The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (2371 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
13.47Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Sunday
.
.
As the Christian weekly day of worship it may perhaps be attested in the New Testament (Acts 20. 7; Revelations 1. 10: see
LORD'S DAY
), but emerges clearly in Rome in the 2nd cent. It was early understood as a weekly commemoration of Christ's resurrection on the first day of the week, but it may also owe something to the early Christians' desire to distance themselves from Jewish customs and worship on a day other than the
Sabbath
.
LORD'S DAY
), but emerges clearly in Rome in the 2nd cent. It was early understood as a weekly commemoration of Christ's resurrection on the first day of the week, but it may also owe something to the early Christians' desire to distance themselves from Jewish customs and worship on a day other than the
Sabbath
.
Sundo
(Chin., Shun-tao). The first Buddhist missionary to Kogury
 , in Korea. Sundo travelled to Kogury
, in Korea. Sundo travelled to Kogury
 in 372, the second year of King Sosurim's reign (371–84), with an envoy dispatched by King Fu Chien (r. 357–85) of the Former Ch’in dynasty (351–94), presenting Buddhist images and scriptures to the Kogury
in 372, the second year of King Sosurim's reign (371–84), with an envoy dispatched by King Fu Chien (r. 357–85) of the Former Ch’in dynasty (351–94), presenting Buddhist images and scriptures to the Kogury
 court. (Another tradition holds that Sundo came from the Eastern Ch’in (317–420) rather than the Former Ch’in.) In either case, this event is regarded as the first introduction of Buddhism to Korea.
court. (Another tradition holds that Sundo came from the Eastern Ch’in (317–420) rather than the Former Ch’in.) In either case, this event is regarded as the first introduction of Buddhism to Korea.
 , in Korea. Sundo travelled to Kogury
, in Korea. Sundo travelled to Kogury in 372, the second year of King Sosurim's reign (371–84), with an envoy dispatched by King Fu Chien (r. 357–85) of the Former Ch’in dynasty (351–94), presenting Buddhist images and scriptures to the Kogury
in 372, the second year of King Sosurim's reign (371–84), with an envoy dispatched by King Fu Chien (r. 357–85) of the Former Ch’in dynasty (351–94), presenting Buddhist images and scriptures to the Kogury court. (Another tradition holds that Sundo came from the Eastern Ch’in (317–420) rather than the Former Ch’in.) In either case, this event is regarded as the first introduction of Buddhism to Korea.
court. (Another tradition holds that Sundo came from the Eastern Ch’in (317–420) rather than the Former Ch’in.) In either case, this event is regarded as the first introduction of Buddhism to Korea.Sunna
(Arab., ‘custom’). Customary practice which, in Islam, may refer to both bad and good examples in the past. But supremely the sunna refers to the way in which the Prophet Mu
 ammad and his Companions (
ammad and his Companions (
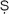 ah
ah
 ba
ba
) lived, and to what they said and did (attending also to that concerning which they were silent). Thus Qur’
 n is the fundamental authority, but the sunna forms the first living commentary on what Qur’
n is the fundamental authority, but the sunna forms the first living commentary on what Qur’
 n means, and thus becomes equally the foundation for Muslim life: the
n means, and thus becomes equally the foundation for Muslim life: the
sunnat al-nab
 , the ‘example of the prophet’, controls Muslim life even in small details. Non-Shi‘ite Muslims are therefore known as
, the ‘example of the prophet’, controls Muslim life even in small details. Non-Shi‘ite Muslims are therefore known as
Ahl al-Sunna wa’l-jam
 ‘a
‘a
, the people of the sunna and of the gathered assembly, i.e. Sunnis. Shi‘ites (
Sh
 ‘a
‘a
) share most of the sunna with them, but place emphasis on the role of the Im
 m in guiding the community, and they also accuse Sunnis of suppressing
m in guiding the community, and they also accuse Sunnis of suppressing
 ad
ad
 th
th
which support Sh
 ‘a beliefs and practices.
‘a beliefs and practices.
 ammad and his Companions (
ammad and his Companions (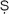 ah
ah ba
ba) lived, and to what they said and did (attending also to that concerning which they were silent). Thus Qur’
 n is the fundamental authority, but the sunna forms the first living commentary on what Qur’
n is the fundamental authority, but the sunna forms the first living commentary on what Qur’ n means, and thus becomes equally the foundation for Muslim life: the
n means, and thus becomes equally the foundation for Muslim life: thesunnat al-nab
 , the ‘example of the prophet’, controls Muslim life even in small details. Non-Shi‘ite Muslims are therefore known as
, the ‘example of the prophet’, controls Muslim life even in small details. Non-Shi‘ite Muslims are therefore known asAhl al-Sunna wa’l-jam
 ‘a
‘a, the people of the sunna and of the gathered assembly, i.e. Sunnis. Shi‘ites (
Sh
 ‘a
‘a) share most of the sunna with them, but place emphasis on the role of the Im
 m in guiding the community, and they also accuse Sunnis of suppressing
m in guiding the community, and they also accuse Sunnis of suppressing ad
ad th
thwhich support Sh
 ‘a beliefs and practices.
‘a beliefs and practices.Other books
Duchess of Milan by Michael Ennis
The Idea of Home by Geraldine Brooks
Feathers in the Wind by Sally Grindley
Magic and Loss: A Novel of Golgotham by Collins, Nancy A.
Dominating Cassidy by Sam Crescent
Adventures of Tom Sawyer (Barnes & Noble Classics Series) by Mark J. Twain
Sophia by Michael Bible
The Healing by David Park
Riding with the Bad Boy (A Dark Motorcycle Club Romance) by Russell, Emma
HeartbeatofSilence by Viola Grace


