Essential Facts on the Go: Internal Medicine (2 page)
Read Essential Facts on the Go: Internal Medicine Online
Authors: Lauren Stern,Vijay Lapsia
Tags: #Medical, #Family & General Practice, #Internal Medicine

Included in these quick reference cards that you can carry with you in the hospital and the clinic are about 75 different topics ranging from Supraventricular Tachycardia to Venous Thromboembolism to Abdominal Pain to Acute Kidney Injury to Hyperkalemia to Diabetic Ketoacidosis to Opportunistic Infections in HIV to Arthritis to Seizures to Oncologic Emergencies. All topics are presented in ways uniquely suited to learning on the go.
Lauren Stern, MD
Vijay Lapsia, MBBS, MD
CARDIOVASCULAR
I_1_a Supraventricular Tachycardia
Atrial flutter
Atrial fibrillation
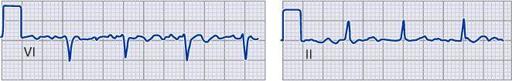
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
Pattern of atrial and ventricular activation and characteristic relationship of P-wave and QRS complex
Reproduced with permission from Longo DL, et al.
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
, 18th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2012.
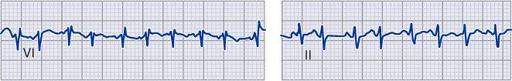
I_1_b Supraventricular Tachycardia
WPW pre-excitation pattern
, with triad of short PR, wide QRS, and delta waves. Polarity of the delta waves (slightly positive in leads V
1
and V
2
and most positive in lead II and lateral chest leads) is consistent with a right-sided bypass tract.
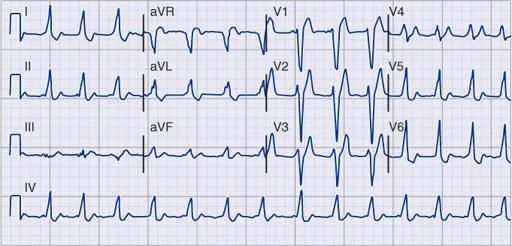
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block.
P-wave rate is about 150/min, with ventricular (QRS) rate of about 75/min. The nonconducted (“extra”) P waves just after the QRS complex are best seen in lead V
1
. Also, note incomplete RBBB and borderline QT prolongation.

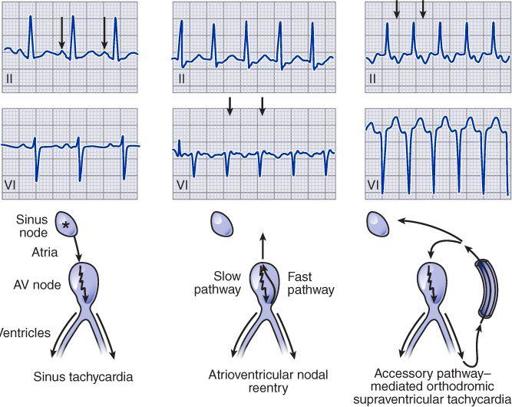
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
(AVNRT) at a rate of 150/min. Note subtle “pseudo” R waves in lead aVR due to retrograde atrial activation, which occurs nearly simultaneously with ventricles in AVNRT. Left-axis deviation consistent with left anterior fascicular block (hemiblock) is also present.

I_2_a
ACLS: Ventricular Tachycardia/Fibrillation
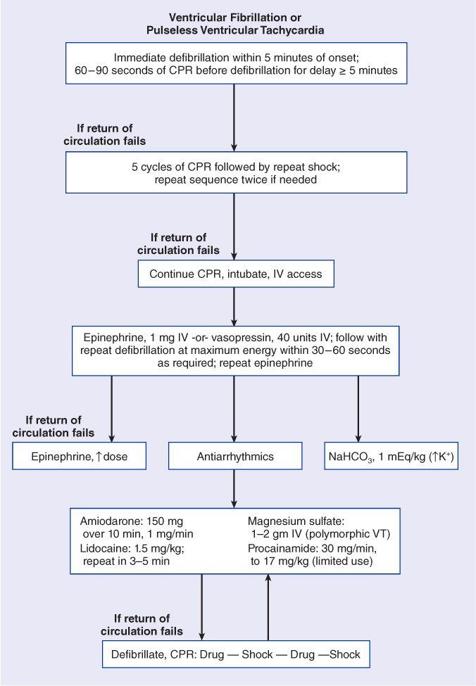
Reproduced with permission from Longo DL, et al.
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
, 18th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2012.
I_2_b
ACLS: Bradyarrhythmia/Asystole/Pulseless Electrical Activitiy
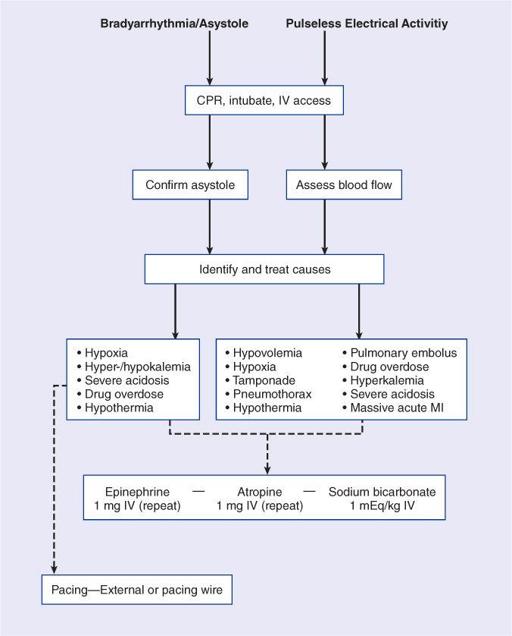
Reproduced with permission from Longo DL, et al.
Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine
, 18th ed. McGraw-Hill, 2012.
I_3_a
Bradyarrhythmias
Sinus slowing and pauses on the ECG
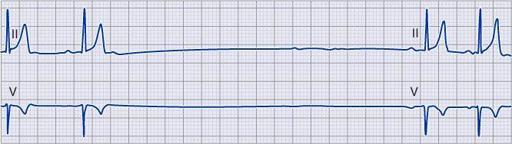
Mobitz type I SA nodal exit block
High-grade AV block
- Multiple nonconducted P waves with a regular narrow complex QRS escape from the AV junction
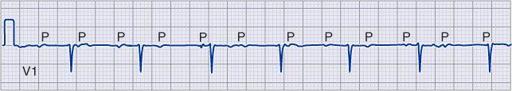
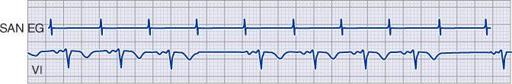
Marked junctional bradycardia
(25 beats/min)

