Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (910 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
5.51Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Estrogens are involved in development and maintenance of the female phenotype, germ cell maturation, and pregnancy. They also are important for many other, non–gender-specific processes, including growth, nervous system maturation, bone metabolism/remodeling, and endothelial responsiveness. The two major biologically active estrogens in nonpregnant humans are estrone (E
1
) and estradiol (E
2
). A third bioactive estrogen, estriol (E
3
), is the main pregnancy estrogen but plays no significant role in nonpregnant women or men.

Normal range:
see Table 16.31.
TABLE 16–31. Normal Ranges of Estrogens
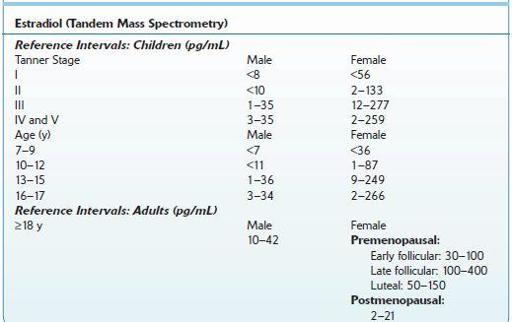
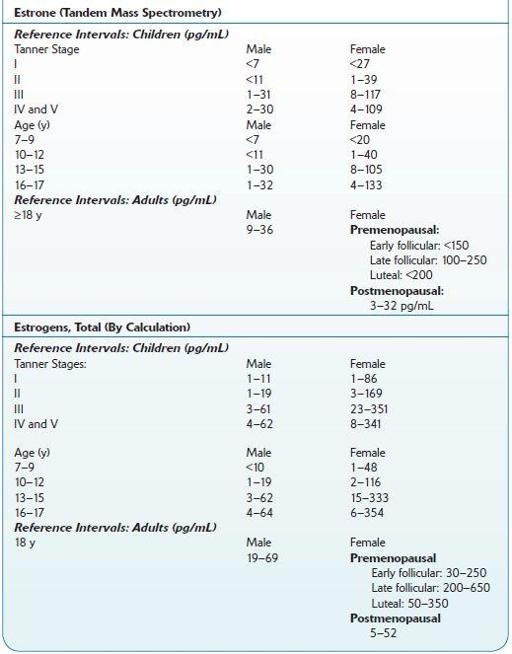
Use
Overall status of estrogens in females or males
Must be interpreted according to phase of the menstrual cycle
Interpretation
Increased In
Estrogen-producing tumors (e.g., granulosa cell tumor, theca-cell tumor, luteoma), secondary to stimulation by hCG-producing tumors (e.g., teratoma, teratocarcinoma)
Pregnancy
Gynecomastia
Decreased In
Ovarian failure
Primary hypofunction of the ovary:
Autoimmune oophoritis is the most common cause; usually associated with other autoimmune endocrinopathies (e.g., Hashimoto thyroiditis, Addison disease, type 1 DM); may cause premature menopause
Other books
Forged by Fire by Sharon M. Draper
Acid Dreams: The Complete Social History of LSD by Martin A. Lee, Bruce Shlain
Wolf Tickets by Banks, Ray
Fake: The Scarab Beetle Series: #3 (The Academy) by Stone, C. L.
Imaginary Grace by Anne Holster
RUNAWAY TWINS (Runaway Twins series #1) by Palamountain, Pete
The Bad Decisions Playlist by Michael Rubens
Offa and the Mercian Wars by Chris Peers
Lost Alpha: Collection (bbw werewolf/shifter romance) by Jessic Ryan
Dead on Cue by Sally Spencer
