Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 (74 page)
Read Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 Online
Authors: Judith A. Muschla,Gary Robert Muschla,Erin Muschla-Berry
Tags: #Education, #Teaching Methods & Materials, #Mathematics, #General

Modeling Multiplication of Fractions
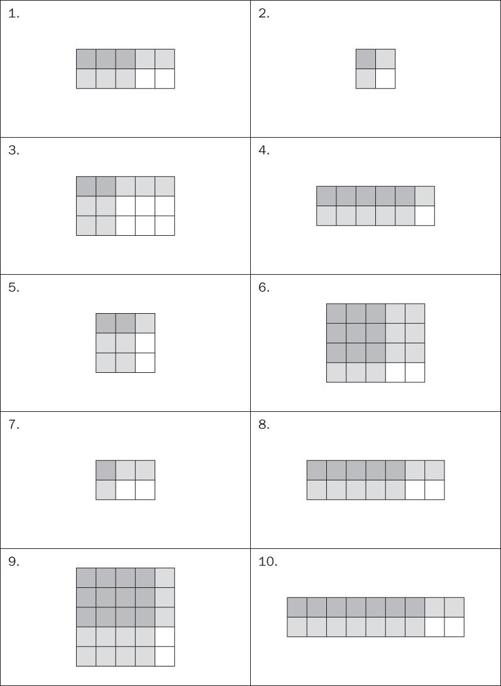
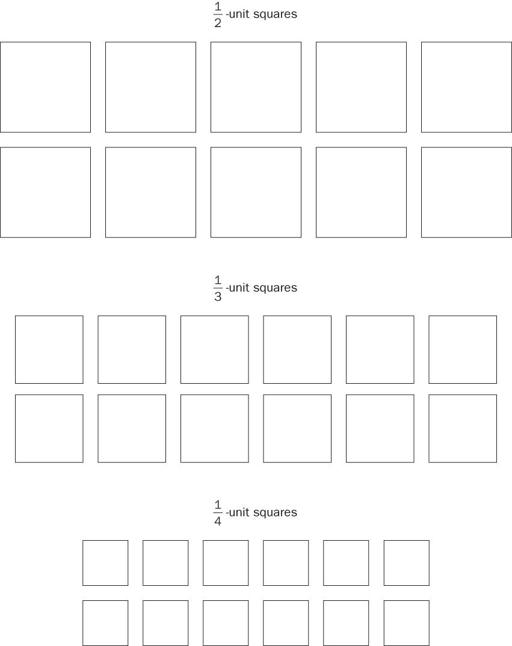
Unit Squares for Constructing Rectangles
Number and Operations—Fractions: 5.NF.5
“Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division to multiply and divide fractions.”
5. “Interpret multiplication as scaling (resizing) by:
a.
“Comparing the size of a product to the size of one factor on the basis of the size of the other factor, without performing the indicated multiplication.
b.
“Explaining why multiplying a given number by a fraction greater than 1 results in a product greater than the given number (recognizing multiplication by whole numbers greater than 1 as a familiar case); explaining why multiplying a given number by a fraction less than 1 results in a product smaller than the given number; and relating the principle of fraction equivalenceto the effect of multiplying
by 1.”
Background
Multiplication is often thought of as a process of repeated addition of the same number that results in a number greater than the numbers multiplied. While this interpretation of multiplication works well for the counting numbers, it does not work for all numbers, particularly when multiplying a given number by a fraction less than 1. In this case, the product will be less than the given number.
Here is an example. If we multiply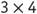 , we can easily see that this is the same as adding
, we can easily see that this is the same as adding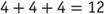 . But when multiplying
. But when multiplying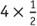 , the product is 2, which is obviously less than 4.
, the product is 2, which is obviously less than 4.
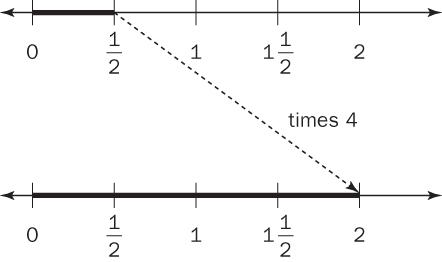
Scaling, which can be thought of as resizing, addresses this problem. A number line can be used for illustrating this. Using the example of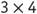 , think of 4 units that are stretched (resized) to be 3 times their original size. On the number line, the original 4 units will have the length of 12 units because they are scaled by a factor of 3.
, think of 4 units that are stretched (resized) to be 3 times their original size. On the number line, the original 4 units will have the length of 12 units because they are scaled by a factor of 3.
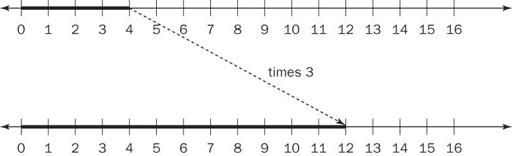
This method also works when multiplying a number by a fraction. Using the example of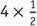 , scaling
, scaling by a factor of 4 results in 2.
by a factor of 4 results in 2.
Activity: Scaling Numbers for Multiplication