Concise Oxford Dictionary of Archaeology (764 page)
Read Concise Oxford Dictionary of Archaeology Online
Authors: Timothy Darvill

BOOK: Concise Oxford Dictionary of Archaeology
6.26Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
UV-VIS
[Ab].
[Ab].
Uxmal, Mexico
[Si].
[Si].
Late Classic and early Post-Classic Stage ceremonial centre flourishing in the Yucatan Peninsula in the period ad 800–1000. Best known for its impressive Puuc style architecture.There are at least three main structures: the pyramid of the Magician, the Monjas, and the Governor's Palace. The Monjas comprises a huge patio surrounded on all four sides by a range of single-room cell blocks. Uxmal was connected by a causeway (
sacbe
) to the site of Kabáh.
[Rep.: J. K. Kowalski , 1987,
The house of the Governor: A Maya Palace at Uxmal, Yucatan, Mexico
. London: Norman]
sacbe
) to the site of Kabáh.
[Rep.: J. K. Kowalski , 1987,
The house of the Governor: A Maya Palace at Uxmal, Yucatan, Mexico
. London: Norman]
V
V
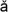 dastra Culture
dastra Culture
[CP].
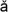 dastra Culture
dastra Culture[CP].
A middle to late Neolithic culture of southwestern Romania and northern Bulgaria, north of the
VESELINOVO CULTURE
, dating to the late 5th millennium
bc
and thus contemporary with stage A–B of the
VIN
 A CULTURE
A CULTURE
of the western Balkans. Named after the type-site tell in the modern village of V
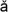 dastra, this culture had a full agricultural economy. Cattle bones from sites of the culture suggest that draught animals were used for traction. Distinctive styles of pottery were made in three main categories: poorly fired coarse tempered wares for storage; decorated bowls in a medium quality ware; and thin-walled rather fine pottery fired grey or black in colour decorated with narrow channelling or fluting.
dastra, this culture had a full agricultural economy. Cattle bones from sites of the culture suggest that draught animals were used for traction. Distinctive styles of pottery were made in three main categories: poorly fired coarse tempered wares for storage; decorated bowls in a medium quality ware; and thin-walled rather fine pottery fired grey or black in colour decorated with narrow channelling or fluting.
VESELINOVO CULTURE
, dating to the late 5th millennium
bc
and thus contemporary with stage A–B of the
VIN
 A CULTURE
A CULTUREof the western Balkans. Named after the type-site tell in the modern village of V
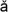 dastra, this culture had a full agricultural economy. Cattle bones from sites of the culture suggest that draught animals were used for traction. Distinctive styles of pottery were made in three main categories: poorly fired coarse tempered wares for storage; decorated bowls in a medium quality ware; and thin-walled rather fine pottery fired grey or black in colour decorated with narrow channelling or fluting.
dastra, this culture had a full agricultural economy. Cattle bones from sites of the culture suggest that draught animals were used for traction. Distinctive styles of pottery were made in three main categories: poorly fired coarse tempered wares for storage; decorated bowls in a medium quality ware; and thin-walled rather fine pottery fired grey or black in colour decorated with narrow channelling or fluting.Valdai Culture
[CP].
[CP].
Early Neolithic period (3500–3000 bc) communities occupying a broad region north of the Upper Volga and Western Dvina rivers in western Russia. Descended from local Mesolithic communities, the Valdai Cultures were hunters and fishers with a flint industry that included many archaic forms such as microlithic tools. Pottery with organic material used as a tempering agent was used, as well as pointed-based vessels with irregularly scattered thin comb impressions and incisions.
Valdivia Culture
[CP].
[CP].
FORMATIVE
period culture dating to the later 4th millennium
bc
on the coast of Ecuador, South America, named after a site of the same name excavated by B. Meggars and C. Evans in the early 1960s. The culture is important in being amongst the earliest in the region to have a developed ceramics industry which used a variety of plastic techniques for decorative motifs. Artefacts suggest a marine-orientated subsistence pattern.
period culture dating to the later 4th millennium
bc
on the coast of Ecuador, South America, named after a site of the same name excavated by B. Meggars and C. Evans in the early 1960s. The culture is important in being amongst the earliest in the region to have a developed ceramics industry which used a variety of plastic techniques for decorative motifs. Artefacts suggest a marine-orientated subsistence pattern.
Other books
A Gentlewoman's Dalliance by Portia Da Costa
Dixie Divas by Brown, Virginia
Legacy of the Highlands by Harriet Schultz
The Name of the Wind by Patrick Rothfuss
Cattle Valley 26 - Shadow Soldier by Carol Lynne
Two Wheels on my Wagon by Paul Howard
To Tempt an Irish Rogue by Kaitlin O'Riley
Dead Stars - Part One (The Emaneska Series) by Ben Galley


