Early Modern England 1485-1714: A Narrative History (18 page)
Read Early Modern England 1485-1714: A Narrative History Online
Authors: Robert Bucholz,Newton Key

Wolsey’s fall surprised many. They had assumed that he was the real power in England. But Henry was no cipher. The Great Cardinal had remained dominant only so long as he accomplished the king’s business. Once he ceased to be useful, he was doomed. His many other liabilities – pride, greed, corruption, unpopularity – meant only that he fell unlamented. The significance to aspiring royal servants, ministers, or favorites was clear. The significance for England and its place in the world was also clear. Henry VIII, for all his swagger, was not a major player in Europe, and England, out on the fringes of Christendom, was not a major power. Finally, note that what had started in the marriage bed as a private matter between husband and wife had become intertwined with high politics, international diplomacy, religious doctrine, even Italian weather. Clearly, the King’s Great Matter went far beyond the obsessions of just one man. That would become even clearer as it moved into its next phase.
The Attack on the Church
The period from 1529 to 1532 used to be seen as one of drift, without a real policy on the part of Henry VIII. But these years saw the rise of three great court factions vying for the king’s ear and, in a manner of speaking, his soul as well. The first, known as the Aragonese faction, consisted of those who supported and advised the queen. They included the Spanish diplomats based at court, Bishops John Fisher (ca. 1469–1535) and Cuthbert Tunstall (1474–1559), and Wolsey’s replacement as lord chancellor, Sir Thomas More. A lawyer, a scholar, and a devout Catholic, More refused to involve himself publicly in the divorce, concentrating instead on prosecuting heretics and clearing out the backlog of business that Wolsey had left in the law courts. Privately, he did what he could to shore up the queen’s support in the council and Parliament. Ranged against him were those who supported Henry’s desire to exchange Queen Catherine for Queen Anne. These included members of the Boleyn family, clergymen who inclined toward Church reform such as Thomas Cranmer (1489–1556), and a shadowy former servant of Wolsey’s named Thomas Cromwell (ca. 1485–1540). Among the clergymen were a number of scholars employed by Henry to search out precedents in what came to be known as the “king’s books.” By 1530 they were asserting the king’s power over the Church in England and so laying the groundwork for the Royal Supremacy. Holding the balance between these two groups was a faction of conservative courtiers led by Thomas Howard, duke of Norfolk, Thomas, Lord Darcy (ca. 1467–1537), and Stephen Gardiner, bishop of Winchester (ca. 1495–1555). Their inclination was toward religious conservatism and against the divorce, but their habit was to do the king’s bidding. Eventually, for most of these men, habit won out over inclination. Increasingly, they began to press Catherine to accept the king’s terms: a divorce, a pension, and the title princess dowager. She stubbornly refused.
While the factional battle raged at court, the king took Cromwell’s suggestion that he solicit the opinions of leading university theologians to convince the pope of the justice of his cause, but these great minds could not agree. In 1529 Henry VIII opened another, more threatening front. He called a Parliament, the first in five years. While much of its business involved the raising of revenue, the king also made it clear that he would entertain petitions of grievance about the Church. The Mercer’s Company of London dutifully offered a series of articles complaining about clerical abuses, which led to legislation. To understand the Church’s vulnerability to such attacks, it is necessary for us to conduct our own inquiry into the condition of the Roman Catholic Church in England.
Unfortunately, historians have been unable to agree on the state of Catholicism in England on the eve of the Reformation. For many years, they simply took the word of Protestant polemicists that the Church was corrupt, ineffective, and out of touch with the great mass of the English people. The laity were portrayed as ignorant of its doctrines and resentful of the high-handed and sometimes hypocritical ways of its clergy. According to this view, most memorably articulated by A. G. Dickens, many, if not most, English men and women yearned for Reformation.
