The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions (1949 page)
Read The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions Online
Authors: John Bowker

BOOK: The Concise Oxford Dictionary of World Religions
6.82Mb size Format: txt, pdf, ePub
, where their devotion to R
 ma is intense.
ma is intense.
 ma is intense.
ma is intense.R
 m
m
 nuja
nuja
 m
m nuja
nuja(11th/12th cent.).
Hindu philosopher, theologian, and source of the school known as
Vi
 i
i

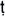
 dvaita-ved
dvaita-ved
 nta
nta
. He was a
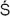 rivai
rivai

 avite
avite
, who sought to give the devotional attitude implicit in that allegiance a more reflective and philosophical foundation. He accepted three means of knowledge:
pratyk
 a
a
(perception),
anum
 na
na
(inference), and
 abda
abda
or

 stra
stra
(verbal testimony). He accepted the basic texts of
Vedanta
philosophy (the
Upani
 ads
ads
Hindu philosopher, theologian, and source of the school known as
Vi
 i
i
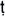
 dvaita-ved
dvaita-ved nta
nta. He was a
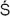 rivai
rivai
 avite
avite, who sought to give the devotional attitude implicit in that allegiance a more reflective and philosophical foundation. He accepted three means of knowledge:
pratyk
 a
a(perception),
anum
 na
na(inference), and
 abda
abdaor

 stra
stra(verbal testimony). He accepted the basic texts of
Vedanta
philosophy (the
Upani
 ads
adsOther books
Light and Wine by Sparrow AuSoleil
The Last Exit to Normal by Michael Harmon
Because the Night (The Night Songs Collection) by Strassel, Kristen
Tell the Truth by Katherine Howell
Wicked Highlander by Donna Grant
A Maze of Death by Philip K. Dick
Donners of the Dead by Karina Halle
DIRE : SEED (The Dire Saga Book 2) by Andrew Seiple
Death Takes Priority by Jean Flowers
Whirl Away by Russell Wangersky


