Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness (170 page)
Read Ross & Wilson Anatomy and Physiology in Health and Illness Online
Authors: Anne Waugh,Allison Grant
Tags: #Medical, #Nursing, #General, #Anatomy

Atopic dermatitis
is associated with allergy and commonly affects atopic individuals, i.e. those prone to hypersensitivity disorders (
p. 374
). Children, who may also suffer from hay fever or asthma (
pp. 254
and
256
), are often affected.
Contact dermatitis
may be caused by:
•
direct contact with irritants, e.g. cosmetics, soap, detergent, strong acids or alkalis, industrial chemicals
•
a hypersensitivity reaction (see
Fig. 15.8, p. 377
) to, e.g., latex, nickel, dyes and other chemicals.
Psoriasis
This condition is genetically determined and characterised by exacerbations and periods of remission of varying duration. It is common, especially between the ages of 15 and 40 years. Cells of the basal layers of the epidermis proliferate and the more rapid upward progress of these cells through the epidermis results in incomplete maturation of the upper layer. The skin is shiny, silver coloured and scaly. Bleeding may occur when scales are scratched or rubbed off. The elbows, knees and scalp are common sites but other parts can also be affected. Trigger factors that lead to exacerbation of the condition include trauma, infection and sunburn. Sometimes psoriasis is associated with arthritis (
p. 423
).
Acne vulgaris
This is commonest in adolescent males and is thought to be caused by increased levels of testosterone after puberty. Sebaceous glands in hair follicles become blocked and then infected, leading to inflammation and pustule formation. In severe cases permanent scarring may result. The most common sites are the face, chest and upper back.
Pressure ulcers
Also known as
decubitus ulcers
or
bedsores
, these occur over ‘pressure points’, areas where the skin may be compressed for long periods between a bony prominence and a hard surface, e.g. a bed or chair. When this occurs, blood flow to the affected area is impaired and ischaemia develops. Initially the skin reddens, and later as ischaemia and necrosis occur the skin sloughs and an ulcer forms that may then enlarge into a cavity. If infection occurs, this can result in septicaemia. Healing takes place by secondary intention (
p. 359
).
Predisposing factors
These may be:
•
extrinsic, e.g. pressure, shearing forces, trauma, immobility, moisture, infection
•
intrinsic, e.g. poor nutritional status, emaciation, incontinence, infection, concurrent illness, sensory impairment, poor circulation, old age.
Burns
These may be caused by many types of trauma including: heat, cold, electricity, ionising radiation and corrosive chemicals, including strong acids or alkalis.
Local damage occurs disrupting the structure and functions of the skin. Infection is a common complication of any burn as the outer barrier formed by the epidermis is lost.
Burns are classified according to their depth:
•
first degree
when only the epidermis is involved, the surface is moist and there are signs of inflammation including redness, swelling and pain. There are no blisters.
•
second degree
when the epidermis and upper dermis are affected. In addition to the signs and symptoms above, blistering is usually present.
•
third degree
(deep) when the epidermis and dermis are destroyed. These burns are usually relatively painless as the sensory nerve endings in the dermis are destroyed. After a few days the destroyed tissue coagulates and forms an
eschar
, or thick scab, which sloughs off after 2 to 3 weeks. In
circumferential burns
, which encircle any area of the body, complications may arise from constriction of the part by eschar, e.g. respiratory impairment may follow circumferential burns of the chest, or the circulation to the distal part of an affected limb may be seriously impaired. Skin grafting is required except for small injuries.
Otherwise, healing, which is prolonged, occurs by secondary intention (
p. 359
) and there is no regeneration of sweat glands, hair follicles or sebaceous glands. Resultant scar tissue often limits movement of affected joints.
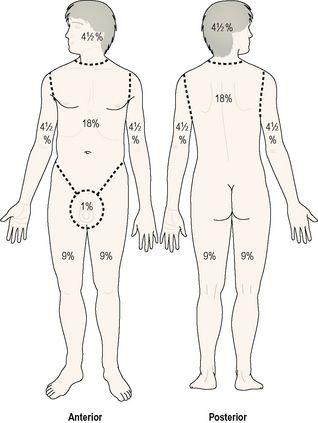
The extent of burns in adults is roughly estimated using the ‘rule of nines’ (
Fig. 14.10
). In adults, hypovolaemic shock usually develops when 15% of the surface area is affected. Fatality is likely in adults with third degree burns if the surface area affected is added to the patient’s age and the total is greater than 80.
Figure 14.10
The ‘rule of nines’ for estimating the extent of burns in adults.
Complications of burns
Although burns affect the skin, when extensive, their systemic consequences can also be life-threatening or fatal.
Dehydration and hypovolaemia
These may occur in extensive burns due to excessive leakage of water and plasma proteins from the surface of the damaged skin.
Shock
This may accompany severe hypovolaemia.
Hypothermia
This develops when excessive heat is lost.
Infection
This may result in septicaemia.
Renal failure
This occurs when the kidney tubules cannot deal with the amount of waste from haemolysed erythrocytes and damaged tissue.
Contractures
These may develop later as fibrous scar tissue contracts distorting the limbs, e.g. the hands, and impairing function.
Malignant tumours
Basal cell carcinoma
This is the least malignant and most common type of skin cancer. It is associated with long-term exposure to sunlight and is therefore most likely to occur on sun-exposed sites, usually the head or neck. It appears as a shiny nodule and later this breaks down, becoming an ulcer with irregular edges, commonly called a
rodent ulcer
. This is locally invasive but seldom metastasises.
Malignant melanoma
This is malignant proliferation of melanocytes, usually originating in a mole that may have an irregular outline. It may ulcerate and bleed and most commonly affects young and middle-aged adults. Predisposing factors are a fair skin and recurrent episodes of intensive exposure to sunlight including repeated episodes of sunburn, especially in childhood. Sites for this tumour show a gender bias, with the lower leg being the commonest site in females and the torso being a common site in males. Metastases usually develop early and are frequently found in lymph nodes. The most common sites of blood-spread metastases are the liver, brain, lungs, bowel and bone marrow.
Kaposi’s sarcoma
In this rare condition, a malignant tumour arises in the walls of lymphatic vessels. A small red-blue patch or nodule develops, usually on the lower limbs.
It is also an AIDS-related disease and has thus become more common. In such cases, multiple lesions may occur and affect many sites of the body.
For a range of self-assessment exercises on thetopics in this chapter, visit
www.rossandwilson.com
.
CHAPTER 15
Resistance and immunity
Non-specific defence mechanisms
366
Defence at body surfaces
366
Phagocytosis
366
Natural antimicrobial substances
366
The inflammatory response
367
Immunological surveillance
369
Immunity
369
Cell-mediated immunity
370
Antibody-mediated (humoral) immunity
371
Acquired immunity
372
Abnormal immune function
374
Hypersensitivity (allergy)
374
Autoimmune diseases
374
Immunodeficiency
376
ANIMATIONS