Why People Believe Weird Things: Pseudoscience, Superstition, and Other Confusions of Our Time (21 page)
Authors: Michael Shermer
Tags: #Creative Ability, #Parapsychology, #Psychology, #Epistemology, #Philosophy & Social Aspects, #Science, #Philosophy, #Creative ability in science, #Skepticism, #Truthfulness and falsehood, #Pseudoscience, #Body; Mind & Spirit, #Belief and doubt, #General, #Parapsychology and science

Hugh Trevor-Roper, in
The European Witch-Craze,
demonstrates how suspicions and accusations built upon one another as the scope and intensity of the feedback loop expanded. He provides this example from the county of Lorraine about the frequency of alleged witch meetings: "At first the interrogators . . . thought that they occurred only once a week, on Thursday; but, as always, the more evidence was pressed, the worse the conclusions that it yielded. Sabbats were found to take place on Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Sunday, and soon Tuesday was found to be booked as a by-day. It was all very alarming and proved the need of ever greater vigilance by the spiritual police" (1969, p. 94). It is remarkable how quickly the feedback loop self-organizes into a full-blown witch craze, and interesting to discover what happens to skeptics who challenge the system. Trevor-Roper was appalled by what he read in the historical documents:
To read these encyclopaedias of witchcraft is a horrible experience. Together they insist that every grotesque detail of demonology is true, that scepticism must be stifled, that sceptics and lawyers who defend witches are themselves witches, that all witches, "good" or "bad," must be burnt, that no excuse, no extenuation is allowable, that mere denunciation by one witch is sufficient evidence to burn another. All agree that witches are multiplying incredibly in Christendom, and that the reason for their increase is the indecent leniency of judges, the indecent immunity of Satan's accomplices, the sceptics, (p. 151)
What is especially curious about the medieval witch craze is that it occurred at the very time experimental science was gaining ground and popularity. This is curious because we often think that science displaces superstition and so one would expect belief in things like witches, demons, and spirits to have decreased as science grew. Not so. As modern examples show, believers in paranormal and other pseudoscientific phenomena try to wrap themselves in the mantle of science because science is a dominating force in our society but they still believe what they believe. Historically, as science grew in importance, the viability of all belief systems began to be directly attached to experimental evidence in favor of specific claims. Thus, scientists of the day found themselves investigating haunted houses and testing accused witches by using methods considered rigorous and scientific. Empirical data for the existence of witches would support belief in Satan which, in turn, would buttress belief in God. But the alliance between religion and science was uneasy. Atheism as a viable philosophical position was growing in popularity, and church authorities put themselves in a double-bind by looking to scientists and intellectuals to respond. As one observer at a seventeenth-century witch trial of an Englishman named Mr. Darrell noted, "Atheists abound in these days and witchcraft is called into question. If neither possession nor witchcraft [exists], why should we think that there are devils? If no devils, no God" (in Walker 1981, p. 71).
The Satanic Panic Witch Craze
The best modern example of a witch craze would have to be the "Satanic panic" of the 1980s. Thousands of Satanic cults were believed to be operating in secrecy throughout America, sacrificing and mutilating animals, sexually abusing children, and practicing Satanic rituals. In
The Satanism Scare,
James Richardson, Joel Best, and David Bromley argue persuasively that public discourse about sexual abuse, Satanism, serial murders, or child pornography is a barometer of larger social fears and anxieties. The Satanic panic was an instance of moral panic, where "a condition, episode, person or group of persons emerges to become defined as a threat to societal values and interests; its nature is presented in a stylized and stereotypical fashion by the mass media; the moral barricades are manned by editors, bishops, politicians and other right-thinking people; socially accredited experts pronounce their diagnoses and solutions; ways of coping are evolved or resorted to; the condition then disappears, submerges or deteriorates" (1991, p. 23). Such events are used as weapons "for various political groups in their campaigns" when someone stands to gain and someone stands to lose by the focus on such events and their outcome. According to these authors, the evidence for widespread Satanic cults, witches' covens, and ritualistic child abuse and animal killings is virtually nonexistent. Sure, there is a handful of colorful figures who are interviewed on talk shows or dress in black and burn incense or introduce late-night movies in a pushup bra, but these are hardly the brutal criminals supposedly disrupting society and corrupting the morals of humanity. Who says they are?