8
But more recently, J. J. Scarisbrick, Christopher Haigh, Eamon Duffy, and others have argued that the Church was both less corrupt and more effective than this picture suggests. English men and women knew and embraced the doctrines and practices of their faith far more enthusiastically than the old historical orthodoxy would admit. Thus, the Reformation was not a grassroots movement welcomed by the faithful, but a dictated solution, imposed from above. In the words of Christopher Haigh, “[i]t was the break with Rome which was to cause the decline of Catholicism, not the decline of Catholicism which led to the break with Rome.”
9
More recently still, historians such as Diarmaid MacCulloch and Ethan Shagan have staked out a middling position between these two extremes which emphasizes both the variety of opinions among the people and their agency – that they were not simply supplicants or passive recipients of Reformation, but active players whose reactions to government initiatives could steer reform down paths unforeseen at Whitehall.
10
Can we sort this out?
Let us begin with some basic facts. In 1529 Roman Catholicism was the official religion of the English state. This meant two things. First, the Church was everpresent in the life of the kingdom and its people. It supplied them with their explanation of the universe and of their own trials and tribulations. It marked the stages of their lives in baptism, marriage, and burial. Its 37 major holy days were their holidays. Their weekly day of rest, the Sabbath, was largely spent attending services and social events at the parish church. Their education took place in its schools. Their disputes over adultery, fornication, drunkenness, blasphemy, inheritance, and debt were tried in its courts; indeed, a number of these offenses were only illegal because they were thought to be an affront to God or his Church. Churchwardens monitored notorious adulterers, brawlers, drunkards, breakers of the peace, and absentees from Sunday services. Church-affiliated guilds regulated the economic life of towns. Monasteries, convents, and Church-run hospitals distributed charity. The Church owned nearly a quarter of the land in England, which meant that for many peasants and workers it was not only their chief source of spiritual wisdom and comfort, but also their landlord, employer, and neighbor. Finally, their parish priest was their primary source of news about the world beyond their villages and towns.
Second, the Catholic Church was the only legal religion in England. To be a member of any other faith, to offer an alternative interpretation of Christianity, to criticize the dogma or practice or even the personnel of the Roman Catholic Church was to risk indictment for heresy and, possibly, burning at the stake. Thus, if anyone was unhappy about his or her faith or clergyman, they were not likely to express their opinions publicly, or to leave evidence for later historians. The evidence which
does
exist demonstrates strong social and material support for the Church and popular participation in many activities, some of them optional. The English people not only attended mass on Sundays and holy days, but they also observed numerous elaborate calendar rituals and plays. They went on pilgrimage to holy places and saints’ shrines, especially that of Thomas à Becket at Canterbury. They joined fraternities and guilds (in effect, clubs) dedicated to particular saints or beliefs and they bought catechisms and devotional books in great numbers. They contributed massively to an explosion of church building and decoration in the fifteenth and early sixteenth centuries, producing such beautiful structures as St. Mary Redcliffe, Bristol, or St. Peter Mancroft, Norwich. The wealthy and the less wealthy endowed or enriched scores of colleges, schools, hospitals, monasteries, convents,
chantries
, shrines, and even individual clergy, often with posthumous bequests. Here was another way in which the Church was everywhere: its physical plant dominated the skyline in town and country. Less spectacularly, ordinary people paid for prayers and candles to free the souls of their deceased relatives from
Purgatory
. This evidence of popular support, combined with the relative lack of evidence for disagreement with Church teaching, has led Haigh, Duffy, and others to argue that, despite significant exceptions, most English men and women in 1529 were orthodox and had no desire to see major changes in their faith.
But even if this is true, and despite the popularity of religious clubs, devotional exercises, and books among a literate minority, this does not mean that all or even most English men and women had a very clear idea of what the doctrines of that faith actually were. People may have joined clubs for their social and economic benefits. Books may have been owned but not read or fully grasped. As with many believers today, most people’s faith seems to have been simple and none-too-consistent. Lay people varied greatly in their devotion to and understanding of Catholic doctrine, with the lowest levels of both in remote areas.
