Predictably Irrational (3 page)
Read Predictably Irrational Online
Authors: Dr. Dan Ariely

In the left side of this illustration we see two options, each of which is better on a different attribute. Option (A) is better on attribute 1âlet's say quality. Option (B) is better on attribute 2âlet's say beauty. Obviously these are two very different options and the choice between them is not simple. Now consider what happens if we add another option, called (âA) (see the right side of the illustration). This option is clearly worse than option (A), but it is also very similar to it, making the comparison between them easy, and suggesting that (A) is not only better than (âA) but also better than (B).
In essence, introducing (âA), the decoy, creates a simple relative comparison with (A), and hence makes (A) look better, not just relative to (âA), but overall as well. As a consequence, the inclusion of (âA) in the set, even if no one ever selects it, makes people more likely to make (A) their final choice.
Does this selection process sound familiar? Remember the pitch put together by the
Economist
? The marketers there knew that we didn't know whether we wanted an Internet subscription or a print subscription. But they figured that, of the three options, the print-and-Internet combination would be the offer we would take.
Here's another example of the decoy effect. Suppose you are planning a honeymoon in Europe. You've already decided to go to one of the major romantic cities and have narrowed your choices to Rome and Paris, your two favorites. The travel agent presents you with the vacation packages for each city, which includes airfare, hotel accommodations, sightseeing tours, and a free breakfast every morning. Which would you select?
For most people, the decision between a week in Rome and a week in Paris is not effortless. Rome has the Coliseum; Paris, the Louvre. Both have a romantic ambience, fabulous food, and fashionable shopping. It's not an easy call. But suppose you were offered a third option: Rome without the free breakfast, called -Rome or the decoy.
If you were to consider these three options (Paris, Rome, -Rome), you would immediately recognize that whereas Rome with the free breakfast is about as appealing as Paris with the free breakfast, the inferior option, which is Rome without the free breakfast, is a step down. The comparison between the clearly inferior option (-Rome) makes Rome with the free breakfast seem even better. In fact, -Rome makes Rome with the free breakfast look so good that you judge it to be even better than the difficult-to-compare option, Paris with the free breakfast.
O
NCE YOU SEE
the decoy effect in action, you realize that it is the secret agent in more decisions than we could imagine. It even helps us decide whom to dateâand, ultimately, whom to marry. Let me describe an experiment that explored just this subject.
As students hurried around MIT one cold weekday, I asked some of them whether they would allow me to take their pictures for a study. In some cases, I got disapproving looks. A few students walked away. But most of them were happy to participate, and before long, the card in my digital camera was filled with images of smiling students. I returned to my office and printed 60 of themâ30 of women and 30 of men.
The following week I made an unusual request of 25 of my undergraduates. I asked them to pair the 30 photographs of men and the 30 of women by physical attractiveness (matching the men with other men, and the women with other women). That is, I had them pair the Brad Pitts and the George Clooneys of MIT, as well as the Woody Allens and the Danny DeVitos (sorry, Woody and Danny). Out of these 30 pairs, I selected the six pairsâthree female pairs and three male pairsâthat my students seemed to agree were most alike.
Now, like Dr. Frankenstein himself, I set about giving these faces my special treatment. Using Photoshop, I mutated the pictures just a bit, creating a slightly but noticeably less attractive version of each of them. I found that just the slightest movement of the nose threw off the symmetry. Using another tool, I enlarged one eye, eliminated some of the hair, and added traces of acne.
No flashes of lightning illuminated my laboratory; nor was there a baying of the hounds on the moor. But this was still a good day for science. By the time I was through, I had the MIT equivalent of George Clooney in his prime (A) and the MIT equivalent of Brad Pitt in his prime (B), and also a George Clooney with a slightly drooping eye and thicker nose (âA, the decoy) and a less symmetrical version of Brad Pitt (-B, another decoy). I followed the same procedure for the less attractive pairs. I had the MIT equivalent of Woody Allen with his usual lopsided grin (A) and Woody Allen with an unnervingly misplaced eye (âA), as well as Danny DeVito (B) and a slightly disfigured version of Danny DeVito (âB).
