The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (2315 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
7.36Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
Soma
(Skt.,
su
, ‘to press’).
1
Intoxicating or hallucinogenic juice or substance, offered in Hinduism to the gods, and ingested by the
brahmans
and other participants in sacrificial rituals. The identification of the plant is uncertain and contested. All 114 hymns of
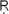 g Veda
g Veda
9 are addressed to Soma. The ways of preparing and drinking soma are carefully described, and it is said to make one acquire the eight powers of the god.
2
Hindu moon god who protects herbs and rides in a chariot drawn by white horses or antelopes. The moon is the cup of soma (above).
su
, ‘to press’).
1
Intoxicating or hallucinogenic juice or substance, offered in Hinduism to the gods, and ingested by the
brahmans
and other participants in sacrificial rituals. The identification of the plant is uncertain and contested. All 114 hymns of
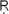 g Veda
g Veda9 are addressed to Soma. The ways of preparing and drinking soma are carefully described, and it is said to make one acquire the eight powers of the god.
2
Hindu moon god who protects herbs and rides in a chariot drawn by white horses or antelopes. The moon is the cup of soma (above).
S
 ma S
ma S
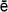 ma
ma
(the body a tomb):
 ma S
ma S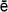 ma
ma(the body a tomb):
Somatic exegesis:
Somayajña
(group of sacrifices):
(group of sacrifices):
S
 n
n
 n
n(Korean). Ch’an/Zen in Korea. During the latter half of the Silla dynasty (668–935), the nine S
 n traditions (‘Nine Mountains’), which comprise S
n traditions (‘Nine Mountains’), which comprise S
 n Buddhism, were founded, seven of them being derived from the lineage of Matsu Tao-i (709–88) of the southern school of Chinese Ch’an. These nine traditions were integrated into the Chogye sect by
n Buddhism, were founded, seven of them being derived from the lineage of Matsu Tao-i (709–88) of the southern school of Chinese Ch’an. These nine traditions were integrated into the Chogye sect by
Chinul
(1158–1210), and it is this Chogye tradition that became dominant at the end of the 16th cent. and continues to this day to be the most influential Buddhist sect in Korea.
 n traditions (‘Nine Mountains’), which comprise S
n traditions (‘Nine Mountains’), which comprise S n Buddhism, were founded, seven of them being derived from the lineage of Matsu Tao-i (709–88) of the southern school of Chinese Ch’an. These nine traditions were integrated into the Chogye sect by
n Buddhism, were founded, seven of them being derived from the lineage of Matsu Tao-i (709–88) of the southern school of Chinese Ch’an. These nine traditions were integrated into the Chogye sect byChinul
(1158–1210), and it is this Chogye tradition that became dominant at the end of the 16th cent. and continues to this day to be the most influential Buddhist sect in Korea.
Other books
The Warrior Who Carried Life by Geoff Ryman
Calling On Fire (Book 1) by Stephanie Beavers
Thwonk by Joan Bauer
Gone Feral: Tracking My Dad Through the Wild by Novella Carpenter
Calling All the Shots by Katherine Garbera
Fangs for Nothing (Vampire Hunting and Other Foolish Endeavors) by Ambrose, Adrianne
Deception at Dark Hall (The Briony Martin Mystery Series) by Coverstone, Stacey
Cold Dawn by Carla Neggers
Attitude by Sheedy, EC
Lost Art of Mixing (9781101609187) by Bauermeister, Erica


