Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis (1072 page)
Authors: Mary A. Williamson Mt(ascp) Phd,L. Michael Snyder Md

BOOK: Wallach's Interpretation of Diagnostic Tests: Pathways to Arriving at a Clinical Diagnosis
9.56Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub

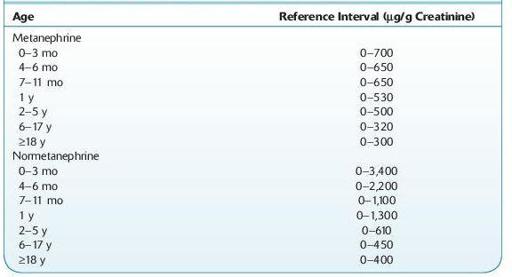
Normal range:
see Table 16.55.
TABLE 16–55. Normal Range for Urine Metanephrines
Use
Confirmation of elevated plasma catecholamine levels
Diagnosis of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma
Diagnosis and follow-up of patients with neuroblastoma and related tumors
First line of test in patients with lower suspicion of pheochromocytoma (patients with resistant hypertension, hyper adrenergic spells, incidentally discovered adrenal mass that does not have imaging characteristics consistent with pheochromocytoma).
Interpretation
Increases occur with catecholamine-secreting neurochromatin tumors such as pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, and neuroblastoma.
Limitations
No caffeine intake should occur before or during collection. MAO inhibitors should be discontinued at least 1 week prior to beginning collection.
Methylglucamine in x-ray contrast medium can cause false-negative test results.
False positives can be caused by stress and drugs, which includes amphetamines and amphetamine-like compounds, appetite suppressants, bromocriptine, buspirone, caffeine, carbidopa–levodopa (Sinemet), clonidine, dexamethasone, diuretics, methyldopa (Aldomet), nose drops, propafenone (Rythmol), tricyclic antidepressants, and vasodilators. The effects of some drugs on catecholamine metabolite results may not be predictable.
Other books
Princely Bastard by Alynn, K. H.
Thursdays in the Park by Hilary Boyd
Bad Things by Tamara Thorne
Long Shot: An MMA Stepbrother Romance by Whitlow, Lexi
A Conflict of Interests by Clive Egleton
Incarnate: Mars Origin "I" Series Book III by Abby L. Vandiver
Chaotic War by Lia Davis
A Matter of Days by Amber Kizer
Reverend Cash: Let Us Prey by Sa'id Salaam
