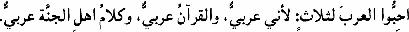Empires of the Word: A Language History of the World (18 page)
Read Empires of the Word: A Language History of the World Online
Authors: Nicholas Ostler
Tags: #History, #Language, #Linguistics, #Nonfiction, #V5

Coptic, then, is another example of a language of the Near East which has been sustained through a period of growing adversity through its association with a distinctive faith. It can be contrasted with a survival a little farther south: Ge’ez, the language of the Ethiopian Church. This is a classical language (related to the ancient languages of South Arabia, and owes its position ultimately to a prehistoric invasion across the Red Sea). Although it survived, like Coptic, through its role in Christian liturgy, its fate is much more like that of Latin or Sanskrit than Coptic. Ethiopia continues to be a Christian country, and Ge’ez is surrounded by daughter and niece languages, Tigrinya, Tigre and Amharic. Ge’ez has been preserved by sentiment and linguistic conservatism, but the linguistic tradition it represents is alive and under no external threat, linguistic, social or religious.
By contrast, what we may call the ‘Shield of Faith’ strategy for language survival has indeed been used quite often in the last couple of hundred years, and far away from the Near East, or Afro-Asiatic languages. It is this, after all, which has preserved ‘Pennsylvania Dutch’, i.e. German, among the separate community of the Amish in the USA.
59
And it is this which since 1865 has preserved Welsh in the Nonconformist chapel community of Argentina, on the wind-swept plains of Patagonia.
60
It could even be claimed that it is being reapplied, with a vengeance, to rebuild the Hebrew language in the new state of Israel.
But we must now turn, as the last part of our review of this area, to another language that has exploited its confessional associations mercilessly, not simply to survive but to expand, and to expand faster and more lastingly than any other language known.
’a
ibbū al ‘araba liθin: li ‘anī ‘arabiyyun, wa al-qur ’ānu ’ arabiyyun, wa kalāmu ’ahli al-jinnati ’arabiyyun.
Love the Arabs for three reasons: because I am an Arab, because the Qur’ān is in Arabic and because the inhabitants of Paradise speak Arabic.
Saying attributed to Muhammad
61
Arabic is another Semitic language closely related to the Aramaic and Akkadian that preceded it in the Near East. Its records actually go back to North Arabian inscriptions of the fourth century BC. But its speakers, mainly desert Bedouin and pastoralists, had remained outside the effective control (and perhaps interest) of all the previous empires in the region.
When they showed their mettle, the results were truly astounding. Within twenty-five years of the prophet Muhammad’s death in 632, they had conquered all of the Fertile Crescent and Persia, and thrust into Armenia and Azerbaijan. Their lightning advance was even more penetrating towards the west: Egypt fell in 641 and the rest of North Africa as far as Tunisia in the next decade. Two generations later, by 712, the Arabic language had become the medium of worship and government in a continuous band of conquered territories from Toledo and Tangier in the west to Samarkand and Sind in the east. No one has ever explained clearly how or why the Arabs could do this.
62
An appeal is usually made to a power vacuum in the east (where the Roman/Byzantine empire and the Sassanian empire of Iran were just recovering from their exhausting war), and the absence of any power to organise resistance in the west.
Whatever caused the feebleness of the defences, a series of successful raids became harmonised into a wave of invasion that rolled on with the momentum of a tsunami. It originated in a small new state, based on the cities of Medina and Mecca in Arabia, which had recently been energised by divine revelation, embracing a new, and startlingly abstract, creed.
Lā ’lāha ill’ Allāhu, wa Mu
ammadun rasūlu ‘llāhi
There is no god but God, and Muhammad is the apostle of God
This
šahādah
, the declaration of Muslim faith, and respected as the first of its ‘pillars’, was elemental in its power; it was a faith turned from shield into sword. Yet its name,
Islām
, is usually translated as ‘submission’ (to God); and its Semitic root slm (also seen in the agent form
muslim
) is also the basis of words for peace (as in Arabic’s own greeting
salām ‘aleykum
, ‘peace with you’). Doubly ironic, then, that this religion, whose name means peaceful acceptance, burst upon the world so mightily by storm.
But the importance of language in Islam went far beyond the production of a telling slogan. Eloquence, the sheer power of the word, as dictated by God and declaimed to all who would listen, played the first role in winning converts for Islam, leaving hearers no explanation for the beauty of Muhammad’s words but divine inspiration. The classic example is ‘Umar ibn al-Khattab, a contemporary of Muhammad and acknowledged authority on oral poetry, determined to oppose, perhaps even to assassinate, him. Exposed directly to the prophet’s words, he could only cry out: ‘How fine and noble is this speech!’ And he was converted.
