Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (933 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
3.03Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
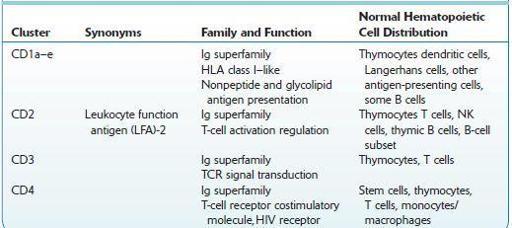
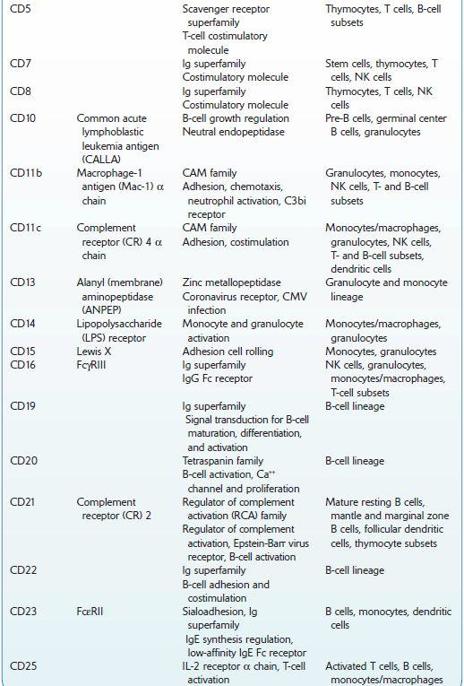
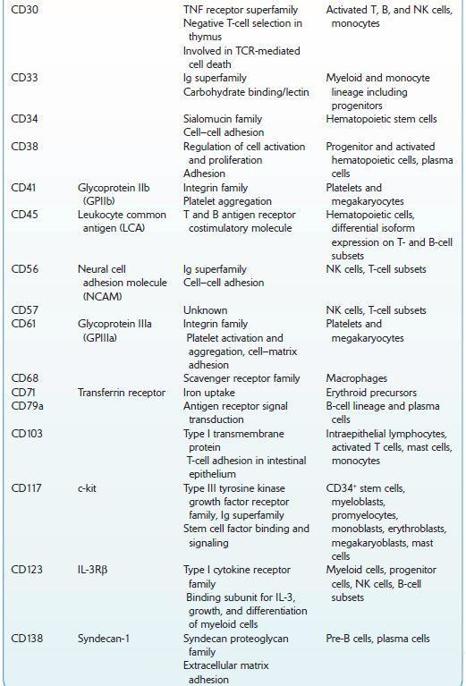
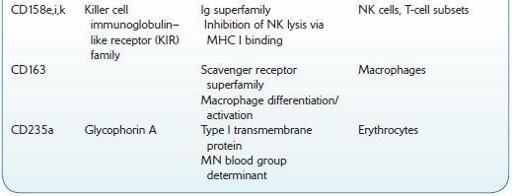
Commonly Used Cluster of Differentiation (CD) Antigens
FOLATE, SERUM AND ERYTHROCYTES (RBCs)
Definition
Folate refers to all derivatives of folic acid. Folate is an essential vitamin present in a wide variety of foods such as dark leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, yeast, beans, eggs, and milk. Folate is vital to normal cell growth and DNA synthesis. A folate deficiency can lead to megaloblastic anemia and ultimately to severe neurologic problems. Folate levels in both serum and RBCs are used to assess folate status. The serum folate level is an indicator of recent folate intake. RBC folate is the best indicator of long-term folate stores. A low RBC folate value may indicate a prolonged folate deficiency. Other names: vitamin B
9
.

Normal range:
Serum folate: >6.5 ng/mL
RBC folate: 280–903 ng/mL
Use
Evaluation of folate deficiency
Interpretation
Increased In
Blind loop syndrome
Other books
The F- It List by Julie Halpern
Unzipped by Lois Greiman
Silence of Scandal by Jackie Williams
Tristan (The Kendall Family #1) by Randi Everheart
Imprudence by Gail Carriger
Just Good Friends by Ruth Ann Nordin
The Education of a Very Young Madam by Ma-Ling Lee
Tailored for Trouble: A Romantic Comedy (Happy Pants) by Mimi Jean Pamfiloff
Badass: Deadly Target (Complete): Military Romantic Suspense by Leslie Johnson, Elle Dawson
The Burning Time by Robin Morgan
