The Washington Manual Internship Survival Guide (21 page)
Read The Washington Manual Internship Survival Guide Online
Authors: Thomas M. de Fer,Eric Knoche,Gina Larossa,Heather Sateia
Tags: #Medical, #Internal Medicine

•
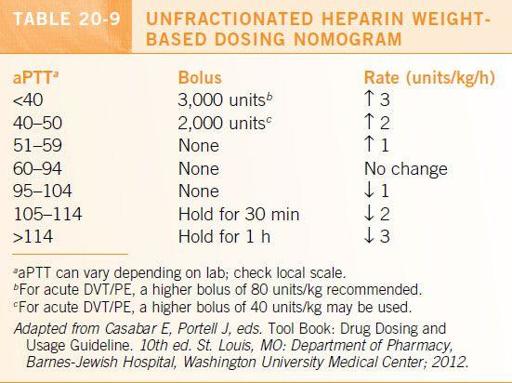
CBC should be monitored every 72 hours while on IV heparin.
•
Dosage adjustments based on aPTT are shown in
Table 20-9
.

Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Dosing
•
Enoxaparin
: 1 mg/kg subcutaneously (SC) q12h (unstable angina, NSTEMI, or venous thromboembolism). For DVT/PE, 1.5 mg/kg q24h is an alternative. If CrCl < 30 mL/min use 1 mg/kg SC q24h.
•
Dalteparin
: 120 units/kg SC q12h (unstable angina or NSTEMI) or 200 units/kg SC q12h (venous thromboembolism).
•
Fondaparinux
(synthetic selective factor Xa inhibitor): 7.5 mg SC q24h (DVT/PE); use 5 mg SC q24h if wt <50 kg, 10 mg SC q24h if wt >100 kg.
•
For all ACS patients, round doses
down
to nearest 10 mg. For all others, round to the nearest 10 mg.
•
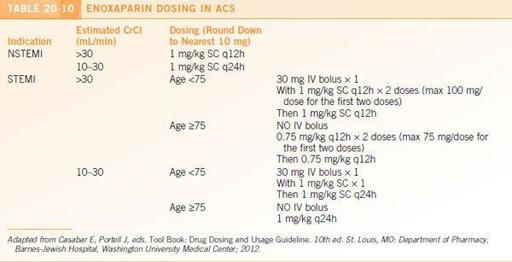
Individual hospitals are likely to have established protocols for LMWH use in ACS. The enoxaparin ACS protocol at Barnes-Jewish Hospital is presented in
Table 20-10
.
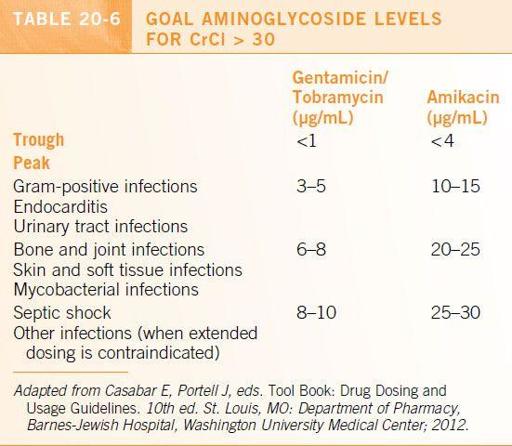