The key is in the answer to the question, "Who needs Satanic cults?" "Talk-show hosts, book publishers, anti-cult groups, fundamentalists, and certain religious groups" is the reply. All thrive from such claims. "Long a staple topic for religious broadcasters and 'trash TV' talk shows," the authors note, "satanism has crept into network news programs and prime-time programming, with news stories, documentaries, and made-for-TV movies about satanic cults. Growing numbers of police officers, child protection workers, and other public officials attend workshops supported by tax dollars to receive formal training in combating the satanist menace" (p. 3). Here is the information exchange fueling the feedback loop and driving the witch craze toward higher levels of complexity.
The motive, like the movement, is repeated historically from century to century as a shunt for personal responsibility—fob off your problems on the nearest enemy, the more evil the better. And who fits the bill better than Satan himself, along with his female co-conspirator, the witch? As sociologist Kai Erikson observed, "Perhaps no other form of crime in history has been a better index to social disruption and change, for outbreaks of witchcraft mania have generally taken place in societies which are experiencing a shift of religious focus—societies, we would say, confronting a relocation of boundaries" (1966, p. 153) Indeed, of the sixteenth- and seventeenth-century witch crazes, anthropologist Marvin Harris noted, "The principal result of the witch-hunt system was that the poor came to believe that they were being victimized by witches and devils instead of princes and popes. Did your roof leak, your cow abort, your oats wither, your wine go sour, your head ache, your baby die? It was the work of the witches. Preoccupied with the fantastic activities of these demons, the distraught, alienated, pauperized masses blamed the rampant Devil instead of the corrupt clergy and the rapacious nobility" (1974, p. 205).
Jeffrey Victor's book,
Satanic Panic: The Creation of a Contemporary Legend
(1993), is the best analysis to date on the subject, and the subtitle summarizes his thesis about the phenomenon. Victor traces the development of the Satanic cult legend by comparing it to other rumor-driven panics and mass hysterias and showing how individuals get caught up in such phenomena. Participation involves a variety of psychological factors and social forces, combined with information input from modern as well as historical sources. In the 1970s, there were rumors about dangerous religious cults, cattle mutilations, and Satanic cult ritual animal sacrifices; in the 1980s, we were bombarded by books, articles, and television programs about multiple personality disorder, Procter & Gamble's "Satanic" logo, ritual child abuse, the McMartin Preschool case, and devil worship; and the 1990s have given us the ritual child abuse scare in England, reports that the Mormon Church was infiltrated by secret Satanists who sexually abuse children in rituals, and the Satanic ritual abuse scare in San Diego (see Victor 1993, pp. 24-25). These cases, and many others, drove the feedback loop forward. But now it is reversing. In 1994, for example, Britain's Ministry of Health conducted a study that found no independent corroboration for eyewitness claims of Satanic abuse of children in Britain. According to Jean La Fontaine, a professor from the London School of Economics, "The alleged disclosures of satanic abuse by younger children were influenced by adults. A small minority involved children pressured or coached by their mothers." What was the driving force? Evangelical Christians, suggests La Fontaine: "The evangelical Christian campaign against new religious movements has been a powerful influence encouraging the identification of satanic abuse" (in Shermer 1994, p. 21).
The Recovered Memory Movement as a Witch Craze
A frightening parallel to the medieval witch crazes is what has come to be known as the "recovered memory movement." Recovered memories are alleged memories of childhood sexual abuse repressed by the victims but recalled decades later through use of special therapeutic techniques, including suggestive questioning, hypnosis, hypnotic age-regression, visualization, sodium amytal ("truth serum") injections, and dream interpretation. What makes this movement a feedback loop is the accelerating rate of information exchange. The therapist usually has the client read books about recovered memories, watch videotapes of talk shows on recovered memories, and participate in group counseling with other women with recovered memories. Absent at the beginning of therapy, memories of childhood sexual abuse are soon created through weeks and months of applying the special therapeutic techniques. Then names are named— father, mother, grandfather, uncle, brother, friends of father, and so on. Next is confrontation with the accused, who inevitably denies the charges, and termination of all relations with the accused. Shattered families are the result (see Hochman 1993).