For each of the 12 photographs, in fact, I now had a regular version as well as an inferior (â) decoy version. (See the illustration for an example of the two conditions used in the study.)
It was now time for the main part of the experiment. I took all the sets of pictures and made my way over to the student union. Approaching one student after another, I asked each to participate. When the students agreed, I handed them a sheet with three pictures (as in the illustration here). Some of them had the regular picture (A), the decoy of that picture (âA), and the other regular picture (B). Others had the regular picture (B), the decoy of that picture (âB), and the other regular picture (A).
For example, a set might include a regular Clooney (A), a decoy Clooney (âA), and a regular Pitt (B); or a regular Pitt (B), a decoy Pitt (âB), and a regular Clooney (A). After selecting a sheet with either male or female pictures, according to their preferences, I asked the students to circle the people they would pick to go on a date with, if they had a choice. All this took quite a while, and when I was done, I had distributed 600 sheets.
What was my motive in all this? Simply to determine if the existence of the distorted picture (âA or âB) would push my participants to choose the similar but undistorted picture. In other words, would a slightly less attractive George Clooney (âA) push the participants to choose the perfect George Clooney over the perfect Brad Pitt?
There were no pictures of Brad Pitt or George Clooney in my experiment, of course. Pictures (A) and (B) showed ordinary students. But do you remember how the existence of a colonial-style house needing a new roof might push you to choose a perfect colonial over a contemporary houseâsimply because the decoy colonial would give you something against which to compare the regular colonial? And in the
Economist
's ad, didn't the print-only option for $125 push people to take the print-and-Internet option for $125? Similarly, would the existence of a less perfect person (âA or âB) push people to choose the perfect one (A or B), simply because the decoy option served as a point of comparison?
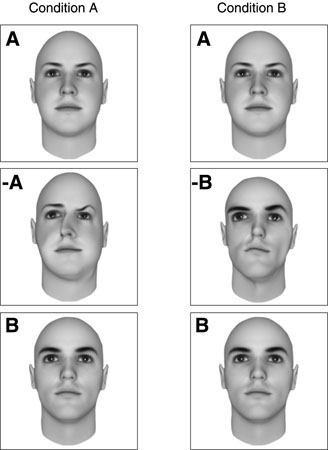
Note: For this illustration, I used computerized faces, not those of the MIT students. And of course, the letters did not appear on the original sheets.
It did. Whenever I handed out a sheet that had a regular picture, its inferior version, and another regular picture, the participants said they would prefer to date the “regular” personâthe one who was similar, but clearly superior, to the distorted versionâover the other, undistorted person on the sheet. This was not just a close callâit happened 75 percent of the time.
To explain the decoy effect further, let me tell you something about bread-making machines. When Williams-Sonoma first introduced a home “bread bakery” machine (for $275), most consumers were not interested. What was a home bread-making machine, anyway? Was it good or bad? Did one really need home-baked bread? Why not just buy a fancy coffeemaker sitting nearby instead? Flustered by poor sales, the manufacturer of the bread machine brought in a marketing research firm, which suggested a fix: introduce an additional model of the bread maker, one that was not only larger but priced about 50 percent higher than the initial machine.
Now sales began to rise (along with many loaves of bread), though it was not the large bread maker that was being sold. Why? Simply because consumers now had two models of bread makers to choose from. Since one was clearly larger and much more expensive than the other, people didn't have to make their decision in a vacuum. They could say: “Well, I don't know much about bread makers, but I do know that if I were to buy one, I'd rather have the smaller one for less money.” And that's when bread makers began to fly off the shelves.
2
OK for bread makers. But let's take a look at the decoy effect in a completely different situation. What if you are single, and hope to appeal to as many attractive potential dating partners as possible at an upcoming singles event? My advice would be to bring a friend who has your basic physical characteristics (similar coloring, body type, facial features), but is slightly less attractive (âyou).
