertools, Book 4 by Jayne Rylon
The Song of the Cid by Anonymous
Five Women by Rona Jaffe
Teach Me Dirty by Jade West
Running Scarred by Jackie Williams