Experts on both sides of this issue estimate that at least one million people have "recovered" memories of sexual abuse since 1988 alone, and this does not count those who really were sexually abused and never forgot it (Crews et al. 1995; Loftus and Ketcham 1994; Pendergrast 1995). Writer Richard Webster, in his fascinating
Why Freud Was Wrong
(1995), traces the movement to a group of psychotherapists in the Boston area who in the 1980s, after reading psychiatrist Judith Herman's 1981 book,
Father-Daughter Incest,
formed therapy groups for incest survivors. Since sexual abuse is a real and tragic phenomenon, this was an important step in bringing it to the attention of society. Unfortunately, the idea that the subconscious is the keeper of repressed memories was also proffered, based on Herman's description of one woman whose "previously repressed memories" of sexual abuse were reconstructed in therapy. In the beginning, membership mostly consisted of those who had always remembered their abuse. But gradually, Webster notes, the process of therapeutic memory reconstruction entered the sessions.
In their pursuit of the hidden memories which supposedly accounted for the symptoms of these women, therapists sometimes used a form of time-limited group therapy. At the beginning of the ten or twelve weekly sessions, patients would be encouraged to set themselves goals. For many patients without memories of incest the goal was to recover such memories. Some of them actually defined their goal by saying "I just want to be in the group and feel I belong." After the fifth session the therapist would remind the group that they had reached the middle of their therapy, with the clear implication that time was running out. As pressure was increased in this way women with no memories would often begin to see images of sexual abuse involving father or other adults, and these images would then be construed as memories or "flashbacks." (1995, p. 519)
The feedback loop for the movement now began to self-organize, encouraged by psychotherapist Jeffrey Masson's 1984 book,
The Assault on Truth,
in which he rejected Freud's claim that childhood sexual abuse was fantasy and argued that Freud's initial position—that the sexual abuse so often recounted by his patients was actual, rampant, and responsible for adult women's neuroses—was the correct one. The movement became a full-blown witch craze when Ellen Bass and Laura Davis published
The Courage to Heal: A Guide for Women Survivors of Child Sexual Abuse
in 1988. One of its conclusions was "If you think you were abused and your life shows the symptoms, then you were" (p. 22). The book sold more than 750,000 copies and triggered a recovered memory industry that involved dozens of similar books, talk-show programs, and magazine and newspaper stories.
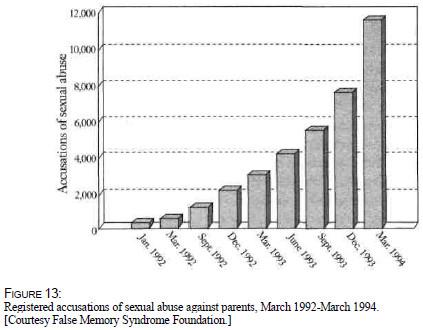
The controversy over recovered versus false memories still rages among psychologists, psychiatrists, lawyers, the media, and the general public. Because childhood sexual abuse does happen, and probably more frequently than any of us like to think, much is at stake when accusations made by the alleged victims themselves are discounted. But what we appear to be experiencing with the recovered memory movement is not an epidemic of childhood sexual abuse but an epidemic of accusations (see figure 13). It's a witch craze, not a sex craze. The supposed numbers alone should make us skeptical. Bass and Davis and others estimate that as many as one-third to one-half of all women were sexually abused as children. Using the conservative percentage, this means that in America alone 42.9 million women were sexually abused. Since they have to be abused by someone, this means about 42.9 million men are sex offenders, bringing us to a total of 85.8 million Americans. Additionally, many of these cases allegedly involve mothers who consent and friends and relatives who participate. This would push the figure to over 100 million Americans (about 38 percent of the entire population) involved in sexual abuse. Impossible. Impossible even if we cut that estimate in half. Something else is going on here.