Language was used in a unique way in the spread of this religion too. The authentic utterances of the prophet, himself illiterate, were soon, in some undocumented way, reduced to writing. The text so arrived at was immediately holy and absolutely authoritative; it could not be changed, although it was permissible (as in the Hebrew scriptures) to annotate it with some dots and dashes to mark the vowel sounds, for the benefit of those whose Arabic was not native, and who consequently might need some help in reading the bare consonants.
*
It was known as the
Qur ‘ān
, ‘recitation’, based on qr’, the common Semitic root for reading aloud, and famously begun when the Angel Gabriel commanded Muhammad:
iqra ’ bismi rabbika alla
ī xalaqa, xalaqa l’’insāna min ‘alaqin
Recite, in the name of your Lord who created, created man from embryo.
63
These distinctive scriptures, a totally closed set, are the great treasure of Islam, constantly pondered and declaimed by the faithful. Their existence seems to have been taken by Muslims as the badge of properly revealed religion, for in their domains holders of other revealed monotheistic faiths, Jews with their TaNaK, Christians with their Testaments, Zoroastrians in Iran with their Avesta, were called likewise
ahl al-kitāb
, ‘people of the book’, and thereby exempt from forcible conversion.
The linguistic effects of the Arab blitzkrieg can only be compared with those of Greek’s wild ride throughout Persia’s domains nine centuries before. They were ultimately to be much more durable than the extension of Greek had been, but like the spread of Greek across the east, the take-up of Arabic did not quite measure up to the spread of temporal power that had caused its advance.
Politically, the Arab campaigns destroyed the hold of the Roman, now Byzantine, empire on the whole of the eastern Mediterranean—excepting only Anatolia. Despite their efforts to take Constantinople, this centre of Roman power survived, and lived on in Christian defiance for another eight centuries. Farther east, the Arabs overran Armenia but did not convert it. More significant was the Arabs’ termination of Sassanian power in Iran and the mountains of Afghanistan. This was the beginning of the end for Zoroastrianism, gradually replaced in popular worship by Islam. Nowadays it survives only in the tiny minority of Parsees who were to flee to India three hundred years later.
Linguistically, the immediate effects were comparable to the political ones: Arabic established itself as the language of religion, wherever Islam was accepted, or imposed. In the sphere of the holy, there was never any contest, since Islam unlike Christianity did not look for vernacular understanding, or seek translation into other languages. The revelation was simple, and expressed only in Arabic. Furthermore, Islam was a religion that insisted on public rituals of prayer in the language, and where the muezzin’s call of the faithful to prayer, in Arabic, has always punctuated everyone’s day.
Allāh akbar
, ‘God is greater.’
In 700, the caliph in Damascus, ‘Abd el Malik, summoned his Greek adviser, Joannes Damascenus, to tell him that he had decided henceforth to ban the Greek language from all public administration. The adviser told his colleagues: ‘You had better seek another profession to earn your living: your present employment has been withdrawn by God.’ He then spent the rest of his long life (655-749) as a monk.
64
This was the aspiration. In practice, for the first few generations administration lingered in the predecessor languages, Greek and Persian, to some extent Aramaic and Coptic, not least because the conquerors were unable to operate the elaborate bureaucratic systems they had seized, and because the methods of recruitment were mostly nepotistic. The same families continued to provide the scribal classes, but by the second century of the Muslim era they were reading and writing in Arabic. The process can be followed in the papyrus trail of Egypt. All documents remain in Greek for a good century after the Muslim conquest; then bilingualism sets in, but Arabic totally replaces Greek only in the late eighth century, after 150 years of Islam.
65
But Arabic is now spoken only in an inner zone within the
Dār-al-islām
, ‘House of Islam’, as a whole. What happened to roll it back? In the long term there was a subtle linguistic limit on Arab success, or rather on the success of Arabic. Arabic progressed from the language of the mosque to establish itself permanently as the common vernacular of the people only in countries that had previously spoken some related language, one that belonged to the Afro-Asiatic (or Hamito-Semitic) family.
*
This Afro-Asiatic zone included the Fertile Crescent, where Arabic replaced Aramaic; Egypt, where it overwhelmed Coptic; Libya and Tunisia, where it finally supplanted Berber and erased—or merged into—Punic; and the Maghreb (the north of modern Algeria and Morocco), where it also pushed Berber back into a set of smaller pockets. The tiny island of Malta, too, which had a Punic background from its origins in the Carthaginian empire, became Arabic-speaking after Arab conquest in 870 AD, belying its millennium of control from Rome since 218 BC. The area of permanent Arabic advance also included at the margin, and rather later, a more southerly zone in Africa, Mauritania in the west, and Chad and Sudan in the east; here Arabic spread later through trade contacts, and would have replaced some Chadic and Cushitic languages.