The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (665 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
5.59Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Dign
 ga
ga
or Di
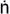
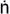
 ga
ga
.
 ga
gaor Di
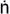
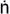
 ga
ga.
Buddhist logician who flourished towards the end of the 5th cent. CE. His greatest work is the
Pram

 a-samuccaya
a-samuccaya
which combines many of his earlier insights into a complete system of epistemology.
Pram

 a-samuccaya
a-samuccayawhich combines many of his earlier insights into a complete system of epistemology.
D
 k
k
 a
a
 k
k a
a(Skt.). Initiation; in Indian religions, the means of access into a religious tradition, religious or social condition. D
 k
k
 a is given by the preceptor or
a is given by the preceptor or
guru
and often involves the giving of a new name to the initiate which symbolizes the end of one condition and birth or entrance into a new.
In Hinduism, in the
Vedas
, d
 k
k
 a was a necessary prerequisite for the
a was a necessary prerequisite for the
soma
sacrifice undergone by the sacrificer (
yajam
 na
na
) and his wife, involving asceticism (
tapas
) and fasting. In the
Upani
 ads
ads
, initiation into an ascetic life involves undergoing hunger, thirst, and abstention from all pleasure (
Chandogya Upani
 ad
ad
3. 17. 2). The importance of d
 k
k
 a carries on into classical and medieval Hinduism where subtraditions within the central traditions of
a carries on into classical and medieval Hinduism where subtraditions within the central traditions of
Vai

 avism
avism
,
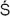 aivism
aivism
, and
Tantrism
all required d
 k
k

 k
k a is given by the preceptor or
a is given by the preceptor orguru
and often involves the giving of a new name to the initiate which symbolizes the end of one condition and birth or entrance into a new.
In Hinduism, in the
Vedas
, d
 k
k a was a necessary prerequisite for the
a was a necessary prerequisite for thesoma
sacrifice undergone by the sacrificer (
yajam
 na
na) and his wife, involving asceticism (
tapas
) and fasting. In the
Upani
 ads
ads, initiation into an ascetic life involves undergoing hunger, thirst, and abstention from all pleasure (
Chandogya Upani
 ad
ad3. 17. 2). The importance of d
 k
k a carries on into classical and medieval Hinduism where subtraditions within the central traditions of
a carries on into classical and medieval Hinduism where subtraditions within the central traditions ofVai

 avism
avism,
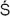 aivism
aivism, and
Tantrism
all required d
 k
k
Other books
NoWayOut by NiaKFoxx
If Nobody Speaks of Remarkable Things by Jon McGregor
Assigned a Guardian by Emily Tilton
Diane Arbus by Patricia Bosworth
Dualed by Elsie Chapman
Luke (Bear Shifter) (New World Shifters) by Elodie Chase
The Filter Trap by Lorentz, A. L.
The Sweetest Seduction, Breakaway Hearts by Crista McHugh


