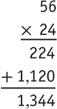Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 (28 page)
Read Teaching the Common Core Math Standards With Hands-On Activities, Grades 3-5 Online
Authors: Judith A. Muschla,Gary Robert Muschla,Erin Muschla-Berry
Tags: #Education, #Teaching Methods & Materials, #Mathematics, #General

5.
Caution students to round their numbers correctly. They should arrive at a consensus for their answers before they begin their posters.
6.
Encourage them to be creative but accurate. Their posters should clearly detail the steps for rounding with their example problems.
7.
Collect the posters at the end of class.
Day Two
1.
Hand the posters back to each group.
2.
Provide a few minutes for students to organize their presentations.
Closure
Have each group share their posters with the class and explain how they rounded their numbers. The posters should serve as visual aids.
Answers
(1)
8,600; 26,750
(2)
4,680; 73,200
(3)
9,030; 91,000
(4)
14,800; 9,000
(5)
4,960; 35,000
(6)
75,000; 6,300
(7)
96,000; 8,500
(8)
42,080; 8,000
(9)
54,900; 4,800
(10)
19,800; 7,000
Number and Operations in Base Ten: 4.NBT.4
“Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic.”
4. “Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.”
Background
The most efficient way to add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers is to line up the digits according to place value. Students should start with the ones, and then work with the tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on. They should regroup, if necessary. To make sure that an answer makes sense, students should estimate their answer before adding or subtracting, and then compare their answer with their estimate.
Activity: A Numbers Chain
Working in pairs or groups of three, students will complete addition and subtraction problems whose answers are related in a chain.
Materials
Scissors; glue sticks; reproducible, “Sums and Differences,” for each pair or group of students.
Procedure
1.
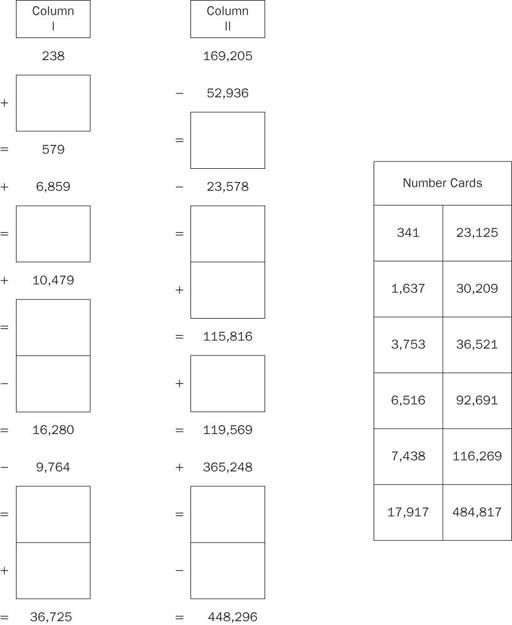
Distribute copies of the reproducible. Explain that Column I and Column II show numbers; addition, subtraction, and equal symbols; and empty boxes. On the right side of the reproducible is a column of number cards.
2.
Explain that students are to cut out the number cards. They are to place the number cards in the empty boxes of the first column so that the column continues as a chain and ends equaling 36,725. They are to do the same with the second column, although this time the chain ends with 448,296.
3.
Instruct your students to place each of the number cards in its correct box in either Column I or Column II. They are then to glue the cards in their appropriate boxes.
Closure
Discuss students' answers and the strategies they used to complete the chains.
Answers
Column I: 341; 7,438; 17,917; 1,637; 6,516; 30,209 Column II: 116,269; 92,691; 23,125; 3,753; 484,817; 36,521
Sums and Differences
Number and Operations in Base Ten: 4.NBT.5
“Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic.”
5. “Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.”
Background
Multiplication is a process in which numbers are multiplied according to place value. Following is an example:
1.
Multiply by the 4 ones.. This is the same as 4 groups of 56.
2.
Multiply by the 2 tens.. This is the same as 20 groups of 56.
3.
Add the partial products..
Activity 1: Finding Errors in Multiplication
Students will find and correct errors in multiplication problems. Then they will select one incorrect problem, write the correct product, and explain the procedure for finding the product using place value.
Materials
One copy of reproducible, “Finding Errors,” for each student.
Procedure
1.
Review the process of multiplication with your students.
2.
Hand out copies of the reproducible. Explain that it contains 12 problems. Some problems are correct, but others have errors. Students are to find the errors in the incorrect problems and correct them.
3.
Explain that after correcting the problems, students are to choose one of the problems they corrected and write an explanation of how to find the correct product using place value.
Closure
Discuss which problems were incorrect and how to correct them. Ask for volunteers to share the problems they chose and the explanations they provided for finding the products.
Answers
Numbers 1, 4, 6, and 11 are correct. The answers to the incorrect problems follow:
(2)
16,394
(3)
7,792
(5)
432
(7)
1,400
(8)
2,304
(9)
2,035
(10)
2,976
(12)
1,073. Explanations for finding the correct product using place value will vary.
Activity 2: Stepping Forward with Multiplication
Working in groups, students will select two multiplication problems, find their products, and illustrate the process of multiplication.
Materials
Rulers; markers; crayons; large drawing paper for each group.
Procedure
1.
Explain to your students that they are to provide two multiplication problems of their own. One is to be a four-digit number multiplied by a one-digit number, and the other is to be a two-digit number multiplied by a two-digit number. Two examples areand
.