This was inevitable given the relatively small amount of liturgical participation demanded of the laity, the unavailability of the Bible, the low literacy rate, and the few priests in such areas. First, lay members of the English Catholic Church were not invited to participate actively in the central rituals or the promulgation of their faith. The mass was said in Latin and heard from the back of the church, through a rood screen (see
plate 4
) while pious congregants recited their own prayers quietly. Communion was required of the faithful only three times a year, confession but once. Nor could most devout Catholics avail themselves of the consolation of Scripture, for there was no readily available English translation of the Bible in pre-Reformation England. The Church’s official version, the Vulgate, was a Latin translation from the end of the fourth century. Most churchmen would have considered it dangerous to make the Bible more widely available, and in 1407 the Church banned the unlicensed translation of Scripture into English. This served to restrict Bible reading to a select few clergymen and scholars. Even if an English translation had been readily available, not all could have read it, for literacy, though growing (see chapter 6), was still largely the preserve of the upper and middle ranks of the population. This meant that while religious books sold well, few ordinary people could have read or understood them. Finally, while estimates for the number of clergy in England vary widely, ranging from 20,000 to 60,000, those numbers were not spread evenly or in the same proportions as the general population across the country. In poorer, rural areas especially, there was, and had been for a long time, a shortage of priests, especially educated priests. In Canterbury diocese toward the end of the fifteenth century, only about one-fifth of the priests were university graduates; in Surrey, one-tenth. That, in turn, meant that many parishes were not being served adequately; their parishioners were not being ministered to or taught Catholic doctrine accurately. All of these factors must have made Reformation easier to swallow: it is difficult to notice or object to changes when one lacks a clear understanding of what is being changed.
In response to these failings, humanist authors such as More, John Colet (1467–1519), Simon Fish (d. 1531), and William Tyndale (ca. 1494–1536), influenced by the satirical and scholarly writings of Erasmus, began to argue for reform of the practice, if not the doctrine, of the English Church. They were concerned, first, not only with the lack of priests, but its consequences: pluralism and absenteeism.
Plate 4
Diagram of the interior of a church before and after the Reformation. Reproduced from S. Doran and C. Durston
, Princes, Pastors and People: The Church and Religion in England, 1529–1689 (
London
, 1991)
by permission of Taylor and Francis Ltd
.
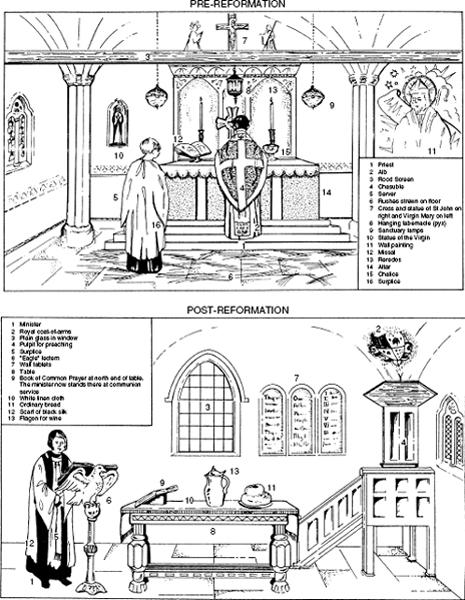
As we have seen, Cardinal Wolsey was a great pluralist, probably out of greed. But for most clergymen, holding multiple livings was necessary both because there were so few priests to go around and because country parishes often paid so poorly (frequently less than £10 a year) that their pastors might have to hold down several just to make ends meet. Since it was impossible for a clergyman holding plural livings to say mass in more than one place at once, he almost necessarily became an absentee; that is, some parishes simply were not served on Sundays. One way of getting around this problem was to hire curates, or deputy priests. But these men were often poorly educated and therefore unable to perform the many tasks demanded of a pastor. The inevitable result was lay ignorance or indifference.
