HTML The Definitive Guide (38 page)
Read HTML The Definitive Guide Online
Authors: Chuck Musciano Bill Kennedy

text
This effect is handy when formatting conventional text with fixed line breaks, such as addresses, song lyrics, or poetry. Notice, for example, the lyrical breaks when the following source is rendered by Netscape:
Heartbreak Hotel
Ever since my baby left me
I've found a new place to dwell.
It's down at the end of lonely street
Called Heartbreak Hotel.
The results are shown in
Figure 4.18
.
Figure 4.18: Give lyrics their breaks (
)
Also notice how the
tag causes text simply to start a new line, while the browser, when encountering the
tag, typically inserts some vertical space between adjacent paragraphs. ,
[
4.7.1.1 The clear attribute
Normally, the
tag tells the browser to stop the current flow of text immediately and resume at the left margin of the next line or against the right border of a left-justified inline graphic or table.
Sometimes you'd rather the current text flow resume below any tables or images currently blocking the left or right margins.
HTML 4.0 provides that capability with the clear attribute for the
tag. It can have one of three values: left, right, or all, each related to one or both of the margins. When the specified margin or both margins are clear of images, the browser resumes the text flow.
Figure 4.19 illustrates the effects of the
clear attribute when Netscape renders the following HTML
fragment:
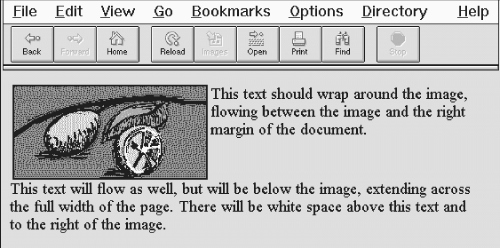
 This text should wrap around the image, flowing between the image and the right margin of the document.
This text should wrap around the image, flowing between the image and the right margin of the document.
This text will flow as well, but will be below the image, extending across the full width of the page. There will be white space above this text and to the right of the image.
Figure 4.19: Clearing images before resuming text flow after the
tag
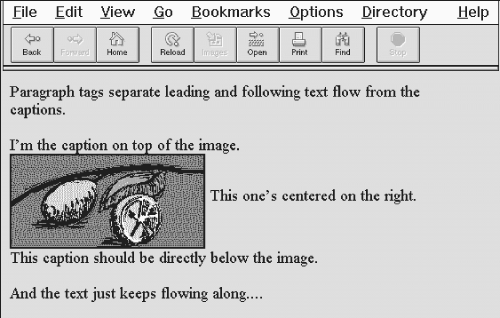
Inline HTML images are just that - normally in line with text, but usually only a single line of text.
Additional lines of text flow below the image unless that image is specially aligned by right or left attribute values for the tag (similarly for
 This one's centered on the right.
This one's centered on the right.