Why? Because the folks you want to attract will have a hard time evaluating you with no comparables around. However, if you are compared with a “âyou,” the decoy friend will do a lot to make you look better, not just in comparison with the decoy but also in general, and in comparison with all the other people around. It may sound irrational (and I can't guarantee this), but the chances are good that you will get some extra attention. Of course, don't just stop at looks. If great conversation will win the day, be sure to pick a friend for the singles event who can't match your smooth delivery and rapier wit. By comparison, you'll sound great.
Now that you know this secret, be careful: when a similar but better-looking friend of the same sex asks you to accompany him or her for a night out, you might wonder whether you have been invited along for your company or merely as a decoy.
R
ELATIVITY HELPS US
make decisions in life. But it can also make us downright miserable. Why? Because jealousy and envy spring from comparing our lot in life with that of others.
It was for good reason, after all, that the Ten Commandments admonished, “Neither shall you desire your neighbor's house nor field, or male or female slave, or donkey or anything that belongs to your neighbor.” This might just be the toughest commandment to follow, considering that by our very nature we are wired to compare.
Modern life makes this weakness even more pronounced. A few years ago, for instance, I met with one of the top executives of one of the big investment companies. Over the course of our conversation he mentioned that one of his employees had recently come to him to complain about his salary.
“How long have you been with the firm?” the executive asked the young man.
“Three years. I came straight from college,” was the answer.
“And when you joined us, how much did you expect to be making in three years?”
“I was hoping to be making about a hundred thousand.”
The executive eyed him curiously.
“And now you are making almost three hundred thousand, so how can you possibly complain?” he asked.
“Well,” the young man stammered, “it's just that a couple of the guys at the desks next to me, they're not any better than I am, and they are making three hundred ten.”
The executive shook his head.
An ironic aspect of this story is that in 1993, federal securities regulators forced companies, for the first time, to reveal details about the pay and perks of their top executives. The idea was that once pay was in the open, boards would be reluctant to give executives outrageous salaries and benefits. This, it was hoped, would stop the rise in executive compensation, which neither regulation, legislation, nor shareholder pressure had been able to stop. And indeed, it needed to stop: in 1976 the average CEO was paid 36 times as much as the average worker. By 1993, the average CEO was paid 131 times as much.
But guess what happened. Once salaries became public information, the media regularly ran special stories ranking CEOs by pay. Rather than suppressing the executive perks, the publicity had CEOs in America comparing their pay with that of everyone else. In response, executives' salaries skyrocketed. The trend was further “helped” by compensation consulting firms (scathingly dubbed “Ratchet, Ratchet, and Bingo” by the investor Warren Buffett) that advised their CEO clients to demand outrageous raises. The result? Now the average CEO makes about 369 times as much as the average workerâabout three times the salary before executive compensation went public.
Keeping that in mind, I had a few questions for the executive I met with.
“What would happen,” I ventured, “if the information in your salary database became known throughout the company?”
The executive looked at me with alarm. “We could get over a lot of things hereâinsider trading, financial scandals, and the likeâbut if everyone knew everyone else's salary, it would be a true catastrophe. All but the highest-paid individual would feel underpaidâand I wouldn't be surprised if they went out and looked for another job.”
Isn't this odd? It has been shown repeatedly that the link between amount of salary and happiness is not as strong as one would expect it to be (in fact, it is rather weak). Studies even find that countries with the “happiest” people are not among those with the highest personal income. Yet we keep pushing toward a higher salary. Much of that can be blamed on sheer envy. As H. L. Mencken, the twentieth-century journalist, satirist, social critic, cynic, and freethinker noted, a man's satisfaction with his salary depends on (are you ready for this?) whether he makes more than his wife's sister's husband. Why the wife's sister's husband? Because (and I have a feeling that Mencken's wife kept him fully informed of her sister's husband's salary) this is a comparison that is salient and readily available.
*