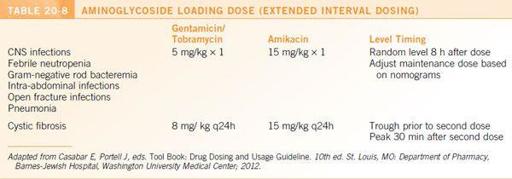
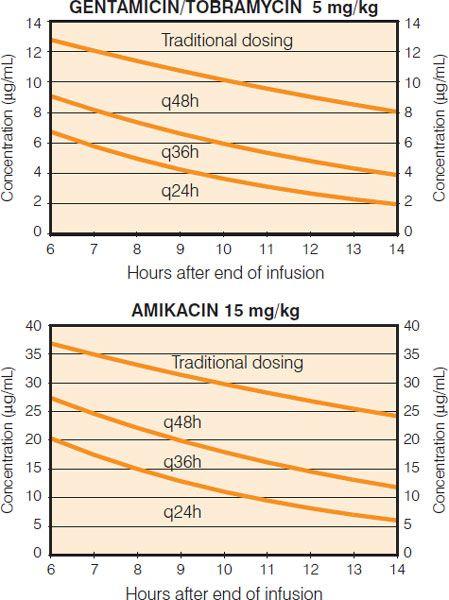
Figure 20-1.
Extended interval aminoglycoside nomogram. (From Barnes-Jewish Hospital Department of Pharmacy, St. Louis: Washington University Medical Center; 2012.)
•
Dosages need to be adjusted in patients with renal failure;
unfractionated heparin is recommended for patients with a CrCl < 10 or on hemodialysis. Antifactor Xa can be checked in patients with CrCl 10 to 30 mL/min
. Risk of bleeding is increased in patients with anti-Xa levels above 0.8 units/mL.
•
Dosing in patient with a BMI >40 is uncertain. Monitoring anti-Xa levels is recommended in these patients.
•
There is currently no validated nomogram for adjusting LMWH dosing based on anti-Xa levels in adults.
Warfarin Dosing
•
Warfarin dosing must be individualized!
•
The onset of action of warfarin is 24 to 72 hours, but full effect is not achieved until 5 to 7 days.
•
Numerous common drugs
increase the effect of warfarin
including amiodarone, azole antifungals, fluoroquinolones, macrolides, metronidazole, TMP/SMX, NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and PPIs.
•
Drugs that
decrease the effect of warfarin
include carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, rifampin, and ritonavir.
•
Initial and subsequent dosing of warfarin may be guided by WarfarinDosing.org (last accessed August 14, 2012), which has been widely used and scrutinized.
•
Atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter, goal INR 2 to 3
:
• For cardioversion, if rhythm has been present >48 hours, anticoagulate for 3 weeks prior to procedure (or perform TEE prior to cardioversion) and 4 weeks afterward.
• For patients with chronic or paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (rate or rhythm control):
Calculate CHADS2 score: 1 point each for CHF, hypertension, age > 75 years, DM; 2 points for prior ischemic stroke or TIA.
If CHADS2 = 0, nothing, or ASA 75 to 325 mg daily
If CHADS2 = 1, warfarin, dabigatran 150 mg BID (75 mg BID if CrCl 15 to 30), or rivaroxaban 20 mg qday (15 mg qday if CrCl 15 to 50) preferred; ASA acceptable if elevated bleeding risk
If CHADS2 ≥2, warfarin dabigatran 150 mg BID (75 mg BID if CrCl 15 to 30) or rivaroxaban 20 mg qday (15 mg qday if CrCl 15 to 50) is recommended.
•
DVT/PE, goal INR 2 to 3
:
• Initial anticoagulation with UFH, LMWH, or fondaparinux; warfarin can be started the same day. Overlap warfarin with one of above for at least 4 to 5 days and until INR ≥ 2 for 2 consecutive days.
• First episode due to reversible risk factor: 3 months of treatment.
• First episode, unprovoked: at least 6 to 12 months of treatment.
• >1 episode: lifelong treatment.
• VTE with cancer: anticoagulation until cancer resolution or development of contraindication. VTE recurrence rates are lower with LMWH than with standard warfarin therapy.
•
Tissue or St. Jude’s valve in aortic position, goal INR 2 to 3
:
• Any tissue valve: 3 months anticoagulation, then ASA 325 mg lifelong.
• St. Jude’s in aortic position: lifelong anticoagulation.
•
Mechanical valve (except St. Jude’s in aortic position), goal INR 2.5 to 3.5
:
• Lifelong anticoagulation.
• Consider adding ASA for caged ball or caged disc valves, CAD, history of stroke, or peripheral embolism.
Treatment of High INR
•
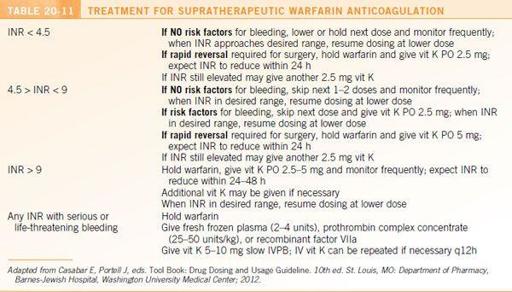
Recommendations for the treatment of supratherapeutic warfarin anticoagulation are presented in
Table 20-11
.
•
Treatment must be individualized!
•
Vitamin K can be given in equivalent dosages PO or IVPB. Subcutaneous administration is not recommended due to unpredictable response.
•
Oral administration is preferred for minor bleeding. IV administration should be reserved for major bleeding.
•
If vitamin K is given IVPB, administer slowly to minimize risk of anaphylactoid reaction.
•
The onset of action of oral vitamin K is 6 to 12 hours and 1 to 2 hours for IV. The peak effect is in 24 to 48 hours and 12 to 14 hours, respectively.
•
Vitamin K is
not
recommended in the following circumstances:
• INR < 4.5 with no active bleeding with and no surgery or procedure planned within 24 hours
• INR ≥ 4.5 and <9 with no risk factors for bleeding or falling with and no surgery or procedure planned within 24 hours
Approach to Consultation
