Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (709 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
13.58Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Definition
A compound used to prevent or treat seizures
Classic agents: carbamazepine (Tegretol), phenobarbital (Luminal), phenytoin (Dilantin), ethosuximide (Zarontin), valproic acid (Depakene, Depakote). Newer agents gabapentin (Neurontin), lamotrigine (Lamictal), oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), vigabatrin (Sabril), topiramate (Topamax), zonisamide (Zonegran)
Use
Treatment of seizure disorders

Normal therapeutic levels:
see Table 16.7
Limitations
Phenobarbital may be detected by immunoassay-based screening tests for barbiturates in urine and serum.
Immunoassay tests are available for semiquantitative analysis in serum of topiramate, valproic acid, phenytoin, phenobarbital (may demonstrate significant cross-reactivity with other barbiturates), and zonisamide.
Lamotrigine, breakdown products or artifacts of topiramate, carbamazepine, 10-OH-carbazepine, and phenytoin may be detected in general drug screens in urine or serum that utilize alkaline or weakly acidic liquid- or solid-phase extractions followed by gas chromatography or GC/MS analysis.
TABLE 16–7. Normal Therapeutic Levels of Anticonvulsants
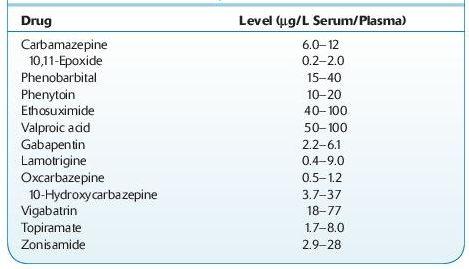
*Submitted By Amanda J. Jenkins, PhD.
For the majority of anticonvulsants, specific tests are required.
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
*
Definition
Other books
First Time Secrets (Vol. 3 – A Time for Everything) by Mason Lee
The Falling of Katja: an Erotic Romance (Anam Céile Chronicles) by Scarlett, Rosalind
The Promise of Provence (Love in Provence Book 1) by Patricia Sands
Missoula by Jon Krakauer
Starlight Dunes by Vickie McKeehan
The Heart Has Reasons by Martine Marchand
What Lies Beneath (Count on Me Series #7) by Melyssa Winchester
Inferno by Adriana Noir
Here by Denise Grover Swank
